What is Corporate Sustainability or Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)?

Business Sustainability
Sustainability is one of the hottest topics of the 21st century, with much coverage in academic literature, on the political scene, in media, as well as in business. The most recognized and quoted definition of sustainability is, “development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their needs” as was devised in 1987 by the United Nation (U.N.) World Commission on Environment and Development (WCED), also known as the ‘Brundtlandt Commission’.
It is being increasingly recognizes that the current approach to development is inadequate and a sustainable one is required. This recognition is being echoed in the business world as well, which brings us to the next concept - corporate sustainability.
Corporate sustainability originated with "green teams"
The idea of "green teams" originated with a group of employees who would gather to share ideas about environmental efforts in the community and the idea grew into corporate sustainability with support from the executive suite. Members of the Corporate Responsibility Officer Association (CROA) are usually the people within organizations who have primary responsibility for sustainability initiatives in the organizations where they work.
The triple bottom line refers to the three factors which contribute to corporate sustainability
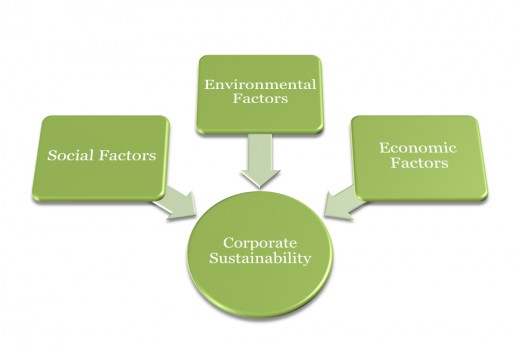
What is Corporate Sustainability?
Corporate sustainability essentially refers to companies’ efforts to reduce the negative effects they have on people, the environment, and on the economies where they operate. The three components - economic, environmental and social are commonly referred to the as the triple bottom line (TBL) framework and are interlinked. The idea is that companies have an effect on the people where they do business, on the local environment, as well as the economy and so companies should take action and commit to reducing negative effects.
Examples of each component of the triple bottom line is explained below:
- Social: This refers to companies' commitment to gender equality, diversity, workplace health and safety, retention initiatives, human rights, etc.
- Economic: This refers to profitability, job creation, expenditures on outsourcing and human capital, etc.
- Environmental: This refers to companies' efforts to decrease the negative impacts their products / services have on air, water, land, biodiversity, peoples' health; their commitments to increase energy efficiency; reducing waste; etc. Environmental initiatives such as reducing carbon footprint are generally considered "low-hanging fruit" which showcase companies efforts to "go green" and help improve organizational reputations.
With an increasing amount of stakeholders - including employees, investors, and customers paying attention to companies' corporate sustainability efforts, companies are re-engineering their supply chains to make them "greener" and are increasingly supporting social causes within communities.

Meaning of Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)
The concept of corporate social responsibility (CSR) has been used interchangeably with the concept of corporate sustainability but it's important to understand that corporate sustainability goes beyond the concept of CSR. Corporate social responsibility, which is also sometimes referred to as corporate citizenship traditionally refer to companies' ethical practices particularly within the society where they operate. Therefore, CSR is only one aspect of the TBL, whereas corporate sustainability entails the social aspect, and goes beyond it to include environmental and economic aspects as well.
Corporate sustainability programs are a good way for companies to show that they are good corporate citizens, and not only concerned with their financial performance. CSR programs that have been popular in recent years include those centered around community health, education and development.
Did you know that corporate sustainability reporting has become the norm amongst the world's largest companies?
A 2011 KPMG study on corporate sustainability reporting revealed that a whopping 95% of the of the largest 250 companies (G250) are now reporting their effects on the people, economy, and the environment where they operate.
Benefits of Corporate Sustainability
It's be being increasingly recognized that incorporating corporate sustainability into business makes good business sense and creates unique business value. Benefits of corporate sustainability initiatives include improved company reputation, enhanced employee morale, and strengthened competitiveness, amongst others.
Corporate sustainability is an important concept that is growing in relevance as the demand for natural resources around the world keeps growing but their supply diminishing. Particularly, large companies that have a heavy social and/or environmental footprint are being encouraged and prompted to account for their performance in difference spheres, increasing transparency, developing employees and using resources more efficiently. "Green business" is a bandwagon many large organizations are driving or at least jumping onto.