How to find the Vertex of a Parabola
A parabola is a curve which is given by a quadratic equation: y = ax2 + bx + c
Every parabola contains a vertex. A vertex is the maximum or minimum point on the curve, at which the gradient of the curve is zero. This article is a tutorial in how to find the coordinates of this vertex
How to Find the Vertex Coordinates
1. Write the parabola equation in the form: y = ax2 + bx + c (where a, b and c are constants)
2. Find the gradient of the parabola by differentiating the parabola equation:
y = ax2 + bx + c differentiates to give dy/dx = 2ax + b
3. Find the value of x which gives a gradient of zero:
dy/dx = 2ax +b = 0 when x = -b / 2a
4. Find the value of y which corresponds to this x, by putting x = -b / 2a back into the parabola equation:
y = a (-b / 2a)2 + b (-b / 2a) + c
= b2 / 4a - b2 / 2a + c
= -b2 / 4a +c
5. The co-ordinates of the vertex are therefore (-b / 2a, -b2 / 4a + c)
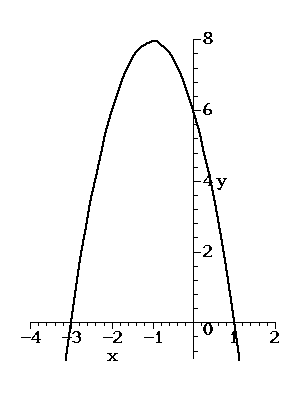
Example
An example parabola is shown in the diagram.
1. The equation of this parabola is y = -2x2 - 4x + 6
2. The gradient is dy/dx = -4x - 4
3. The gradient is zero when x = -1
4. When x = -1, y = -2(-1)2 - 4(-1) + 6 = -2 + 4 + 6 = 8
5. The vertex coordinates are therefore (-1, 8)
Mathematics Textbooks

Maximum or Minimum?
One last question remains to be answered. How do we know whether the vertex we have found from the equation is a maximum or a minimum point?
There is a simple test, which can be performed as follows:
1. Take the equation for the gradient, dy/dx, and differentiate it again by x, to get d2y/dx2.
2. This quantity d2y/dx2 is the rate of change of the gradient.
If d2y/dx2 <0, then the gradient is decreasing as x increases. This means that the gradient of the parabola is positive on the left of the vertex and negative on the right. The vertex is a maximum.
If d2y/dx2 >0, then the gradient is increasing as x increases. This means that the gradient of the parabola is negative on the left of the vertex and positive on the right. The vertex is a minimum.