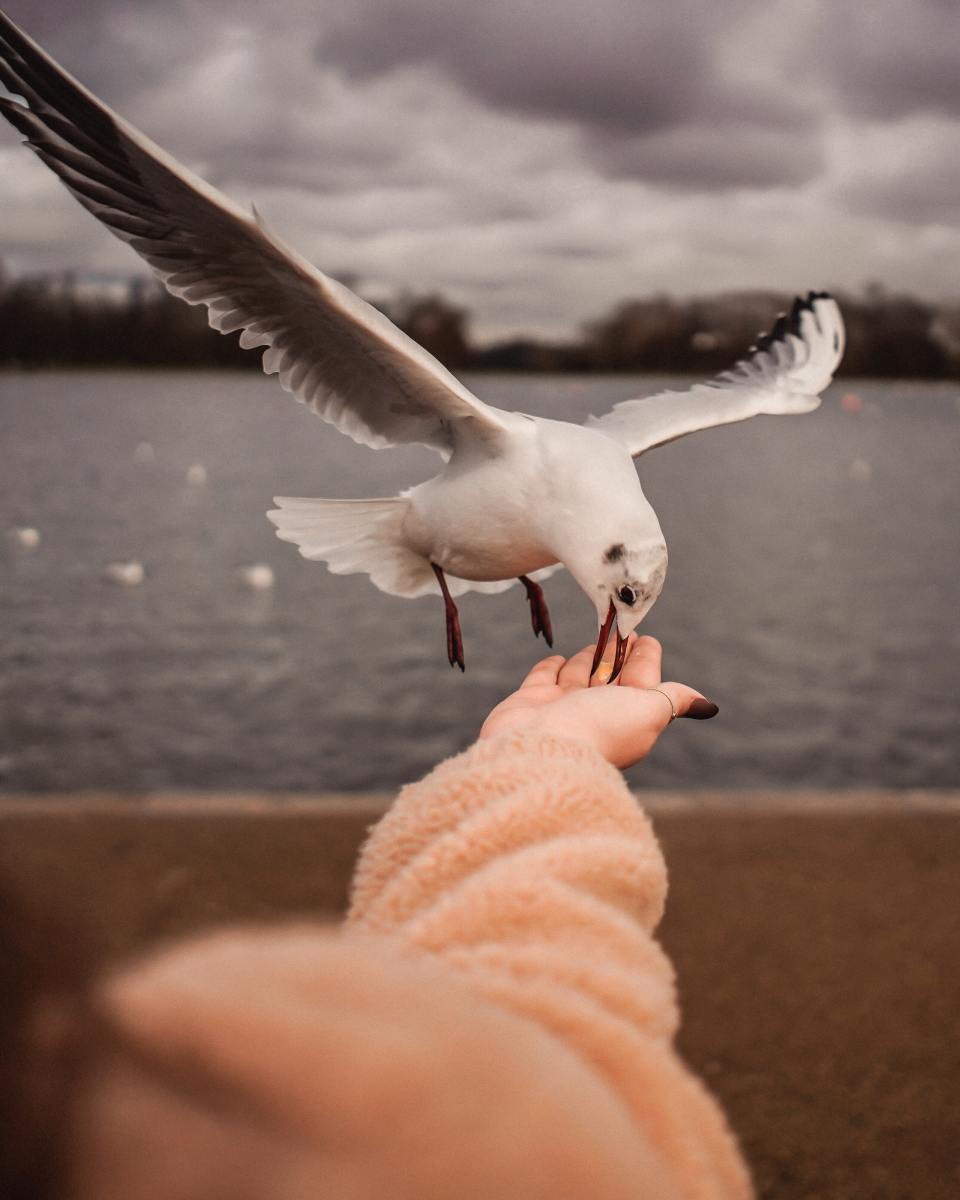
Flagship Species Defined and Their Role in Conservation

What is a flagship species?
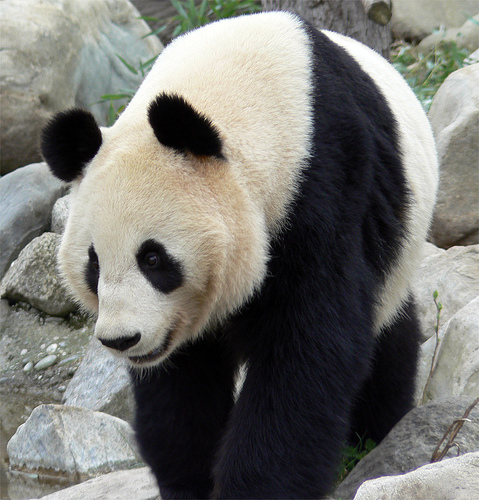
A flagship species is a species that serves as a conservation ambassador. These are the poster children of environmental conservation. They are most often large, conspicuous, widely recognized species. Think African elephant. Many of them also have a warm fuzzy quality as well. Think panda bear.
These animals, the bears and tigers and whales and the like, are what biologists refer to as charismatic megafauna. They are the big animals that we are drawn to. They are conspicuous, familiar, and quite often cute or majestic. And we would rather save them than a tree or a rock or a patch of grass. Conservationists know that and they use it. Because it works.
Role in Conservation
Flagship species are often chosen by conservation groups to raise public awareness for a particular cause. The logo of the World Wildlife Fund is a Giant Panda. Think about it. Are you more likely to donate to a fund protecting the Asian jungle in general, or to one that is saving the tigers? Would you mind sending a donation today to conserve a vast span of arctic tundra? No? What about to save a polar bear? For the right price we will even send you your own little plush critter. Sound familiar? I guarantee a commercial full of romping bears will grab your attention and hold it a lot better than one of ice and flat ground. Or some obscure bacterium.


Why should we fall for their game?
Well, for one thing, flagship species do need saving. They might be endangered or declining enough to cause concern. They also are usually umbrella species. Protecting them also protects a large number of other species that exist under their umbrella. If you want to save an elephant, you have to protect it from immediate dangers like poaching. You also have to ensure that it has adequate food and habitat. This requires preserving a fairly large expanse of savanna, and all of the things it contains. By saving the tiger, you are saving its prey species and the jungle itself.
In some cases, flagship species have the added bonus of being a keystone species. Keystone species have a large impact on the ecosystem that they are a part of. So large that it is disproportionate to their population size. Even a small change in their numbers can lead to a drastic change in the ecosystem. The African elephant is a perfect example. Their feeding habits alter the structure of the environment so much that without them it would be drastically different.
Saving the planet one fuzzy critter at a time
Saving one species at a time is a noble goal. Losing any species to extinction is a devastating event for the planet and for the human race. Also noble is saving ecosystems. Many conservationist take an ecosystem approach to conservation, valuing the whole system over one or a few spcecies.The components of an ecosystem, living and nonliving, function together to provide valuable functions essential to life on this planet. They clean our water, provide our oxygen, supply us with food, and more. So if getting you to save a polar bear is what it takes to make steps towards halting global climate change, or saving sea turtles will save the beaches and oceans, then that is what will go on the posters and in the commercials and on the websites. And that is fine.
- Celebrate American Wetlands Month
America's Wetland Month is a celebration and a call for awareness concerning the loss of wetlands across our country. - Flagship Species of the WWF
World Wildlife Fund is committed to endangered species protection. See how we are ensuring that the world our children inherit will be home to the same species we enjoy today.