The Coronavirus Impact on Hospitality, Tourism, & Global Supply Chain

The COVID-19 an epidemic does not require a formal introduction due to its infamous reputation now; the virus has fast spread across multiple continents since it was first detected in a wet market in China. The virus which was first discovered in Wuhan, China has now infiltrated neighboring countries like a plague striking fear in the hearts of fellow citizens in the affected countries. Due to its nature and ability to spread from person to person through bodily fluid and contact with the carrier, the virus has already made its presence known not only in the Asia-Pacific region but in Europe, North America, Africa, and the Middle East. There have been reports of panic-buying of essentials in Hong Kong and Singapore, in which, folks are taking matters into their own hands to ensure their safety in case the situation took a turn for the worse.
The Trail Leading to the Discovery of the COVID-19
It has been almost three months since the COVID-19 made its presence known to the world back in December 2019. Back then, it was not known that the virus could have such detrimental consequences. However, red flags begin to appear when medical personnel started noticing the spike in the number of people falling ill with flu-like symptoms, but not responding to regular treatment. Things spiraled out of control when patients began to get severely ill and succumbing to the illness. Upon further investigation, medical personnel attending to the patients concluded that those groups of people were in a way connected to the same source that may have been the epicenter of the particular strain of virus outbreak.
In the news
According to Al-Jazeera news, there have been 70,548 reported cases of the COVID-19 as of February 18, 2020. The figures are pretty alarming given the short span of time the virus was first reported and the shocking reports of casualties resulting from the spread of the virus. Mainland China was covered in the gloom with the devastating news of the rise in the number of death tolls amounting to 1, 770 people during the time of reporting. Since the outbreak, there have been new cases of infections reported around the globe on a daily basis. This is particularly depressing since there is no vaccine or cure for the virus at the present moment.
As the number of reported cases and death tolls continue to escalate, the economic impact is beginning to become more evident. Although humanity should come first and lives matter, it is hard to dismiss the fact that the COVID-19 epidemic is having an adverse impression on our ecological economics. The economy took on a bleak outlook after the prolonged onset of the virus and the threat of the epidemic has even thrown China, the world’s prominent economic powerhouse, off guard with its unprecedented challenge to the Chinese economy. The current situation has also sparked fears of a global economic slowdown should it spiral out of control.
Since the outbreak, there have been more than a dozen Chinese cities on lockdown to avoid the spread of the virus and flights to and from mainland China are halved. Macau took matters seriously and went to the extent of even banning the entry of Hubei residents without a virus-free declaration. Hong Kong proceeded to close all but three of its 14 border crossings with the mainland. This was viewed as the largest quarantine in human history that means over 50,000,000 people were unable to travel in and out of Hubei, the major commercial and industrial province where Wuhan is located.
Impact on the Airline Industry
The airline industry took a big blow as more than 100 flights to China and Taiwan were canceled, after Taiwan proceeded to extend an existing ban on visitors from China. Foreign nationals, who were traveling from China were denied entry starting from February 7. The Taiwanese regional airline - Mandarin Airline based in Taipei also took preventive measures by suspending flights from the island to Wuhan, Hubei’s capital until February 29. In other parts of the world, the Filipino government and numerous other countries also imposed a travel ban on all of China, including Hong Kong and Macau.
Due to the outbreak of the COVID-19, many people are taking preventive measures to keep themselves safe and reduce the risk of infection by limiting travel to anywhere near reported spots with a high risk of catching the virus. Not only that, but the travel ban issued to limit movement from high-risk areas to other parts of the world has also dampened the activities of the airline industry with lesser flights allowed to enter or exit from the location pinpointed.
A feature from the ‘Aviation Week’ publication highlights the findings on the effect of the COVID-19 outbreak on the industry and found that a huge number of carriers have canceled their flights all the way through March and some even shut down operations temporarily. The reason behind the move was in an effort to limit the spread of the potentially life-threatening virus, in which the World Health Organization (WHO) has declared as a ‘public health emergency of international concern” due to the rapid rate of it spreading to 18 countries outside of China as of January 31.
The Billions in Airline Revenue Lost due to the COVID-19
A Forbes report published on February 14 stated that the epidemic could potentially lower the global airline revenue by up to USD 5 billion in the first quarter of the year. The revenue hit is a result of about 40% overall reduction in passenger capacity, which translates to almost 20 million passengers less than projected for the period. According to the U.N.’s International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO), the set-back in revenue was based on preliminary forecasts relating to the expected economic impacts from COVID-19 travel bans on international air connectivity.
The fact that Chinese outbound tourism is a major factor in Europe, Singapore, Macau, and the United States, the realization of the travel ban impact is finally settling in. Chinese nationals have for the longest time been one of the biggest spenders in global tourism. With the travel restriction in place, there will almost certainly be a big impact particularly on Asian countries heavily reliant on Chinese tourism spending. For instance, Vietnam’s tourism sector is estimated to see a reduction of about two million Chinese visitors due to the virus, which could result in a loss of about USD 1.8-2 billion of lost tourism revenue, as reported by the official ‘Voice of Vietnam Radio’.
Impact of COVID-19 in the Hotel Industry
The hospitality and tourism industry was hit hard by the COVID-19 outbreak, whereby hotels are seeing a drastic drop in its occupancy rates and reduction in number of travelers. The outbreak of the contagious disease has got everyone on their guard, resulting in cancelled travelling plans and hotel bookings.
Hotels all around the globe are feeling the heat as a result of the virus outbreak, and are worried about the bleak outlook of the industry with the death toll and infection cases on the rise.
One of the world's largest hotel brand, Wyndham Hotels and Resorts has reportedly closed about 70% of its hotels in China. The properties that remain open are also not seeing much check-ins as the number of guests decline in the face of the outbreak. Its Chief Financial Officer Michele Allen was quoted as saying that the situation is expected to continue through at least until the end of March.
Another renowned property, Wynn Resorts has also closed down its properties in Macau in the face of the outbreak and was reported to be losing as much as $2.6 million per day as long as their properties remain closed.
Countries that rely heavily on Chinese tourist such as Thailand are severely affected as hotels and resort in the country continue to experience low occupancy rates. For instance, some hotel owners in Phuket even get their employees to go on unpaid leave to reduce operating cost. In all seriousness of the current situation, hotels are also affected even into the month of March, whereby the booking rate is only between 40 to 50 per cent occupancy, compared with the normal occupancy rate of 70 to 80 per cent.
COVID-19 outbreak affecting the global supply chain
The COVID-19 outbreak has the potential to cause severe economic and market dislocation. Globalization has encouraged companies to build supply chains that cut across national borders, thus, making economies much more interconnected. The virus is snarling supply chains and disrupting companies.
Closure of Chinese factories has also inadvertently disrupted supply to the automobile and electronics companies around the world that depend on China for parts. Car plants across China such as Volkswagen, Toyota, Daimler, and General Motors have been ordered to remain closed following the Lunar New Year holiday, preventing global automakers from resuming operations in the world's largest car market. The outbreak will force carmakers in China to slash production by about 15% in the first quarter, according to S&P Global Ratings. Additionally, the Nikkei Asian Review also revealed that China has prevented Foxconn from re-opening its plants due to the spread of the COVID-19, a move that has disrupted the production of not only Apple and Amazon products, but, also the Android category involving brands like Huawei.
Fears of the economic impact have sparked global anxiety resulting in stock markets plunge, falling oil prices and several international brands such as Apple, Uniqlo and Starbucks have temporarily shut down stores in China. Starbucks was reported to have closed more than half of its 4,300 stores in China and Disney has closed both the Shanghai park and the Hong Kong park for the time being until further notice. Following this move, Disney anticipates being set back by about USD 175 million combined operating income if they remain closed for two months due to the Coronavirus outbreak, which has reduced the presence of people in many of China’s public areas.
The current situation revolving the COVID-19 epidemic seems to bring back memories of the SARS epidemic in 2003, which hit China's economy severely that year. However, the only difference is that China today is a global superpower and the world's second-largest economy. This means that whatever happens in China now matters much more than it did during SARS. The virus outbreak will likely be a dent to the Chinese dream but a decline in the hefty Chinese economy will be felt around the world and the impact of this will only be known in the weeks and months to come, depending on the direction in which the present situation is headed.
Impact of the COVID-19 on the World’s Economic Powerhouse
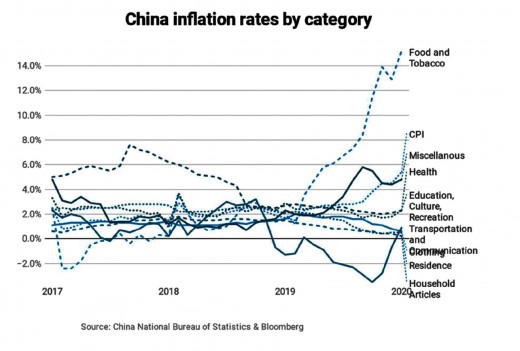
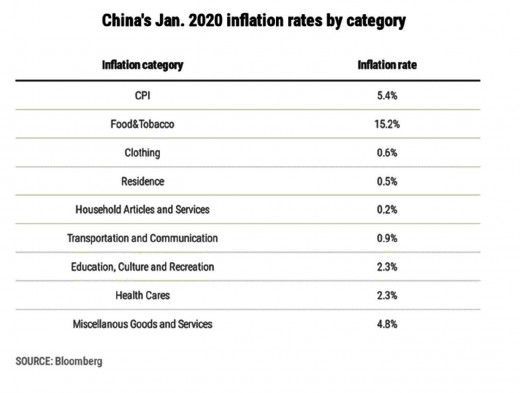
With the high rate of infection and the increasing death toll due to the COVID-19 outbreak, China has experienced an adverse effect on its factory output, consumer spending, tourism, and commodity prices have seen major drops. With the dire situation, the Chinese economy seems to be facing a tough time and is experiencing a soaring inflation rate. China’s overall consumer price index (CPI), which had been at 1.5% in January 2017 and fluctuated between 2% - 3% during most of 2019, leaped to 5.4% in January 2020.
The phenomenon of shuttered facilities and involuntarily idled workers have resulted in reduced production and the tightened control on product supplies has caused the price to skyrocket. In theory, China's overall inflation rate is not that huge, but the rapid increase is a cause for concern. Some inflation is benign and is usually the byproduct of economic growth. If the pattern doesn't moderate or slow down anytime soon, the country might be forced to focus less on growth but more on price stability. When inflation gets out of control, the repercussion in terms of spiraling prices can make living too expensive for people. This will significantly send tremors throughout the global economy. With China having about 18% of the world's population, a curb in consumer buying due to higher prices could ripple through the world.
Conclusion
The Asian government has planned to brace for economic impacts of the COVID-19 outbreak; Japan cautions the drop in growth, Malaysia will announce a stimulus package, and Singapore could see a recession. The Japan Policymakers on February 14 braced for a sharp contraction in October-December development and warned of a slump in output and consumption due to the Coronavirus outbreak, as Asian economies raised the alarm over darkening economic outlooks.