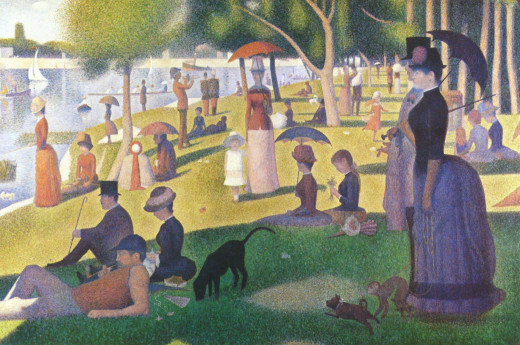An Overview of 19th Century Art

The Context of 19th Century Art
The Art Movement that directly preceded the 19th Century Movement was Baroque. In particular the sub-genre of Neo-Classicism was the main art movement at the turn of the 19th Century. It had an interest in Classical values and moral seriousness. The 19th Century saw a new era of art in which France played a major role. Artists became freer to explore the boundaries of art- they were freed from having to create art that had some kind of social utility and abandoned convention. By the end of the 19th Century most artists would stay true to their vision of what art was at cost of patronage, financial gain and general public opinion.
Sub-Genres of the 19th Century Art Movement
All of the major Art Movements are made up of several sub-genres. The 19th Century can be divided into 13 such sub-genres as follows:
•Romanticism- a direct response to Neo-Classicalism which rejected rules and reason in favour of human emotions and intuitions.
•Orientalism- art which portrayed the Near and Middle East in a manner which did not reflect the truth but which flattered the preconceived ideas and fantasies of these, then, far off lands in the minds of the people of Europe.
•Medievalism- a reaction against the increasingly commercialness of the art world. It took its influence from the Medieval art which preceded the Renaissance.
•Pre-Raphaelitism- started by the pre-Raphaelite Brotherhood, Millais, Holman-Hunt and Rossetti. They used vivid colours in their work and portrayed natural features in great detail.
•Realism- abandoned the conventions regarding what should be painted. They included much more mundane subject matter including scenes of poverty and labour.
•Materialism- a sub-genre influenced by the philosophical movement of the same name. Materialism is a complete rejection of Idealism stating that we are a product of our environment- gender, class, nationality etc.- rather than, as Idealism would have it, a product of our soul.
•Impressionism- developed in France in the second half of the 19th Century. Impressionists rejected the tradition of representing the world accurately and instead concentrated on how paint could be used to capture sensory impressions.
•Neo-Impressionism- a sub genre that cared less about creating movement and spontaneity and more about design and colour, giving their paintings a stiffness.
•Secessionism- There were three main secession movements- Munich, Berlin and Vienna- they abandoned the traditions of the Art Academies and asked for their work to be exhibited independently
•Aestheticism- linked to the literary movement headed by Oscar Wilde and of the same name, it sought to free art from any moral, social or political purpose and make it more about the aesthetics
•Symbolism- influenced by spiritualism and a response against the 19th Century focus of science and technology, it portrayed disturbing images.
•Post-Impressionism- a broad term to describe work from the 1880s through to the early 20th Century. It's emphasis was on form and design.
Major Artists of the 19th Century
Romanticism:
- William Blake
- Casper David Friedrich
- Mallord William Turner
Orientalism:
- Eugene Delacroix
- William Holman Hunt
- Chales Gleyre
Pre-Raphaelitism:
- John Everett Millais
- William Morris
- Dante Gabriel Rossetti
Realism
- Edgar Degas
- Edouard Manet
- James Tissot
Materialism
- Gustave Courbet
- Jean-Francois Millet
- Henri Fantin Latour
Medievalism:
- John Everett Millais
- Peter Van Cornelius
- Edward Burne-Jones
Impressionism
- Paul Cezanne
- Claude Monet
- Pierre-Auguste Renoir
Neo-Impression
- Camille Pissarro
- Paul Signac
- Georges Seurat
Seccessionism
- Gustav Klimt
- Egon Schiele
- Franz Von Stuck
Aestheticism
- Edward Burne Jones
- Albert Moore
- Abbott McNeill Whistler
Symbolism
- Odilon Redon
- Edvard Munch
- Henri Rousseau
Post Impressionism
- Vincent Van Gogh
- Paul Gaugin
- Maurice De Vlaminick













Some Famous Artworks from the 19th Century
- Romanticism: Tree with Crows- Friedrich
- Orientalism: The Turkish Bath- Ingres
- Medievalism: Claudio and Isabella- Hunt
- Pre-Raphaelitism: Ophelia- Millais
- Realism: Olympia- Manet
- Materialism: Luncheon of the Boating Party- Renoir
- Impressionism: Rouen Cathedral West Facade Monet
- Neo-Impressionism: Sunday Afternoon on the Island of La Grande Jatte- Seurat
- Seccessionism: The Kiss- Klimt
- Aestheticism: Nocturne: Black and Gold- The Falling Rocket –Whistler
- Symbolism: Rousseau- The Centennial of Independence
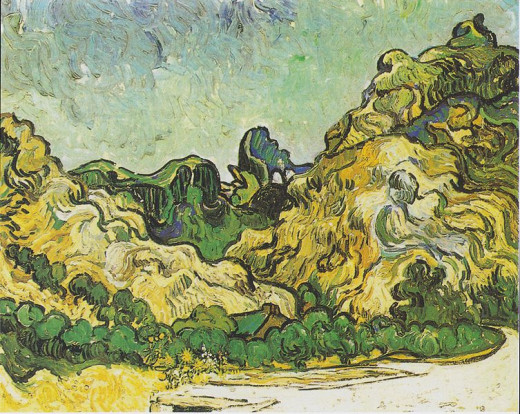
- Post-Impressionism: Mountains at St Remy- Van Gogh