Explanation of Ring, Bus, and Star Network Topology Types
In the computer networking field, one of the backbones of networking is the network topology. In layman's terms, a network topology is the skeleton of a network - the topology used determines how data flows from one point to another within said network, and provides a path for troubleshooting and maintenance to the network administrator in case of network failure.
Even a network built at home falls into one topology or another, though a great many home networks fall under one category: the star topology. More about that in a moment, though. Read on to find out about the three most common network topologies!

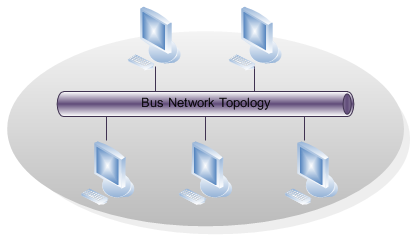
Bus Topology
Starting at the most simple point, a bus topology consists of two major parts: the devices, and the central cable. The cable connects to all devices, and it is through this cable that the devices can connect to one another. This cable is called the backbone, or as the topology is named, the bus. The primary advantage to a bus topology is its simple construction and the low cost associated with it. The disadvantage of this topology is that if the cable, or backbone, suffers from a malfunction or needs repair, the entire network will be out of service and as a result, the business using this topology will be without internet or intranet connectivity. Organization of a bus topology is simple - each device, be it a computer, the server, a printer or a fax machine, is directly connected to the network's bus.
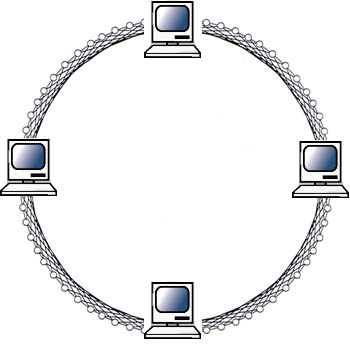
Ring Topology
A ring topology takes the concept of nodes as described above, and forms a circular path for data to travel from a node which is connected with two others. The concept of the ring topology is that each node within it is connected in a circular fashion, meaning all nodes share all data which is passed through the network. The data which passes through the network may be called a ‘token,' and for this reason this topology is sometimes referred to as a ‘token ring.' This topology has the advantage of being self-sufficient in that a server is not required to manage interconnectivity from one computer to another. The ring topology can be set up to double on itself by organizing the ring to work "clockwise" or "counterclockwise" giving the ring-connected network the opportunity to function even if one computer or device fails within the topology. There are a few disadvantages to this topology, however. A ring topology is costly, as each computer is required to have a network adapter card. A ring is more difficult to incorporate additional nodes into after the initial setup, and each addition to the network changes the way the ring operates. Because the data travels through the entire network, a ring topology is much slower than the other topologies, but based on the aforementioned advantages, may be the right solution for a company seeking stability and consistency of data and shared resources.
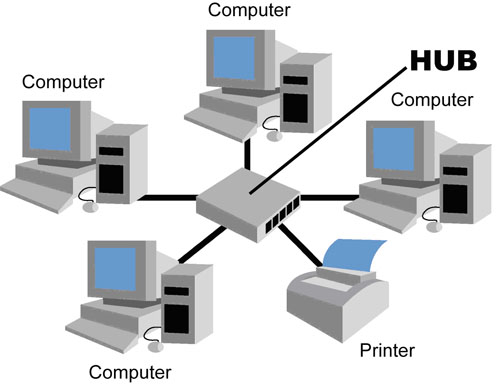
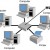
Star Topology
The star network topology makes use of a hub to connect to each device. Each connection to the hub is called a node. The hub receives and transmits data from each node to its destination. There are many benefits involved in using a star topology. Primary amongst these is the ease of maintenance on the hub itself, which does not require any changes to be made to the rest of the network. Once an update is applied to the hub, each node connected to the hub receives the new update. Problems within a star topology can be tracked and diagnosed easily, and fixed by only having to take one node out of service, rather than the whole network. The downside to this topology is that because the hub is the focus for the network, major activity by multiple nodes will slow the entire network down. The hub is the heart of a star topology, and just as the heart must beat to keep the human body alive, the hub must be functional for the network to work. If the heart fails, the human dies, and it is the same for a hub in this network topology.