6 Common Misconceptions about Evolution by Natural Selection
Evolution by natural selection is a scientific fact. Skeptics who argue against the legitimacy of the theory of evolution often do so out of a complete misunderstanding of the way evolution by natural selection actually works and how we know what we know about it. Below I have listed some of the questions uninformed skeptics have proposed as a challenge to the validity of a worldview based on evolutionary theory. All of these misunderstandings are easily explained as I shall demonstrate with a thorough rebuttal to each in turn. Furthermore, I will deal with some of the ways in which, particularly in North America, the theory of evolution has come into conflict with biblical creationism.
1. If evolution is just a theory, why should it be taught as fact?
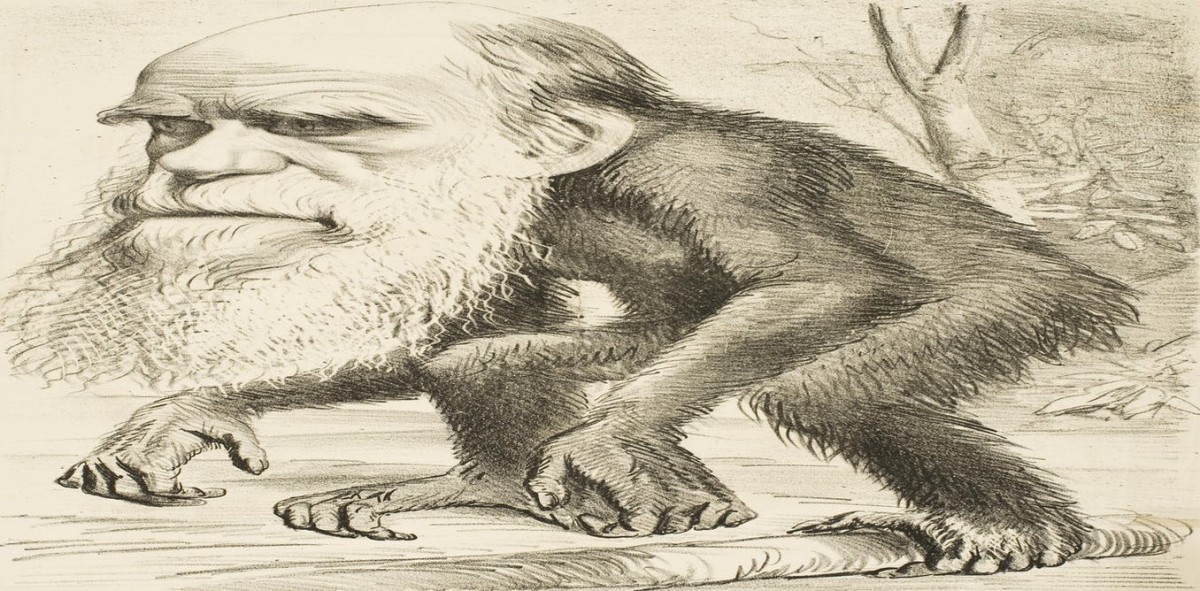
There is a difference between scientific theory and the popular definition of theory. Within the context of science, a theory is something for which there is evidence that can be observed and demonstrated. The notion of a spherical earth that orbits around the sun is a scientific theory based on consistent astronomical and mathematical observations and calculations. This was a theory that developed over the course of hundreds of years as more and more evidence was found to support it, finally culminating in the incontrovertible evidence of extraterrestrial photography. A scientific theory is based on evidence that can be observed and demonstrated in the natural world, and the theory of evolution is no exception to this. Since Charles Darwin first proposed the theory of evolution by natural selection based on his observations as a naturalist, further evidence has come to light. The incontrovertible evidence for evolution by natural selection has been found in DNA, the fossil record, the anatomy of modern organisms, etc. The evidence in support of evolution continues to grow and justify the teaching of natural selection as fact. If there existed scientific evidence against the theory of evolution, we would have to take that into account and then teach a different theory as fact.

2. If we come from monkeys, why are there still monkeys?
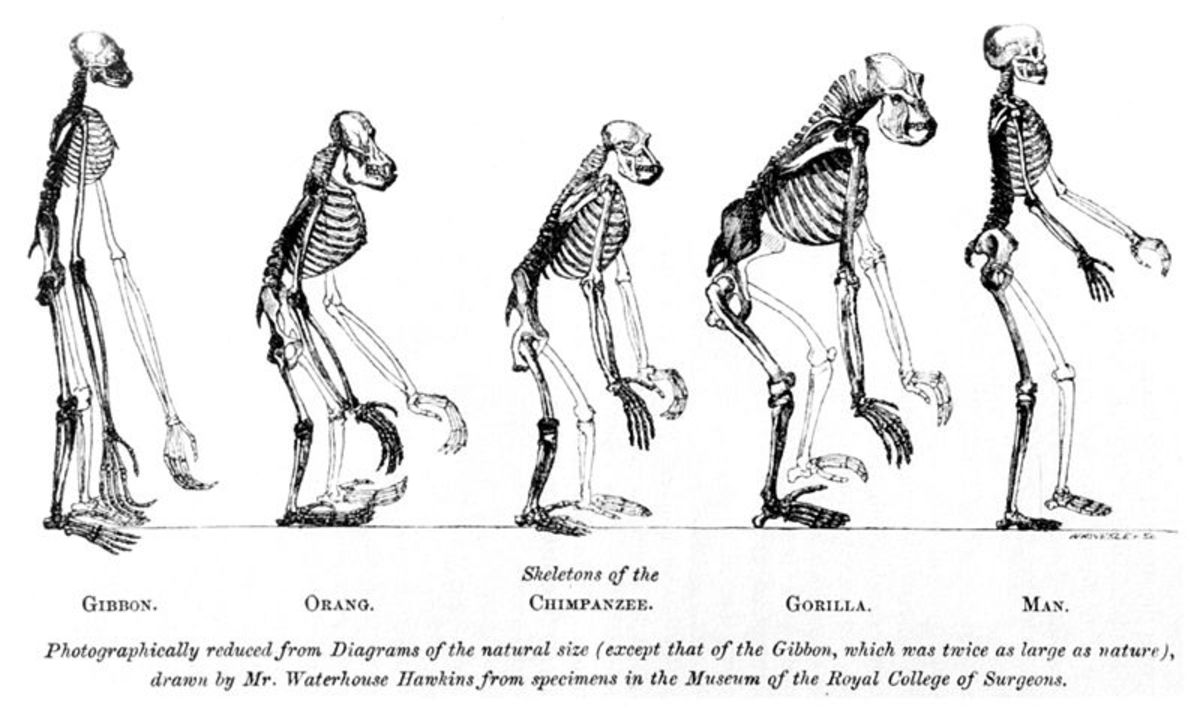
This is one of the best examples of a basic misunderstanding of how evolution by natural selection works. I would go so far as to argue that this is also indicative of a lack of understanding of biology within a broader context of scientific illiteracy. We did not evolve from monkeys. Humans belong to the primate family. Our closest living relatives are chimpanzees. That means that humans and chimpanzees evolved from the same ancestor. This ancestor was neither a human or a chimpanzee. Since then, both humans and chimpanzees have evolved on their own evolutionary trajectories, distinct from one another. Humans, just as well as other apes, have been evolving into distinct species. With time, intermediary species go extinct, which underscores the distinction between related species. This principle applies to all species. For example, llamas and alpacas also descend from a fairly recent common ancestor. It would be just as illogical to suppose llamas evolved from alpacas as it would be to suppose that humans evolved from chimpanzees, as some uninformed commentators have suggested.
Another way of understanding the source of this misconception is the incorrect popular assumption that evolution is a steady upward trajectory, and that human domination of the planet is a sign of our having reached the top of some sort of evolutionary hierarchy. Humans are no more or less evolved than other apes, we are simply different from one another. Humanity as it exists today is not the highly evolved standard against which all other species are measured. The variety of reasons why we seem so distinct from the rest of the animal kingdom is very complex and nuanced. There is no theoretical evolutionary ideal. Natural selection is a process whereby traits that promote a species' survival are more likely to be passed on genetically.

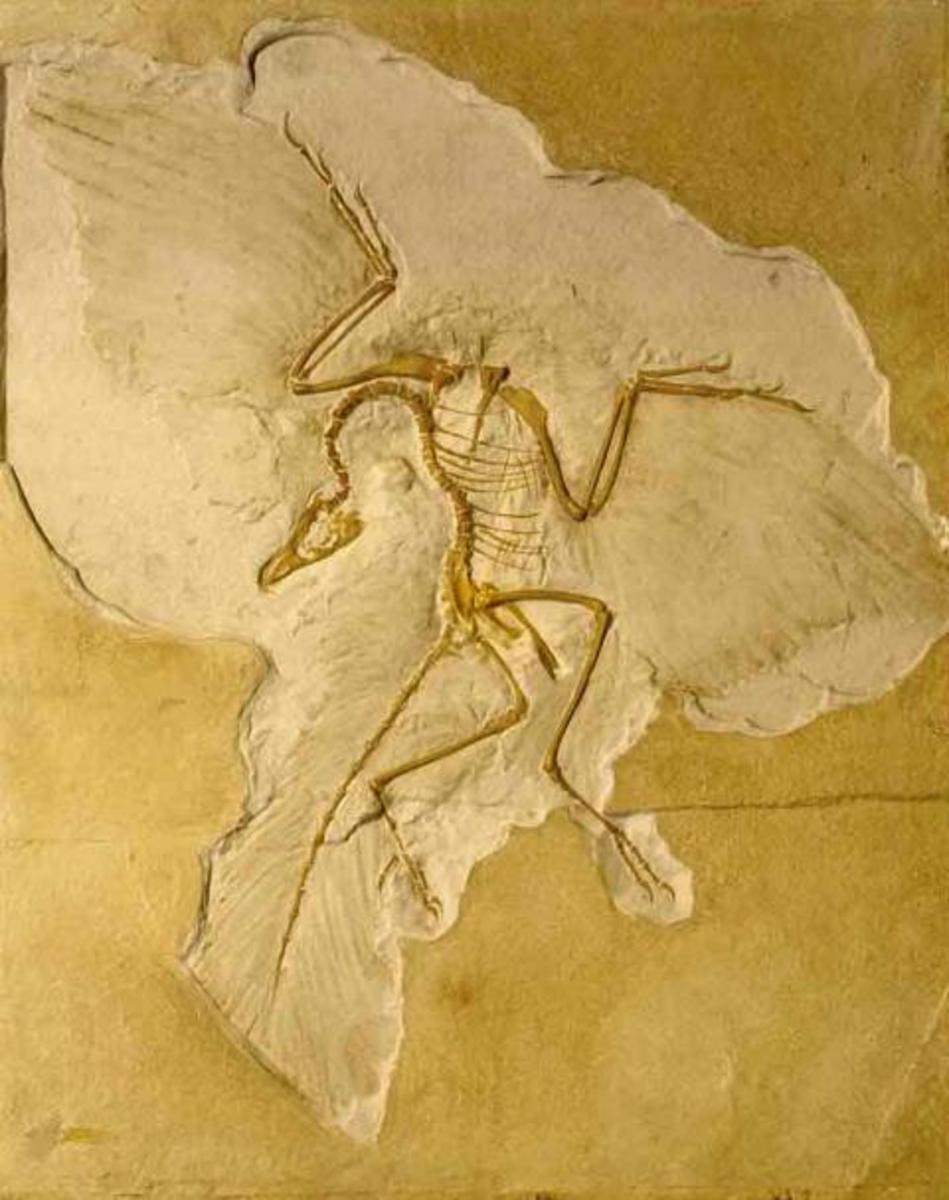
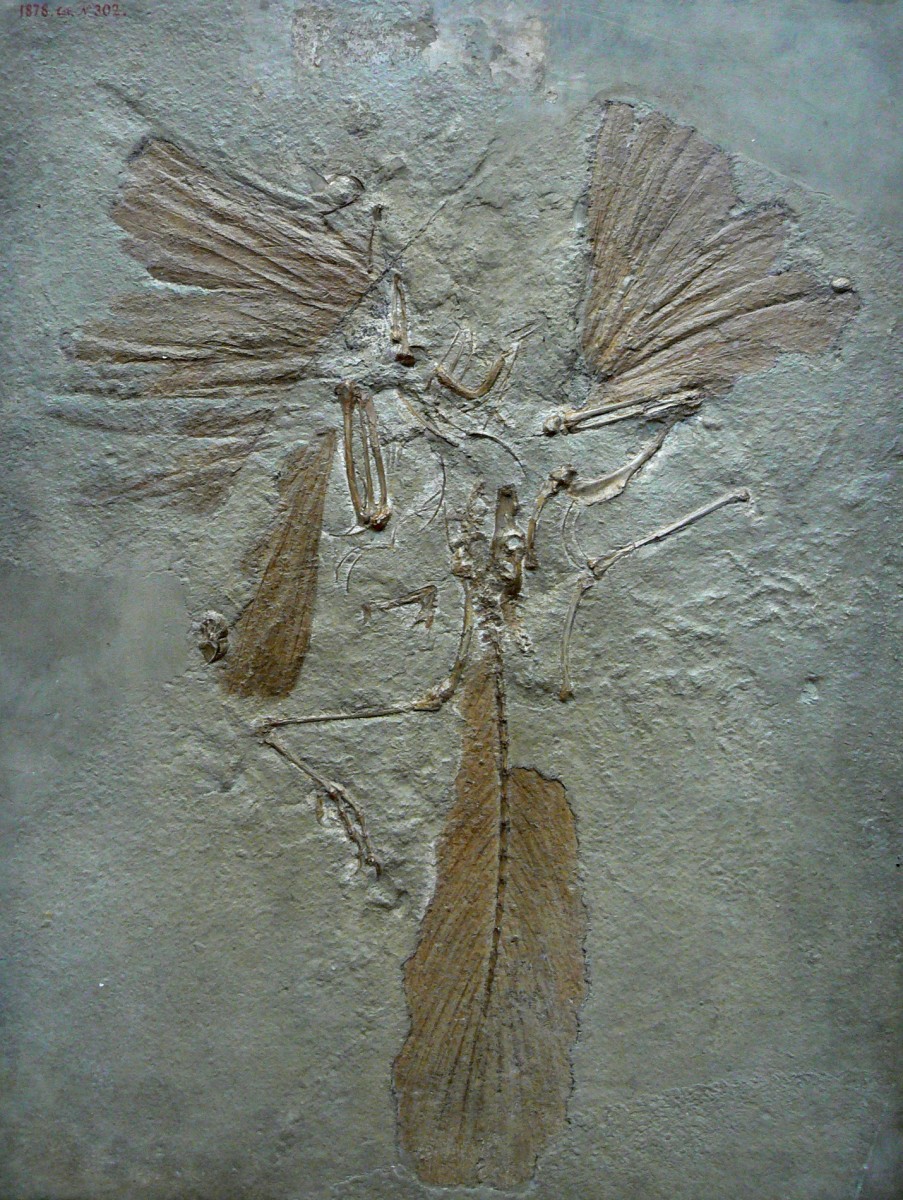
3. Where is the missing link?
Despite popular belief, the missing link has been found. In fact, an overwhelming multiplicity of "missing links" amongst a variety of different species have been unearthed in the fossil record. The concept of the missing link is actually outdated. Even without the fossil evidence of extinct intermediary species between various related species, the relationship between these modern species is still apparent. For example, consider again the relationship between humans and chimpanzees. The theory of evolution recently following Darwin's revelation was not without significant flaws. Victorian Era evolutionary theory assumed a veritable evolutionary hierarchy with humans at the top (of course). Since then, evidence has shown that humans and chimpanzees, for example, are more closely related to one another than chimpanzees are related to orangutans. Both the notion of the missing link and of an evolutionary hierarchy are scientific anachronisms on which modern assumptions about evolution should not be predicated.
4. If evolution is real, why aren't we still evolving?
Understanding the process of evolution by natural selection requires extensive use of abstract thought billions of years throughout the history of life as we know it. Evolution is not something that happens spontaneously and visibly throughout the course of one generation. We are still evolving, but it is such a gradual process that we are not able to perceive it in action. Organisms themselves do not evolve, evolution by natural selection is a process whereby the following generation is a precise, but not exact, reproduction of the previous generation. Because of variability and genetic mutation from one generation to the next, new traits arise which either promote the survival of the organism in question, reduce its chances for survival, or are neutral in terms of survival. Some people ask, for example, how a heart could have gradually evolved into existence if we could not survive without a complete heart. The answer is that the simpler life forms from which more complex life forms evolved did not need as complex of a heard as, say, modern mammals have. Every aspect of anatomy changes gradually from one generation to the next. Again, deep and comprehensive critical thought is crucial to a full understanding of the long and complex history of evolution.
5. How is belief in evolution different from belief in religious faith?
My final two points directly address misconceptions about evolution commonly held by adherents to the creationist explanation for existence.
Understanding evolution is not a matter of belief. The theory of evolution is based on evidence, whereas creationism requires faith in religious scripture which does not provide evidence for this particular claim. Evolution is a scientific theory, the details of which are subject to change based on mounting evidence. Evolutionary theory has changed significantly since the Victorian Era. Darwin, for example, was completely wrong in his theories regarding the genetic explanation for natural selection. Since then, geneticists have further elucidated the details of evolutionary theory with scientific procedures not available to Darwin. The creation myth, conversely, does not change in light of scientific advances. Interpretation of scripture may go up for review, but religious fundamentalism is predicated on taking such accounts as the creation myth literally without any actual evidence.
6. How can the earth be so perfect for life if it was not designed?
Within the context of a creationist perspective, the assumption is that the world was created to support life and was then populated accordingly by an intelligent designer. According to evolution by natural selection, it actually worked the other way around. Life as we know it evolved to adapt to the environment in which it found itself. We do not yet have scientific proof for how life began, but it was most likely the result of a chemical reaction resulting in the first self-replicating molecule. Since that moment, life as we know it has replicated itself based on traits which are most conducive to survival in its environment. Therefore, the world was not designed to support life, rather life evolved to survive in the world.