Astronomy, History and Modern astronomy

What is Astronomy?
Astronomy is that branch of science which deals with the scientific study of celestial objects (such as stars, planets, comets, and galaxies) and phenomena that occur outside Earth’s atmosphere.Astronomy deals with the evolution , physics, chemistry, meteorology and motion of these celestial objects.
The field of modern astronomy is divided into two major branches viz observational and theoretical astronomy.
-
Observational astronomy deals with acquiring and analysing data, mainly using basic principles of physics.
-
Theoretical astronomy deals with designing analytical models to describe astronomical objects and phenomena.
The two fields complement each other, with theoretical astronomy seeking to explain the observational results, and observations being used to confirm theoretical results.
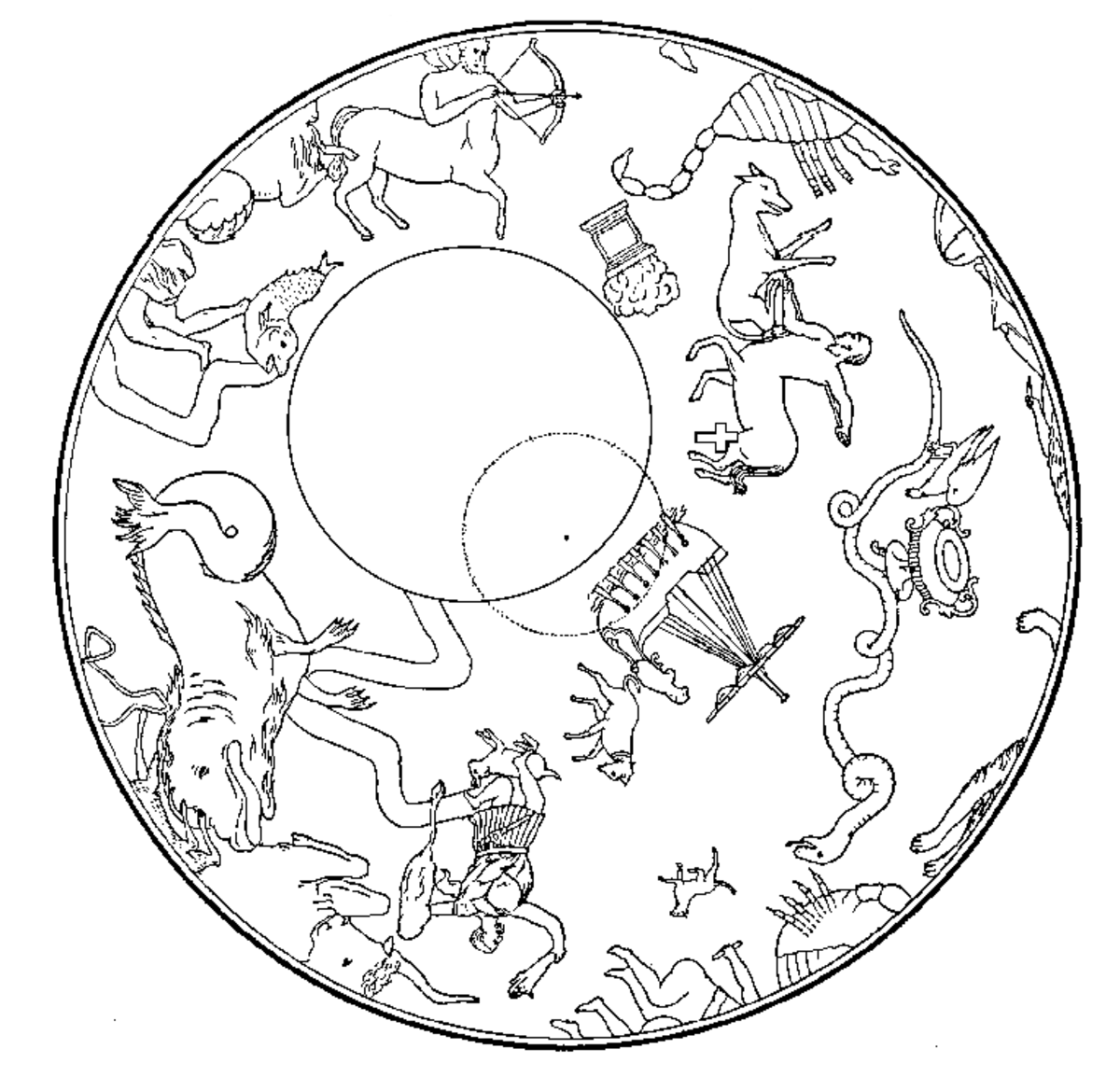
Astronomy is said to be the one of the oldest sciences dating back to antiquity. Researchers have been able to find its roots in religious, mythological, cosmological, calendrical, and astrological beliefs and practices of prehistory. Various artefacts have been found by the researchers so far that help us to understand how early civilizations performed methodical observations of the night sky and used that for social and religious purposes.
History of Astronomy
Early civilizations associated astronomy mostly with religion. They identified these celestial objects with Gods and Spirits. They performed various methodical observations of the sky at night and observed the movement of these celestial objects and associated it with seasons, rain, drought and tides. Earlier astronomers were mostly priests and that they understood celestial objects and events to be manifestations of the sanctified, hence early astronomy's connection to the stars and their movement is now called as Astrology.
Various ancient structures are considered to be built according to the astronomy. The biggest example of which is Stonehenge which supposedly fulfilled astronomical, religious, and social functions.
Calendars of the world have often been set by observations of the Sun and Moon (marking the day, month and year), and were important to agricultural societies, in which the harvest depended on planting at the correct time of year, and for which the nearly full moon was the only lighting for night-time travel into city markets.

Early civilizations and Astronomy
Early civilizations, like Harappan, Mayans,Greek, Egyptians and Ancient Chinese civilizations used astronomy to keep track of time .
Harappan Astronomy
The Harappan civilisation lasted from about 7,000 BC to 2,000 BC. Harrapans were literate, they used the Dravidian language and were well versed with the astronomy. Various artefacts show how they mapped their cities according to the astronomy. The star-calendar used by the Vedic ritualists was adopted by the Aryans in India,Linkages between ancient Harappan scripts and latter Vedic texts suggest that Harappan priest-astronomers tracked progress of Mercury, Venus and Saturn, and most likely all of the planets. They also appeared to have mapped the sky. Some of the pieces of recovered tablets show what appears to be a discussion of the North Star in one case and the star cluster, Pleides, in another.

Greek Astronomy
Greek astronomy is the astronomy written in Greek language it includes ancient Greek, Hellenistic,Greco-Roman, and late antiquity eras. It is not limited geographically to or Greece to ethnic Greeks. The development of astronomy by Greeks is considered as the major phase in early Astronomy. Most of the constellation of the northern hemisphere have been derived from the Greek astronomy even names of many stars, asteroids and planets have been derived from it. Greek astronomy was influenced by Egyptian and Babylonian astronomy and in turn it influenced Indian, Arabic and Western astronomy.
Egyptian Astronomy
The Egyptian astronomy is believed to began from 5th melennium BCE. The stone circles of Nabta Playa are believed to be based on the astronomical alignments. Egyptians also made use of 365 day calendar in 3rd melennium BCE and even studied the sky to determine the annual floods in river Nile. The Egyptian pyramids were carefully aligned with the pole star, the temple of Amun-Re is aligned with the rising of the mid-winter sun. Astronomy played a very important role in determining the date of various religious festivals, the priests of the temples studied the sky and movement of the celestial objects to determine the date for the religious festivals.



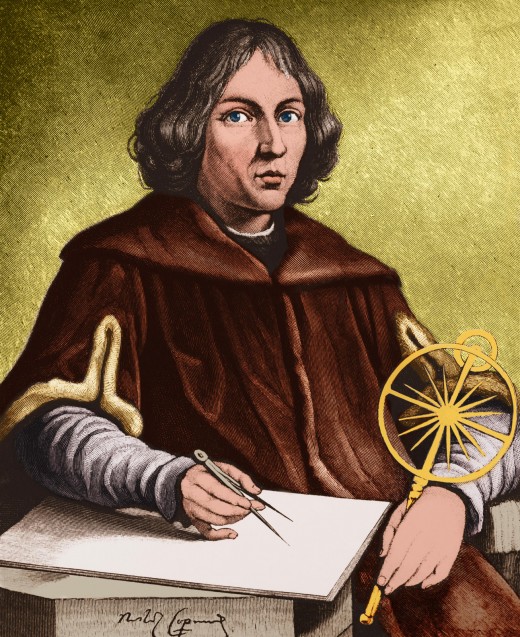
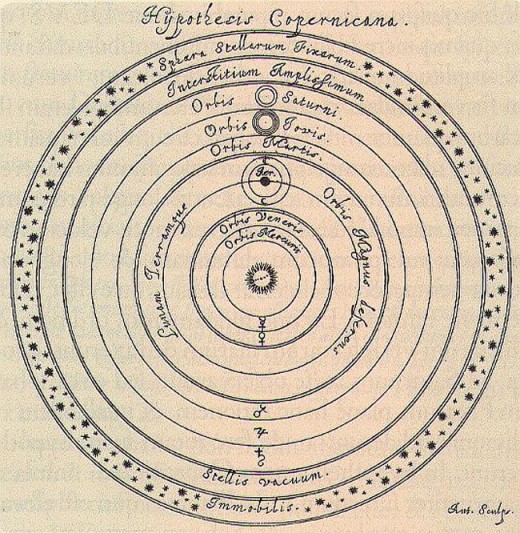
Birth of Modern Astronomy
It was in 1530 when the real rejuvenation of the modern astronomy took place with the Theory of solar system commonly known as the Copernican system given by Nicolaus Copernicus. Nicolaus Copernicus was a cathedral cleric in a small Polish city who played a leading role in the emergence of modern science. Although in his lifetime he was not able to prove that Earth revolves about the Sun, he presented such compelling arguments for this idea that he turned the tide of cosmological thought and laid the foundations upon which Galileo and Kepler so effectively built in the following century.
Many of the modern scientific concepts of observation, experimentation, and the testing of hypotheses through careful quantitative measurements were pioneered by a man Galileo Galilee who lived nearly a century after Copernicus.
The new ideas of Copernicus and Galileo began a revolution in our conception of the cosmos.

Archeoastronomy
The study of the astronomical practices, celestial lore, mythologies, religions and world-views of all ancient cultures we call archaeoastronomy. It may be discribed as the "anthropology of astronomy", to distinguish it from the "history of astronomy".
Archaeoastronomy uses a lot of methods to get the evidence of past practices including archaeology, anthropology, astronomy, statistics and probability, and history.
Because there are many methods and they use data from different sources, integrating them into a single argument has been a long-term difficulty for archaeoastronomers.
Archaeoastronomy can be applied to all cultures and all time periods. The meanings of the sky vary from culture to culture; nevertheless there are scientific methods which can be applied across cultures when examining ancient beliefs.
Methodology
There is no one way to do archaeoastronomy. The divisions between archaeoastronomers tend to depend on the location of kind of data available to the researcher. In the Old World, there is little data but the sites themselves; in the New World, the sites were supplemented by ethnographic and historic data.so, there are two major methods of doing archeoastronomy one is Green Archeoastronomy and other is Brown Archeoastronomy. Green is based primarily on statistics and is particularly apt for prehistoric sites where the social evidence is relatively scant compared to the historic period. Where as brown archaeoastronomy has been identified as being closer to the history of astronomy or to cultural history, in so far as it draws on historical and ethnographic records to enrich its understanding of early astronomies and their relations to calendars and rituals.
"The cosmos is all that is or ever was or ever will be. Our feeblest contemplations of the Cosmos stir us—there is a tingling in the spine, a catch in the voice, a faint sensation, as if a distant memory, or falling from a height. We know we are approaching the greatest of mysteries." |source
This content is accurate and true to the best of the author’s knowledge and is not meant to substitute for formal and individualized advice from a qualified professional.