Understand Surgery: Microtia Repair
What Is Microtia?
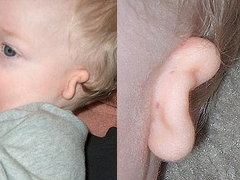
Microtia is a birth defect defined as “the lack of an ear.” In the United States, microtia affects 1/6000 births annually. Approximately 63% of the patients are male and the remaining 58% of the patients are female. Microtia most commonly occurs on the right side, but has a 9% chance of showing up on both sides of the head.
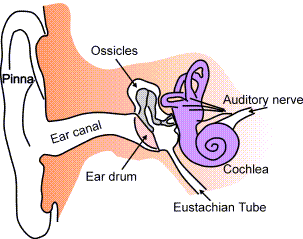
Inside of the Ear
The Etiology of Microtia Repair
The etiology (medical origin) of microtia is typically unknown, but there are several maternal factors that may contribute to the risk of developing this birth defect. These maternal factors include: intrauterine tissue ischemia (reduced blood flood to the uterus), potentially caused by a compressed artery within the womb. Other factors may be age, medication, first trimester rubella, and genetic factors. Microtia is frequently associated with two syndromes: Goldenhar syndrome and Treacher-Collins syndrome.
Historically the first documented microtia repairs occurred within the late 1500s. These procedures involved the use of cheek or scalp flaps for grafting a transplant. In the late 1920s homologous grafts, typically from the patient's mothers, began to emerge. The technique was soon abandoned because of postoperative complications with tissue rejection. Today we use the autologous (taken from the patient) rib graft procedure; originating in the 1940’s, the autologous rib graft procedure constitutes a major advantage because the graft will grow with the child patient.
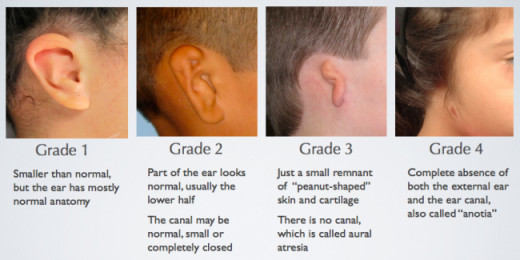
Microtia is divided into four grades of severity
Grade
| Description
|
|---|---|
Grade 1
| Exhibits a smaller than average pinna, and occasionally displays signs of malformation, but normal characteristics of the external are still present.
|
Grade 2
| The pinna is less developed than grade 1, and structures (like the helix and antihelix) are less defined.
|
Grade 3
| The pinna is completely absent, leaving behind a vertical remnant of skin. The remnant contains unorganized cartilage, but typically the patient has a well formed earlobe. In extreme cases, microtia may cause damage to the middle ear (eardrum) resulting in hearing impairment on the affected side.
|
Grade 4
| Total absence of the ear.
|
(Simplified)
Steps
| Procedure
| Type of Anesthesia
|
|---|---|---|
Step 1
| The surgeon uses a template to construct a new ear from the patient's rib cartilage, and attaches it to the afflicted side.
| General
|
Step 2
| The surgeon positions the earlobe appropriately and lobular tissue is shaped to maintain vascular integrity.
| Local (Must Meet Age Requirement)
|
Step 3
| The surgeon uses grafted skin from the stomach or buttocks to go behind the ear and lift the framework of the structure as necessary.
| General
|
Step 4
| The surgeon removes scalpel hair with a laser and finishes any necessary touch up work.
| Local or General
|
The Surgical Steps Of Microtia Repair
Microtia repair by autologous rib graft is generally performed in 3 to 4 stages, but before the operative team begins the procedure the surgeon must draft a template to map the construction of the ear. This is typically done by drawing up a template from the patients healthy ear and reversing the image so that both sides match. If the microtia is bilateral a sibling or other model will be used to create the template. The lateral canthus, alar nasal cartilage, and the corner of the mouth serve as landmarks to estimate the position of the graft, while the appropriate measurements are taken and used to determine the precise location of the new auricle.
Stage one of an autologous microtia reconstruction begins first with general anesthesia. The procedure is then initiated by securing the cartilaginous graft from the donor site on the contralateral chest wall. The surgeon will then remove the necessary cartilage (which will represent the main framework of the new graft) from the floating rib cartilage. The chest wound is then closed. The surgeon’s next step is to remove the perichondrium from the cartilage by using a periosteal elevator ( or freer), a scalpel, and a chisel. After isolating the perichondrium, the surgeon uses the autologous material to sculpt the main framework of the patient’s graft until it resembles the template. The surgeon then fashions the helical rim and attaches it to the main framework with a non-absorbable suture such as silk or stainless wire. After completing the graft, the surgeon sets it aside and makes an incision pocket on the recipient site. The surgeon then carefully inserts the graft and closes the wound. A wound vacuum/drainage device is employed to ensure that the wound site is clean of debris and secretions. A bulky wound dressing is applied to the surgical site and left in place for five to seven days; additional temporary protective equipment may be applied to keep young children from disrupting the healing process. The patient is restricted from using a hair dryer, participating in contact sports, and swimming for up to 6 weeks
Stage two of microtia reconstruction involves the transposition of the earlobe if one is available, and any existing lobular tissue is moved into position as a flap to maintain the integrity of the vascular structures. Unusable tissue is removed, and the surgeon ends the procedure by suturing the wound and applying a light dressing. Although it is technically okay to perform stage two simultaneously with stage one, additional risks of vascular compromise and and esthetic outcome should be considered with caution; it is recommended that the earlobe transposition is performed once the first surgical wound has completed the healing process. As long as the patient is age appropriate, the transposition of the earlobe may be performed under local anesthesia.
Stage three of microtia reconstruction focuses on the elevation of the posterior aspect of the framework of the ear. This stage of reconstruction usually involves grafted skin from either the lower abdomen or buttocks; because of the invasive nature of skin grafting, the procedure is performed under general anesthesia.
The fourth stage of microtia repair may or may not be necessary. The procedure involves the removal of any scalp hair found on the new ear, as well as other minor modifications including: creating a tragus, and/or a false conical shaped entry to stimulate the auditory meatus and external ear canal. Any of the stages reconstruction may be combined if deemed appropriate.
Before and After (Includes Surgical Footage)
Reference
1. Junge, Teri. ( January 2014) "Microtia Repair." The Surgical Technologist, pgs. 17-23.
Results of A Positive Prognosis
- Microtia-Atresia - Long-Term Results
Microtia, Atresia, Reconstructive Ear Surgery by Dr. Burt Brent