Energy Sources Primer: Non-Renewable Options

Energy- electricity to run our households, the fuel which runs our cars - to be honest I take it all for granted when I get up in the morning. But the start to my day, not to mention my entire day, would be very difficult without the various sources of energy we obtain from the earth. Looking into energy sources and their uses is a bit of a departure from my normal health and medical articles. One of the major reasons why I write is to learn and it occurred to me with all this talk about renewable energy and gas prices on the rise I don’t really have the basics tucked away in my brain about where our energy comes from. I spent some time looking into the basics- the different categories and sources of energy and how we use them for electricity, heat, and transportation- and put them together in this beginner’s article and a follow-up on renewable resources. These articles only serve as the basics to energy, since there are so many different paths these basics can go down- the economic aspects, the environmental angle as well as a much deeper look into energy production and consumption. Here is just the starting off point.
First, there are the four types of non-renewable energy sources, the fossil fuels- coal, crude oil (petroleum), and natural gas-as well as uranium as a source for nuclear energy. All three fossil fuels take an extremely long time to come about which gives them the status of non-renewable, added to the fact that we are currently using them up at a much faster rate than they will be produced. All three are made as a result of time, pressure, and heat in the earth’s layers and are chiefly made up of hydrocarbons. Each can be used directly or converted for use to give us electricity, heat, and fuel for our automobiles largely through their combustibility. And unfortunately this combustion of these resources contributes significantly to the greenhouse effect by releasing the chief greenhouse gas, carbon dioxide as a byproduct of their burning. Uranium is also a non-renewable resource but categorically is distinct from the three fossil fuels.

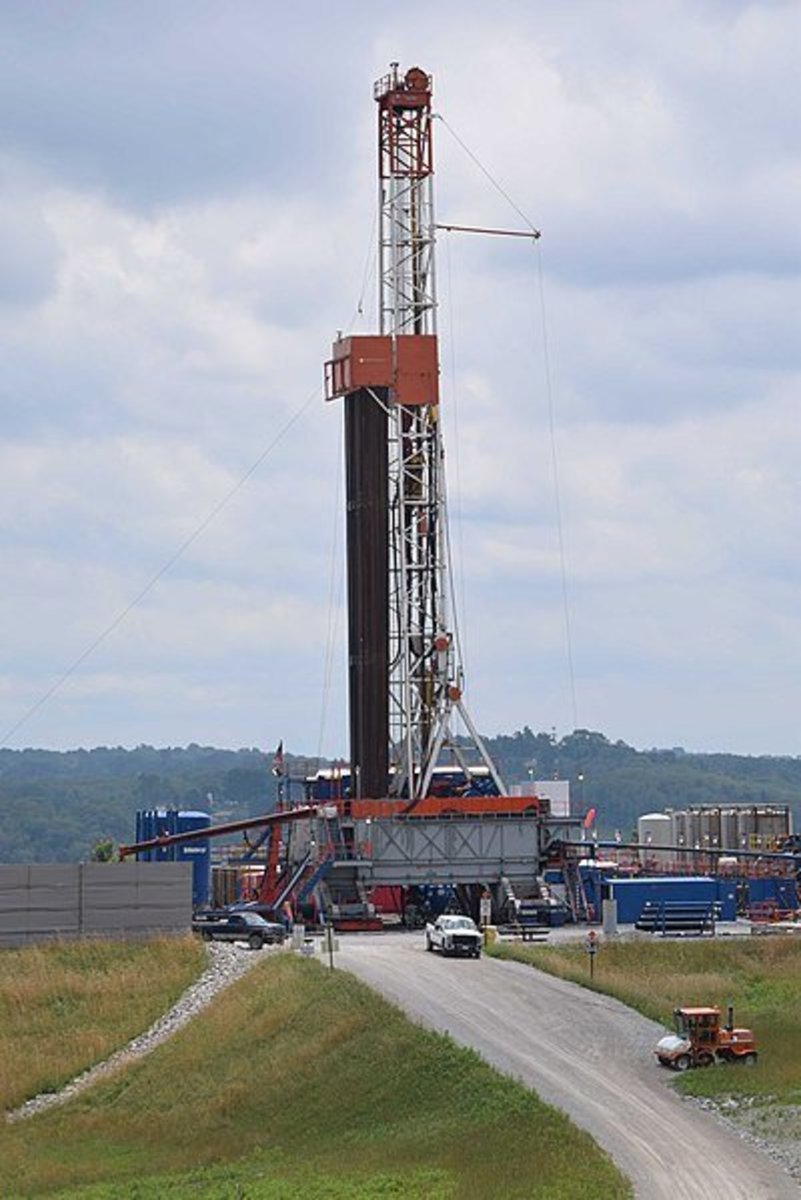
Natural Gas is chiefly composed of hydrocarbons, largely consisting of methane (CH4), the simplest hydrocarbon. Other hydrocarbons such as ethane (C2H5), propane (C3H8) and butane (C4H10) are found in it. In addition Natural Gas (NG) contains carbon dioxide, nitrogen, and hydrogen sulfide. It comes from rock formations and coal beds, often found with oil but can also be found underground on its own. The specifics of the underground environment dictate how difficult the extraction process can be. Currently in order to maximize this form of energy, methods are being developed to make historically difficult-to-extract natural gas reservoirs less difficult to get at. These natural gas formations are referred to as unconventional formations, and they include deep formations and tight formations-the names indicate why they are difficult to extract. Also shale formations are an example of unconventional sources since the sedimentary rock shale is tricky to extract from due to its impermeable status compared to others like limestone and sandstone.
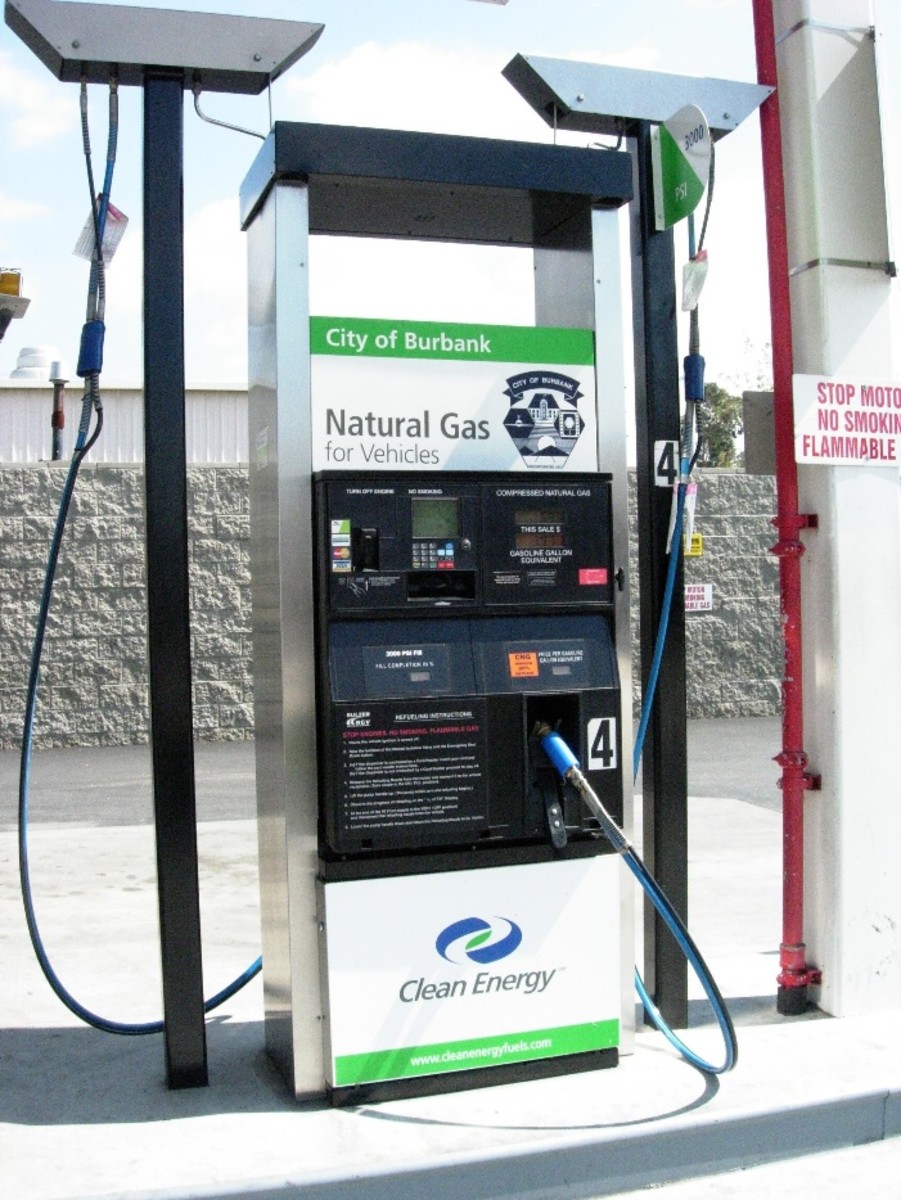
Natural gas can be piped to homes and buildings for electricity and heat. If piping is not an option due to a remote location Compressed Natural Gas (CNG) is an alternative, albeit an expensive one. NG can also be used for transportation fuel in both automobiles and aviation. NG is transported in either the compressed or liquefied form (abbreviated as LNG), then decompressed or regasified, respectively, when it reaches its destination whether that be across an ocean, a highway, or through a pipeline network. Propane and butane are removed when Natural Gas is converted to LNG. Natural gas is the cleanest fossil fuel, gauged by its CO2 emissions. It certainly does contribute to the greenhouse effect via releasing CO2, the major greenhouse gas, into the environment but it has the dubious honor of being the cleanest in comparison to crude oil and coal. It also produces less sulfur dioxide and nitrous oxides as well in comparison (it generally does not contain sulfur in the first place). Currently the US has over 300,000 miles of pipeline for natural gas. The world’s NG will last an estimated 100 years, the largest quantities being found in Eastern Europe and the Middle East with US behind them. Currently the US is attempting to use more of our own ‘home-grown’ natural gas in order to decrease our reliance on foreign oil, much of the US’s stash in located in shale formations.
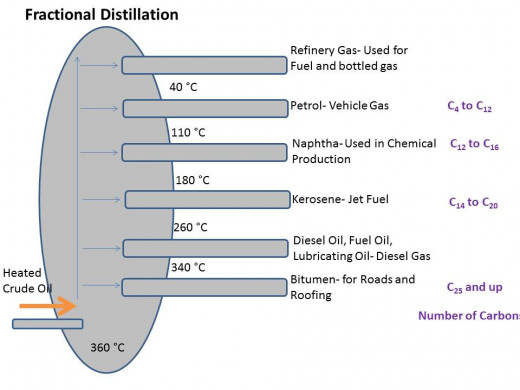
Crude oil can be refined via boiling into a variety of fuels, including gasoline (petrol) and diesel fuel (petrodiesel), fuel oils for ships and furnaces, jet fuel, kerosene, and liquefied petroleum gas. As well petrochemicals are extracted from crude oil and contribute to the materials of a wide variety of products including fertilizers, plastics, and medicine. Crude oil is obtained from rocks, underground traps, and sand; made from a geochemical process involving pressure and time which converts organic materials to crude oil. It is a naturally occurring flammable liquid, made up of a mixture of hydrocarbons and other liquid organic chemicals. The Middle East has over 50% of the world’s supply, followed by North America. Reservoirs of crude oil are generally found near boundaries of tectonic plates. Oil, and natural gas as well since the two are often found together underground, makes its way up close to the earth’s surface through various types of sedimentary rock based on the given rock’s permeability. Sandstone and limestone are permeable and thus oil and natural gas can pass through them. As previously mentioned, shale is relatively impermeable. It often functions as the barrier between these fossil fuels and the earth’s surface. Wells are drilled through the impermeable rock layers to get to the more permeable layers that contain these non-renewable resources. In the process of oil mining some comes up into the well on its own, so to speak, while other portions are coaxed out of the reservoir with the help of water and/or steam and gas pumped into it. It is predicted that oil will be exhausted in about 30 years or so. In comparison to coal, it burns cleaner and is less expensive as it yields more energy in a comparable sample.
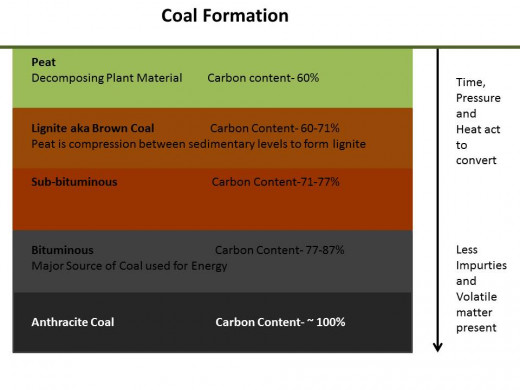
Coal is a type of sedimentary rock found in strata known as coal beds or coal seams. It is primarily composed of carbon with varying amounts of hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen. It is formed over time in several distinct varieties on its way to becoming coal. Dead plants are converted first to peat, the earliest precursor of coal, and then to lignite also known as brown coal, then sub-bituminous coal to bituminous coal, then to anthracite coal. Each transisitional form of coal, other than peat and graphite-the form made after anthracite, can be used for fuel with varying efficiency. The carbon content increases in the varieties starting with only about 10% carbon in peat and going to almost 100% carbon in anthracite coal. Coal is combusted, or burned, via a reduction-oxidation reaction where it is the reductant. It donates electrons to an oxidant, generally oxygen. This reaction, known as an exothermic reaction, gives off energy.
Coal is the major source of electricity. Although, in the US, hydraulic fracturing of tight shale for Natural Gas is now less expensive and thus closing the gap on the source of electricity. The EIA reports in 2008, the US utilized coal for half of its electricity, whereas in 2012 coal was down to 42% and expected to continue to decrease, as the use of Natural Gas for electricity rises. Other than being a major contributor for electricity, coal can also be used for residential heating and cooking. Coal can be gasified into syngas, a mixture of CO2 and H20, or liquefied to be used as a transportation fuel. But that being said the vast majority of coal mined in the US is used for electricity. Coal has the highest CO2 emission rate out of the three major fossil fuels however this can be minimized if proper cleaning equipment is put into smokestacks. The toxic ash leftover from the electricity-generating process also poses an environmental problem. In addition the process of coal mining is harmful to the local environment around the mines and also puts miners at high risk when the work is done underground. At the current rate of usage the world-wide coal supply should last for about 200 years. The US has the largest supply of coal compared to the rest of the world, with Russia somewhat close behind.
The other major source of non-renewable energy is nuclear energy which uses uranium to generate the heat necessary to allow for turbines to generate electricity. Nuclear energy can be used for heating, cooking, and transportation. Although it may seem a good alternative to the fossil fuels since it does not contribute greenhouse gasses to the environment the use of nuclear energy comes with the warning of nuclear accidents, seen most recently in Japan and some time ago, but still engrained in memory, in Chernobyl. In addition to the huge risk factor of an accident, overall the systems necessary to produce nuclear energy from uranium are costly to set up and come with strict regulations. Currently nuclear energy contributes about 19% of the US’s energy for electricity generation in 2011.
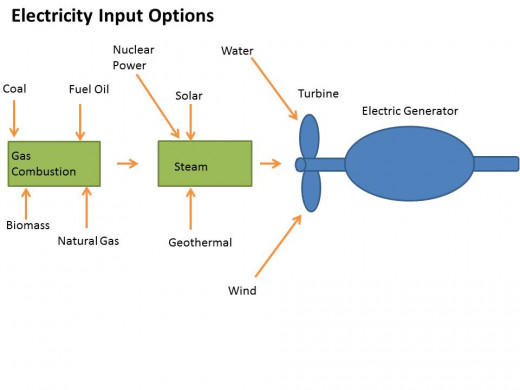
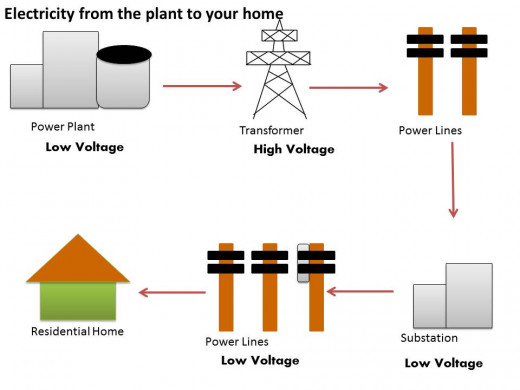
Electricity can be generated by burning the three fossil fuels discussed above-NG, coal, or crude oil-this heat is used to convert water to steam and the steam drives turbine generators to make electricity. The heat can also come from the fission, or splitting, of uranium to make nuclear energy. When prompted by an energy source, the shaft of the turbine will turn, spinning its blades. This mechanical energy is taken in by the generator to produce an electric current that is carried through copper wires. The generator contains magnets that produce a magnetic field, this field forces electrons out of their atom’s shell and these electrons in transit yield what we know as electricity. Electricity turbines need an energy source at the start to get things going but these non-renewable resources make up only half of the options available. Renewable resources can be used to power turbines for electricity, as well can be used for transportation fuel and residential/commercial needs for heating and cooking. Check out part two of this article for more information on renewable resources.