Human Origins - Charles Darwin and the Theory of Evolution

Human Origins - Charles Darwin and the Theory of Evolution
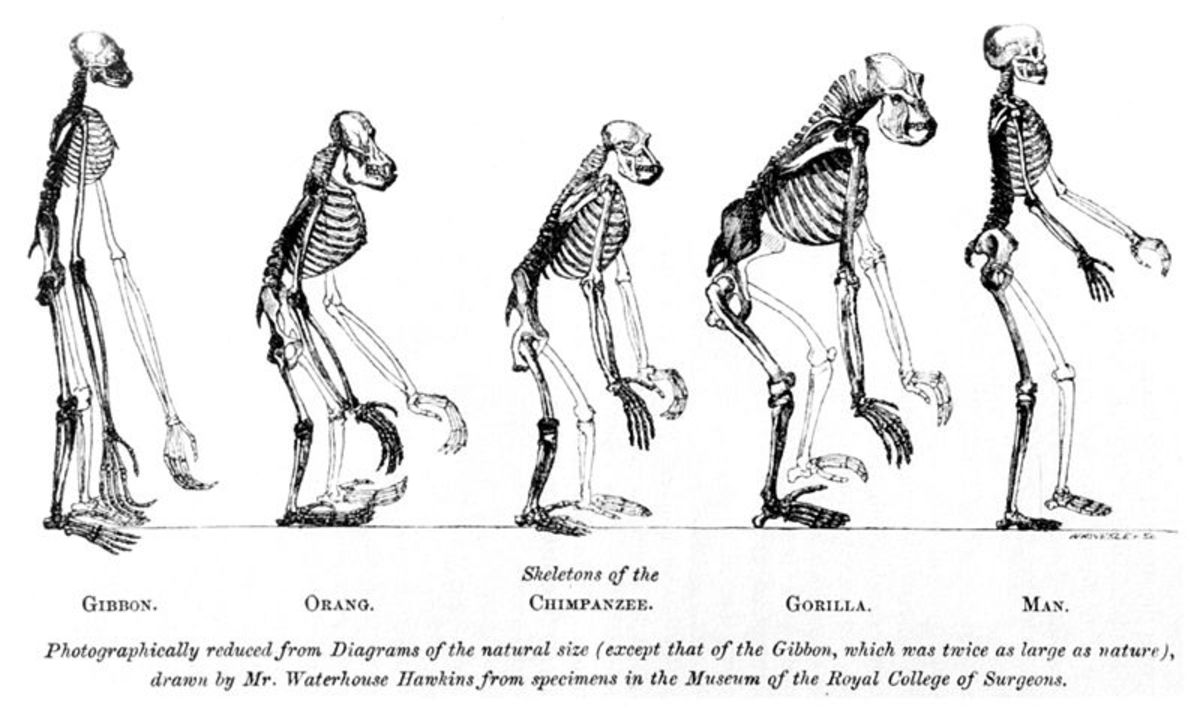
Evolution is the genetic transformation of populations over time. In this sense, a population is a group of living things randomly mate with one another. A species on the other hand is a group of populations whose members can interbreed. If two populations of a species are separated and grow genetically apart they won't be able to produce fertile offspring together anymore. It is at this point where they become different species.
Before evolutionary theory was developed, the general consensus in Europe was based on religious doctrine, which was that species did not change. During the Renaissance however, scientists started looking at nature in a more open-minded way. Over time they collected evidence that species did in fact change over time. Some of the most important early theorists of evolution were French naturalists George-Louis Leclerc, Comte de Buffon(1707-88), and Jean-Baptiste Lamarck(1744-1829).
It was Charles Darwin(1809-82) however who developed the theory of natural selection which is still supported today. While doing field research Darwin noticed that members of a population sometimes had different traits among them. Thinking about this, he realized that some of these variations in traits must be more useful for survival than others. He also realized that the individuals with the most favorable trait based on the environment, was more likely to survive and pass on the favorable trait to their offspring, thereby increasing its prevalence in the population. To illustrate, in a recent study of Galapagos finches, it was revealed that the beaks of the finches increased significantly in length over several generations of drought. Then it was found that longer beaks allowed the finches to break open large seeds more easily, which was their only food source during the drought. Finches with this trait was more likely to survive and more likely to pass on this trait to their offspring.
The next breakthrough in evolutionary theory came at the turn of the twentieth century, when the work of Austrian monk Gregor Mendel(1822-84) was rediscovered. Experimenting with pea plants, Mendel developed a set of laws which explained how traits were passed on from one generation to the next. Darwin's work did not include a mechanism for trait inheritance, so Mendel's work helped to strengthen his theory. Later on theorists improved upon Mendel's theory and discovered that genes were the basic unit of heredity, which lead to the modern definition of evolution as change of genetic composition of a population over time.
To sum up - Charles Darwin is considered to be the founder of modern evolutionary theory, but his theory have been improved upon since and was built upon the theories of other theorists before him.
More Human Origins
- Human Origins - Who Were The Neanderthals?
Human Origins - Who Were The Neanderthals? - Find out more here about human origins and in particular the Neanderthals. - Human Origins - The Study of Human Fossils and Other Methods
Human Origins - The Study of Human Fossils and Other Methods - Find out how human origins are studied by using such methods as the study of human fossils, the archeological record, and genetic analysis. - Human Origins - What Makes Us Human?
Human Origins - What Makes Us Human? - In this chapter of human origins, find out what it is that makes us human, if anything. We all feel we are unique from other primates, but has it been prov
Subscribe to Your Kowledge's RSS Feed
- http://hubpages.com/author/Your+Knowledge/latest/?rss
For more educational articles like these to improve your knowledge and impress your friends.
Source: The Bedside Baccalaureate