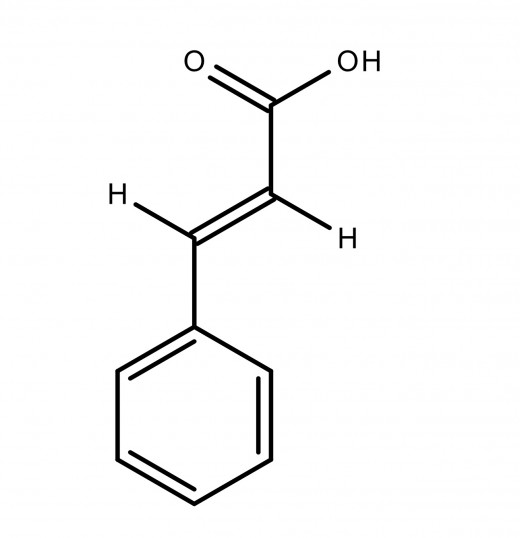
Cinnamic Acid
What is it?
Cinnamic acid is an odourless white crystalline acid, which is slightly soluble in water, and freely soluble in many other solvents, e.g.organic solvents. It has a role in plant metabolite and can be used in flavourings, synthetic indigo and certain pharmaceuticals.
Chemical properties
Chemical formula: C9H8O2
Molar Mass: 148.16 gmol-1
Melting point: -57.12°C
Boiling point: 178.1°C
Density: 1.2475 gcm-3
Water solubility: 500 mgL-1
Acidity (pKa): 4.44
Cinnamic acid exists as trans and cis isomers, but the transform is the one most often found in nature. It is obtained from cinnamon bark and balsam resins. It was first isolated in 1872 by F. Beilstein and A. Kuhlberg.
Laboratory chemical safety summary (the boring bit)
Hazard statement: Causes skin irritation
Precautionary statements: Wash hands thoroughly after handling. Wear protective gloves. If on skin wash with plenty of water. If skin irritation occurs call poison centre or doctor. Remove contaminated clothing and do not use until washed. Store locked up.
Hazard statement: Causes serious eye irritation
Precautionary statements: Wash hands thoroughly after handling. Wear eye protection. If in eyes remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do and rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. If eye irritation persists get medical advice. Dispose of leftover chemicals responsibly.
Hazard statements: May cause respiratory irritation
Precautionary statements: Avoid breathing vapours. Use only outdoors or in a well-ventilated area. If inhaled remove victim to fresh air and keep at rest in a position comfortable for breathing. Store in a well-ventilated place. Keep container tightly closed.
Safety guidelines taken from EU standard.
A laboratory chemical safety summary is done before a practical takes place in a lab to ensure safety procedures are carried out correctly.