What is a Volcano? How Volcanoes Form & Erupt

What is a volcano?
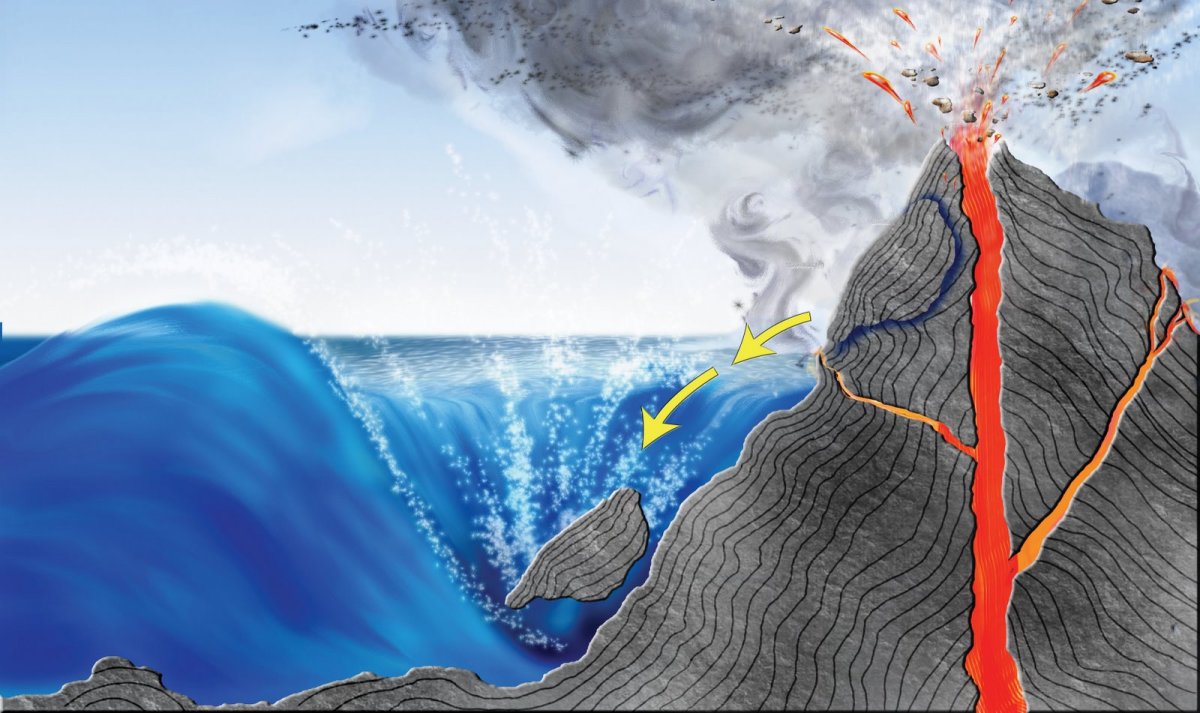
By definition, a volcano is an opening in the earth's crust where hot magma (lava), gases, and ash can escape from deep below the planet's surface.
What makes volcanoes really cool is that they can create new landmasses from the cooling magma.
The entire Hawaiian island chain was created from underwater volcanic hot spots that expel magma. After the magma cooled and hardened, it formed land. Vegetation started growing on the islands and animals started making this newly created tropical paradise their home. However, volcanoes don't just make island chains overnight. Hawaii is a work-in-progress and is over 28 million years in the making!

Where Volcanoes Form
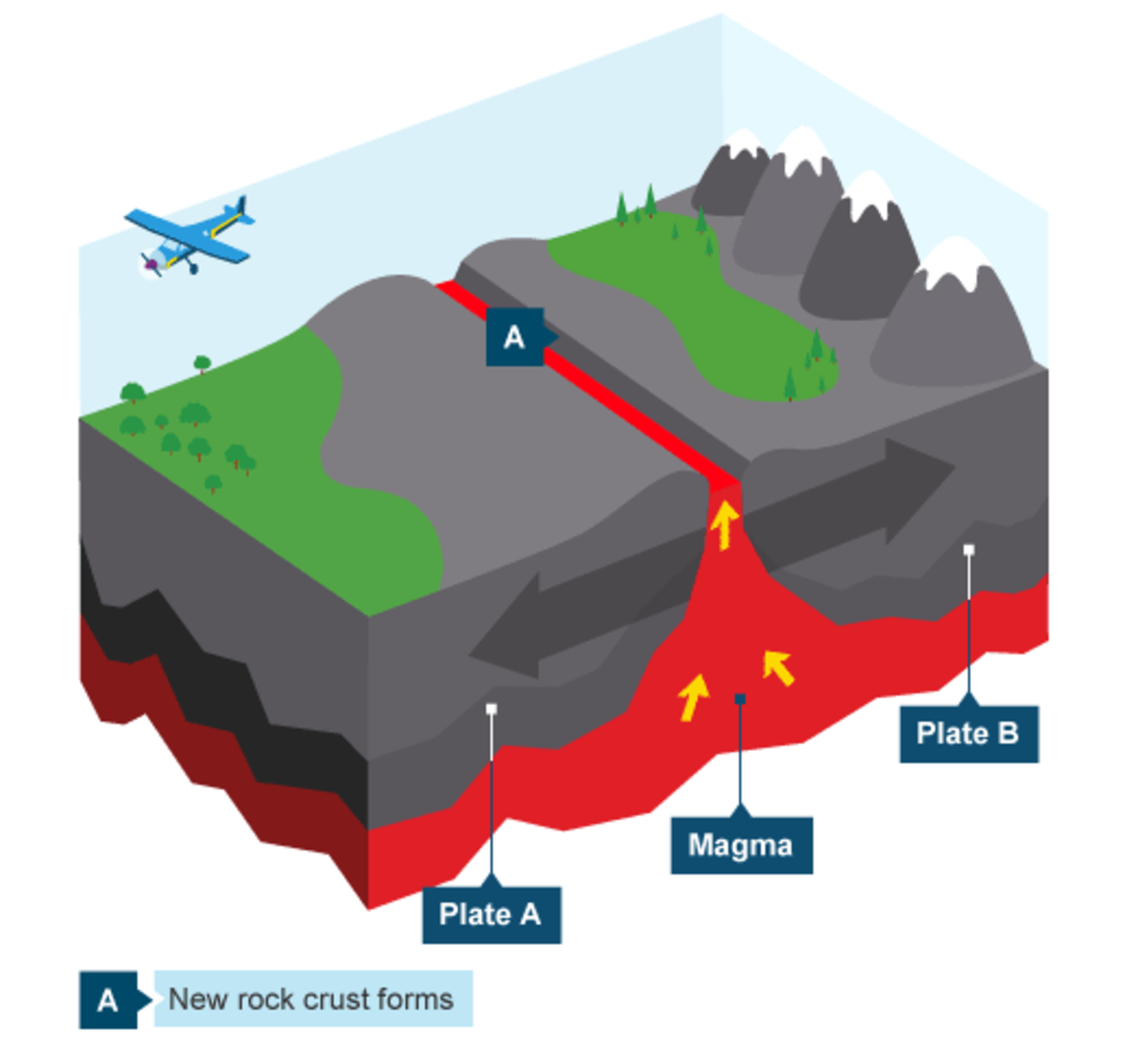
Volcanoes are generally found where tectonic plates meet. Volcanoes on the mid-Atlantic Ridge (Iceland is on the mid-Atlantic ridge) are formed from tectonic plates that are pulling apart (or divergent plates.) Convergent plates (or plates that are pushing together) are guilty of creating the Pacific Ring of Fire.
The Ring of Fire stretches from New Zealand on up through Indonesia, the Philippines, Japan, on to Russia and then east to Alaska. From Alaska down the western coast of Canada and the US. From there, the Ring of Fire extends all the way down the western coast of Mexico on through Central and South America until it reaches the southern tip of South America.
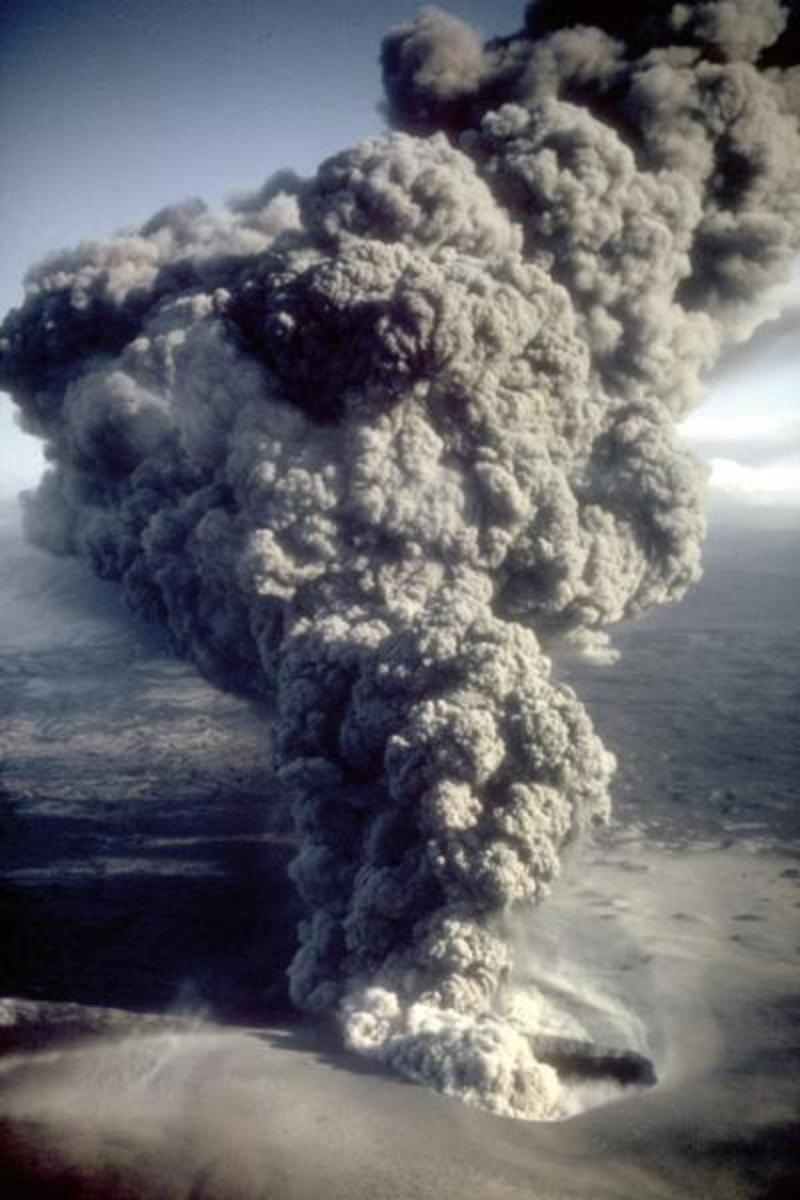
The Ring of Fire is known for some infamous volcanoes such as Krakatoa in Indonesia, Mt. Pinatubo in the Philippines, Mt Fuji in Japan, and Mount St. Helens in the State of Washington.

What's a Volcanic Hotspot?
A volcanic hot spot is an area under the earth's crust that stays fixed in place as tectonic plates move over them. As a plate moves over a hot spot, new volcanoes are created. After a while, these volcanoes become permanently dormant and are replaced by a new volcano elsewhere on the plate (where the hot spot is.)
The Hawaiian islands were created by a volcanic hot spot. Over time, as the plates move, volcanoes will add more islands to the Hawaiian island chain.

Volcanic Eruptions Throughout History
Volcano
| Year
| Death Toll
|
|---|---|---|
Mt. Tambora, Indonesia
| April 1816
| 92,000 + 100,000 (famine)
|
Mt. Pelee, West Indies
| April/May 1902
| 40,000
|
Mt. Krakatoa, Indonesia
| August 1883
| 36,000 (tsunami)
|
Nevado del Ruiz, Columbia
| November 1985
| 23,000 (mudslide)
|
Mt. Unzen, Japan
| 1792
| ~14,000 (tsunami)
|
Mt. Vesuvius, Italy
| 79
| 10,000 (Pompeii)
|
Laki, Iceland
| June 1783 - February 1784
| 9300 (famine)
|
Mt. Kelut, Indonesia
| May 1919
| 5100 (mudslide)
|

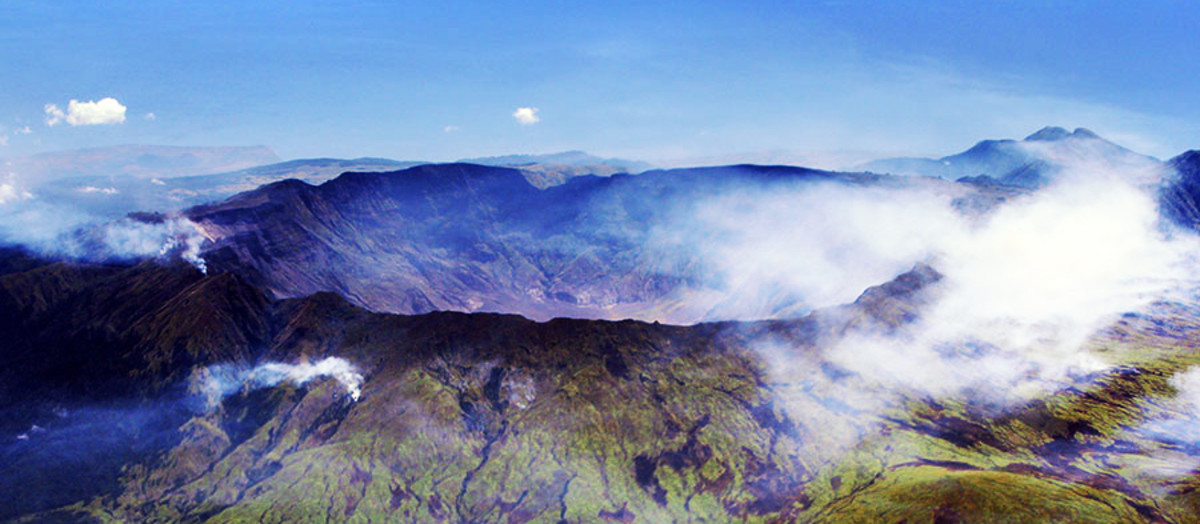
The Different Types of Volcanoes
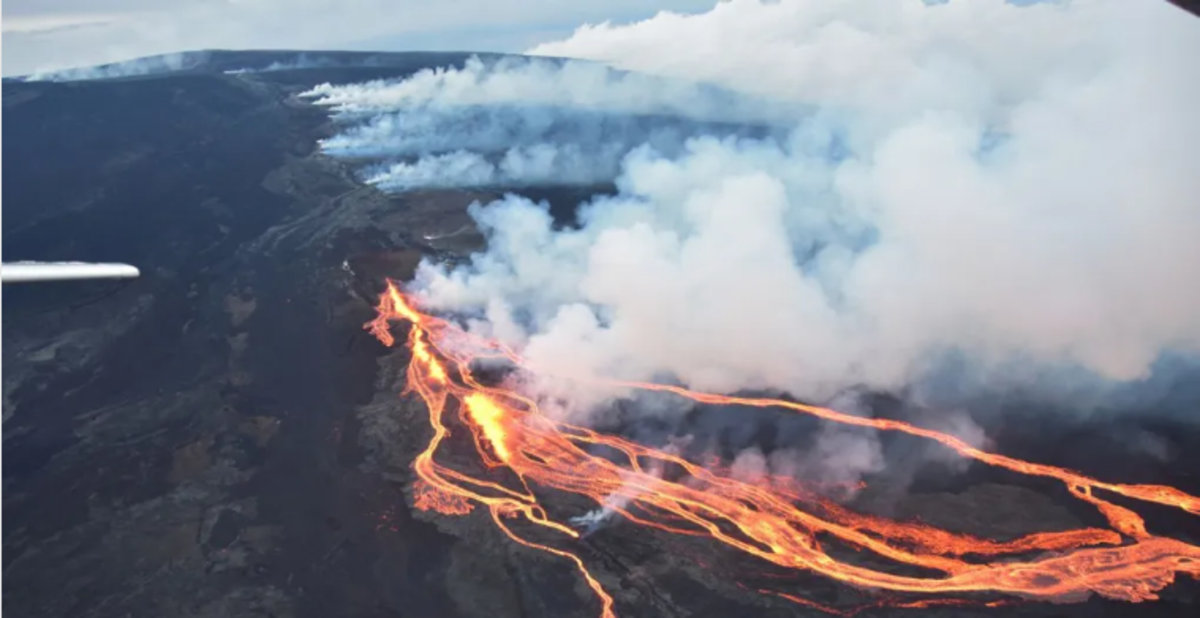
The very word "volcano" brings forth images of a cone-shaped mountain, perhaps with lava spewing out. Sometimes volcanoes have multiple cones which are caused by vents that form on the surface. Puʻu ʻŌʻō is a cone formed from a vent on Hawaii's Kīlauea volcano.

Some volcanoes aren't cone-shaped at all! One type, called fissure vents, don't have explosive activity but are simply flat channels that lava slowly flows along. Many cone-shaped volcanoes also have fissure vents.
Very broad volcanoes, called shield volcanoes, don't erupt as violently as their cone-shaped counterparts, but the lava is a much lower viscosity than lava from fissure vents. This leads to the very broad shield-like shape of these volcanoes.
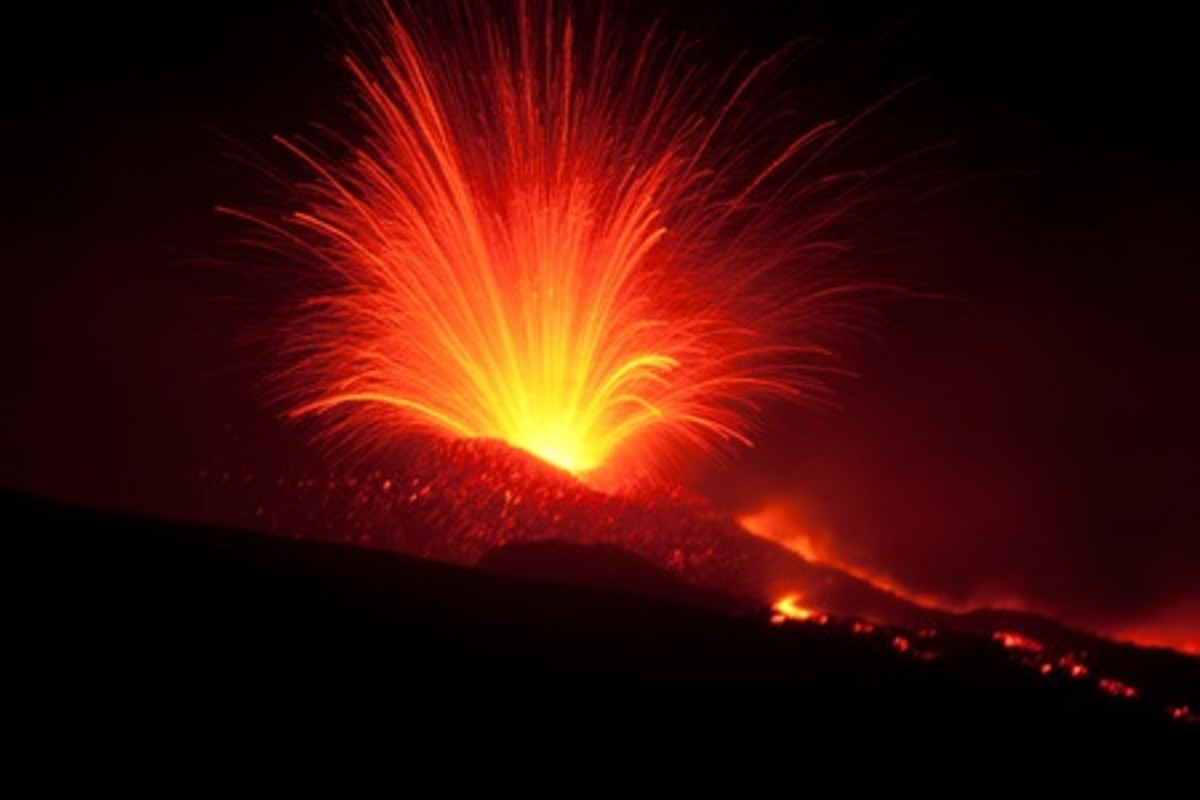
A lava dome is often found in the crater of a previous eruption and look kind of like a mini-volcano inside of a much larger volcano. The eruption from this type of volcano is usually very violent, but the lava has a very high viscosity so it doesn't flow very far. Mount St. Helens is a perfect example of a lava dome.
When highly viscous lava is forced up through a volcano, it can form what is called a cryptodome, which is essentially a bulge. A cryptodome formed on Mount St. Helens shortly before it erupted in 1980.

Volcano Facts
- When Krakatoa erupted in 1883, the explosion was heard nearly 3000 miles away. It was the loudest sound heard in modern history.
- Pumice, a volcanic rock, is the only rock that can float in water.
- The 1991 eruption of Mount Pinatubo released 22 million tons of sulfur dioxide lowering the global temperature by 0.5 degrees Celsius.
- Mauna Loa, a Hawaiian volcano is actually taller (from base to top) than Mount Everest, but Everest is higher in elevation.

© 2012 Melanie Palen Shebel