Learn Chinese Easily - Conversational Chinese
Learning Chinese Language
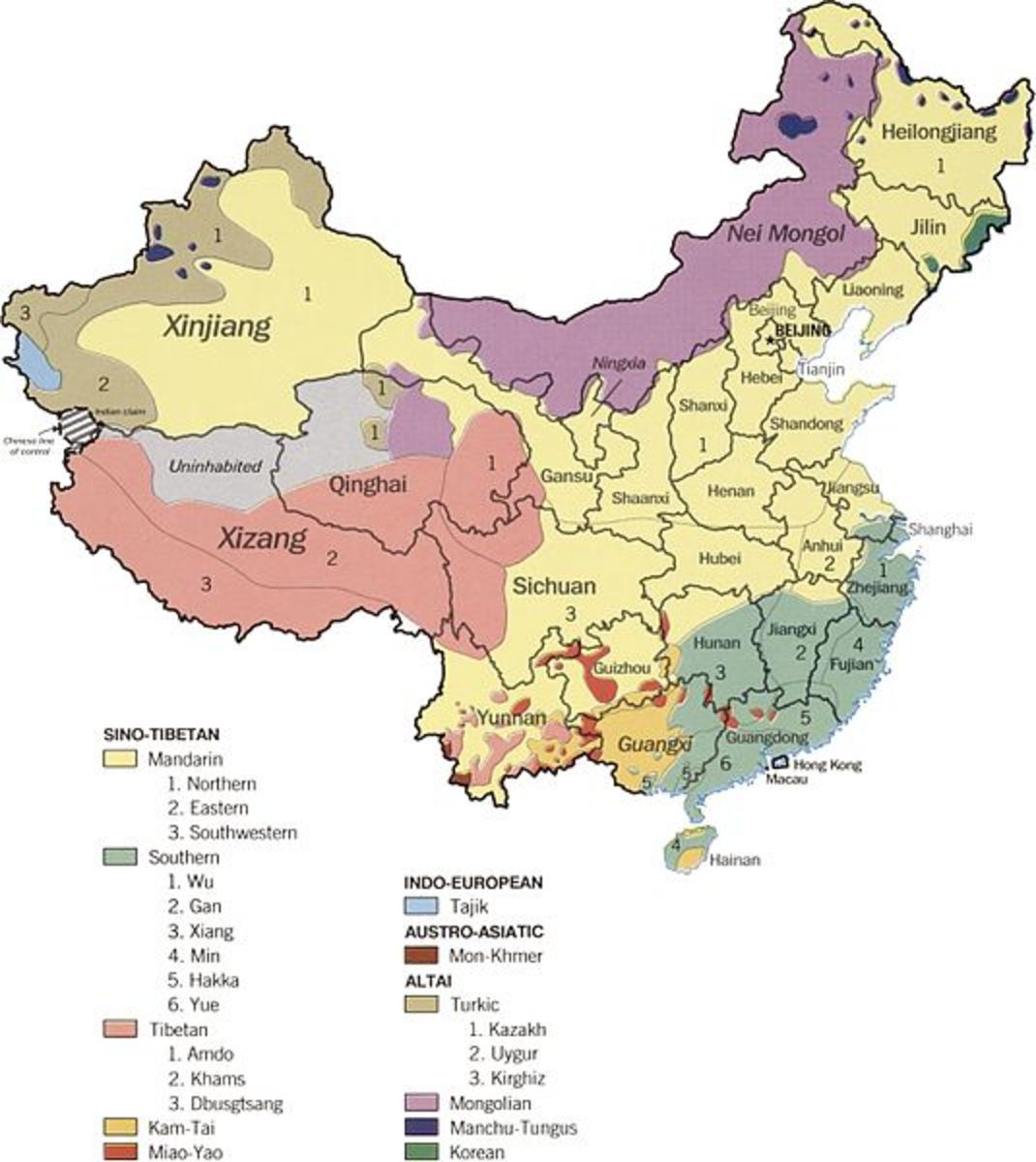
The earliest form of Written Chinese was recorded over an unbelievable 6000 years ago when figures and symbols were used instead of the characteristic strokes modern Chinese language is known for these days. Since then, the early Chinese language has evolved several times in its history. The earliest known form of patterned stroked Chinese language has origins dating back 1120BC, over 3000 years ago, when bronze artifacts in the Zhou Dynasty was discovered with inscriptions. Further evolution has since taken place, over almost twenty dynasties later, the Chinese language have evolved, branched off and now the spoken Chinese language has over 13 sub-languages and dialect, making it the most in the world.
SunSeven in Chinese

With over one billion people in the world speaking some form of Chinese, spoken Chinese is by far the most used language in the world. Most countries in the Asian world uses some form of the Chinese language so practicing the language would definitely benefit those living, visiting or doing business in the Asian world. Currently, two systems are being used for Chinese characters; the traditional Chinese (used widely in Macau and Hong Kong) and simplified Chinese (practiced in Singapore and Malaysia). These two systems co-relate with each other and mostly differ only in the number of characters.
Chinese Language Learning Materials
With China quickly becoming an economic powerhouse and countries like Hong Kong, Taiwan and Singapore having a growing economy, learning the Chinese language would definitely be beneficial in the modern business world. It is well known that locals are more open to those who have embraced the language and culture and with your knowledge of the Chinese language; even basic conversational words will give you the added advantage if you wish to strike up a business deal with an Asian Chinese speaking partner. Learning the language will only benefit any business minded individual as most business dealings are headed east, where production costs are cheaper and production rate goes at an outstanding speed.
Learning the Chinese language will only serve to benefit those with an avid interest in one of the oldest cultures known to mankind; the Chinese culture. With its colorful past of the era of the Chinese Dynasties, the art of Chinese calligraphy, the beautiful water color paintings, the practices of the Chinese society and how China has revolutionized to cope and take advantage of the current world, linguistics and culture experts will definitely learn to appreciate the many facets of the culture by first picking up the language.
Basic Mandarin Chinese
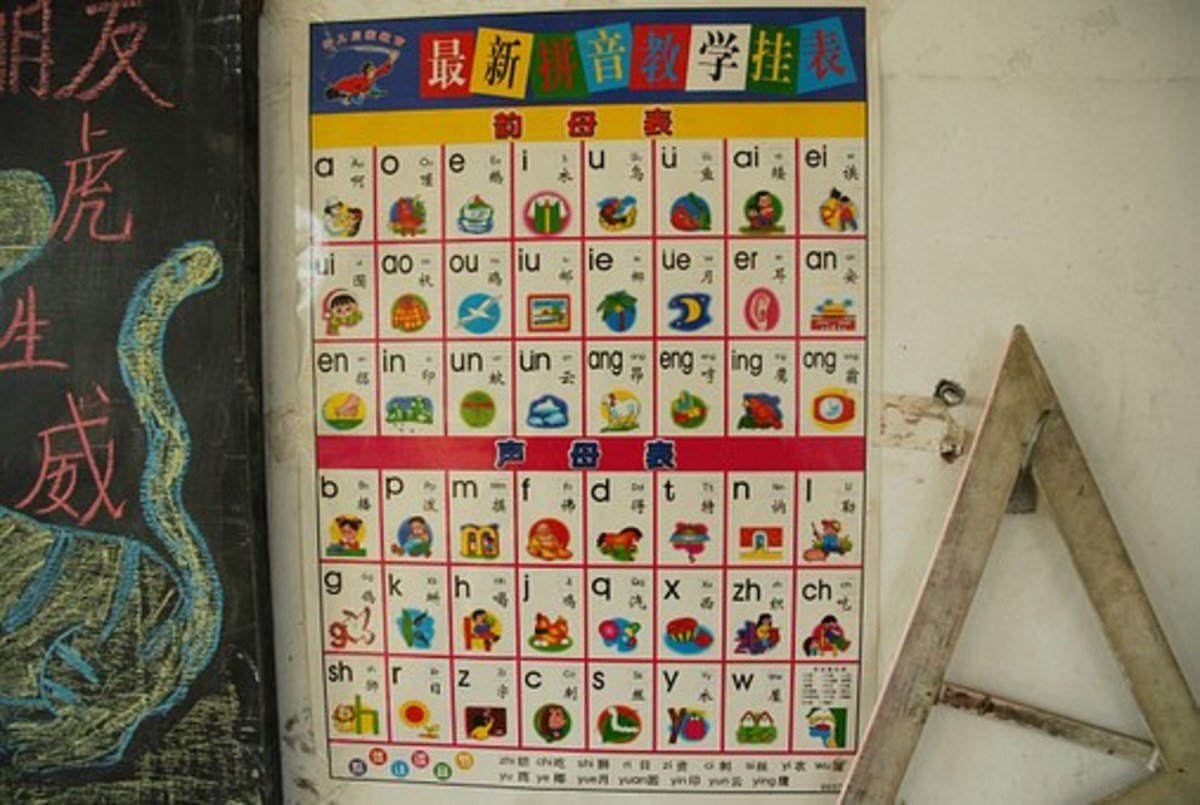
Most who have been in contact with the Chinese Language but not picked it up generally assume that there are millions of Chinese characters to learn, this is one of the misconceptions that throws people off from learning the Chinese language. In actual fact, the language only has over 20,000 characters and most get by with only 6000 characters and 400 spoken monosyllables. While some may argue that the number is still considerably larger than the English language, as a business trader or a traveler, one can get by with the most basic conversational Chinese. We take a look at some of the basic words and terms, along with numbers you can use in your quest to pick up the Chinese language.
Basic Conversational Chinese
English
| Chinese equivalent
|
|---|---|
Hello
| ni hao
|
How are you
| ni hao ma
|
Very good
| hen hao
|
No good
| bu hao
|
Thank you
| xie xie
|
No (or Do not want)
| bu yao
|
Very expensive
| hen gui
|
Goodbye
| zai jian
|
Excuse me
| jie guo
|
I do not want
| wo bu yao
|
Eat
| chi fan
|
Come here
| guo lai
|
Can you help me?
| ni neng bangzhu wo ma?
|
What is your name
| ni jiao shenme mingzi
|
You are welcome
| bu yong xie
|
My name is…
| wo jiao…
|
I am fine
| wo hen hao
|
Good morning
| zao shang hao
|
Good evening
| wan shang hao
|
See you tomorrow!
| Míngtiān jiàn!
|
What's your name?
| Nín guì xìng?
|
Learn Basic Conversational Chinese
Mandarin Chinese Lesson - Numbers 1 to 10
How to Count in Chinese
Numbers
| Chinese equivalent
| |
|---|---|---|
Zero
| 0
| ling
|
One
| 1
| yī
|
Two
| 2
| èr
|
Three
| 3
| sān
|
Four
| 4
| sì
|
Five
| 5
| wǔ
|
Six
| 6
| liù
|
Seven
| 7
| qī
|
Eight
| 8
| bā
|
Nine
| 9
| jiǔ
|
Ten
| 10
| shí
|
Eleven
| 11
| shíyī
|
Twelve
| 12
| shí'èr
|
Thirteen
| 13
| shísān
|
Twenty
| 20
| èrshí
|
Twenty one
| 21
| èrshíyī
|
Twenty two
| 22
| èrshíèr
|
Thirty
| 30
| sānshí
|
Forty
| 40
| sìshí
|
Fifty
| 50
| wǔshi
|
Ninety nine
| 99
| jiǔshíjiǔ
|
One Hundred
| 100
| yībǎi
|
One hundred and one
| 101
| yībǎilíngyī
|
One hundred and two
| 102
| yībǎilíngèr
|
One hundred and ten
| 110
| yībǎiyīshí
|
One hundred and twenty
| 120
| yībǎi'èrshí
|
Two hundred
| 200
| èrbǎi
|
Three hundred
| 300
| sānbǎi
|
Nine hundred and ninety nine
| 999
| jiǔbǎijiǔshǐjiǔ
|
One thousand
| 1000
| yīqiān
|
One thousand and one
| 1001
| yīqiānlíngyī
|
One thousand and ten
| 1010
| yīqiānlíngshí
|
One thousand ans one hundred
| 1100
| yīqiānyībǎi
|
Nine thousand nine hundred and ninety nine
| 9999
| jiǔqiānjiǔbǎijiǔshíjiǔ
|
Ten thousand
| 10000
| yīwàn
|
One million
| 1000000
| yībǎiwàn
|
One billion
| 100000000
| yīyì
|
Learn numbers in Chinese
While these words and numbers are basic survival Chinese that will probably get you from one place to another and do simple transactions, it will take you a while longer to familiarize with the environment and people. Do remember that in some provinces, many Chinese speak with an accent so it may take you a while to understand them as well. It would be best to enroll yourself in a school that will teach you spoken as well as written Chinese to fully understand the language and have that edge in the modern business world. Good luck and hao yun!