IUPAC Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry
More to come within a week, including:
- multiple functional groups
- functional group priority
- cyclic hydrocarbons
- quiz on naming organic molecules
-Cordless, 8th March 2011
Organic chemistry and naming organic molecule is a common part of more high school chemistry classes. Naming organic molecules through the IUPAC (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry) system is very straight forward, as long as you follow through some steps and rules! This hub will cover some of the most basic rules around naming organic molecules.
Key to some notation used in this article:
- R: Radical, another part of a molecule
- C: Carbon
- H: Hydrogen
- O: Oxygen
- X: Halogen
- -: Single bond
- =: Double bone
1. Locate and name the hydrocarbon chain
Hydrocarbon chains are chains of carbon atoms with hydrogen's attached. The first step is to identify the longest continuous hydrocarbon chain, as this name will be the base of the organic molecule name.
If all the carbons are connected through single bonds, the hydrocarbon chain is an alkane. If there is a double bond, it is an alkene. If there is a triple bond, it is an alkyne.
Next count the amount of carbons that make up the hydrocarbon chain. Find the corresponding preffix in the following list:
1. Meth-
2. Eth-
3. Prop-
4. But-
5. Pent-
6. Hex-
7. Hept-
8. Oct-
9. Non-
10. Dec-
Now replace the 'alk-' with the corresponding numerical prefix.
For example if the hydrocarbon chain is:
- 5 carbons long with only single bonds, it is a pentane
- 3 carbons long with a triple bond, it is a propyne
- 8 carbons long with a double bond, it is a octene
If you have an alkene or alkyne with more than 3 carbons, you have to specify between what carbons the second or triple bond is located. Add a number (X-) before the name, to indicate the first carbon (with the lowest number) that the double/triple bond is located on.
- C - C - C = C, this molecule would be called 1-butene
- C - C - C = C - C - C - C - C, this molecule would be called 3-octene
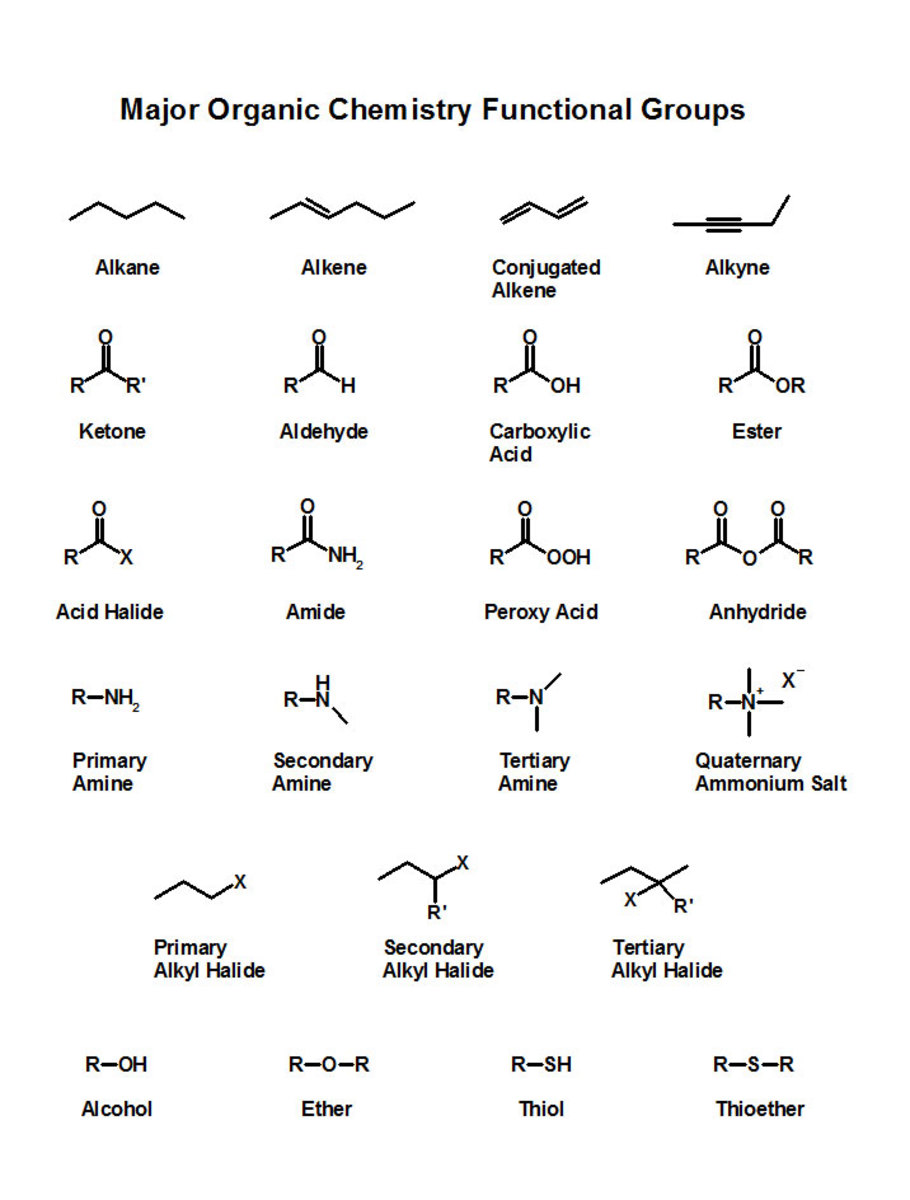
2. Functional groups
Next you have to identify the functional groups of the organic molecule. Functional groups can be described as smaller tails or chains that hang of the main hydrocarbon chain. Each functional group have their own affix or name which is added to the name of the main hydrocarbon chain.
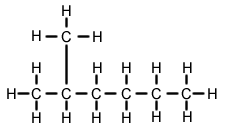
Alkyl Groups: A smaller hydrocarbon chain that hangs of the main hydrocarbon chain.
Identify the alkyl group and how many carbons are in it. Use the corresponding numerical prefix along with -yl. Final add the name of the main hydrocarbon chain.
If the main hydrocarbon chain has more than 2 carbons, you have to signify on which carbon the alkyl group is located. Simply add a number, then the name of the alkyl group, and the main hydrocarbon chain.
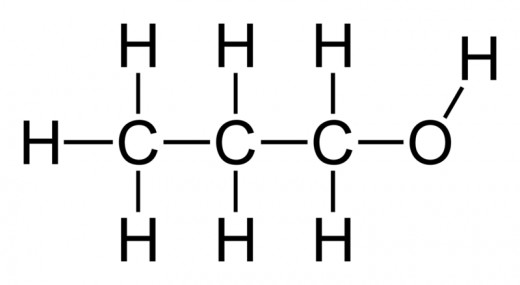
Alcohols: A hydroxide (R - OH) group that hangs of the main hydrocarbon chain.
Simply drop the ending of the main hydrocarbon chain, and add -ol. For main hydrocarbon chains with more than 2 carbons, you have to specify on which carbon the alcohol group is located by adding the number of the carbon.
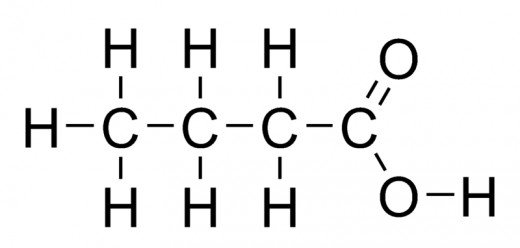
Carboxylic acids: An acid group: One of the terminal carbons of the main hydrocarbon chain has a hydroxide group, as well as an oxygen bonded to it through a double bond (R - COOH).
As before, identify the main hydrocarbon chain, then drop the ending, and add -oic acid. A carboxylic acid will only be located on the end of a hydrocarbon chain, on a 'terminating carbon'.
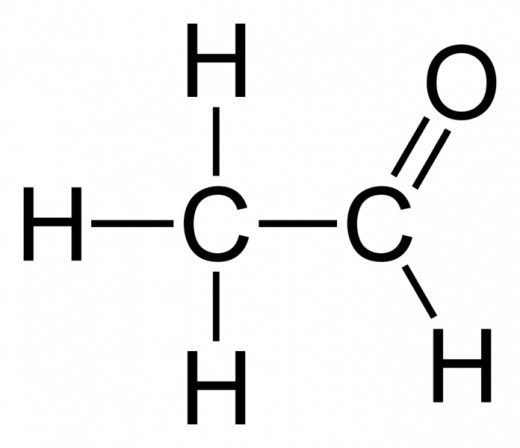
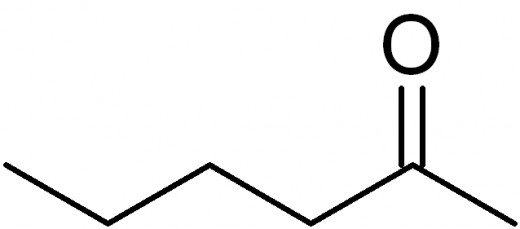
Aldehydes and Ketones: A oxygen bonded through a double bond to a carbon (R = O). If it is located on a terminating carbon, it is an aldehyde. If it located on a carbon within the chain, it is a ketone.
To name an aldehyde, drop the end of the main hydrocarbon chain, and add -al.
To name a ketone, drop the end of the main hydrocarbon chain, and add -one. Remember that you can only have a ketone if the main hydrocarbon chain is more than 3 carbons long. If the main hydrocarbon chain has 4 or more carbons, you must specify to which carbon the oxygen is bonded.
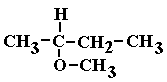
Ethers: Ethers are two hydrocarbon chains which are linked together by an oxygen atom (R1- O - R2) .
You should have two chains connected via the oxygen atom. Identify the shorter, drop the ending, and add -oxy. The longer chain is simply named as if it were a common hydrocarbon chain (eg. -ane).
If the oxygen bond connection is not via a terminal carbon, remember to add a number to the name to make it clear to which carbon the oxygen is bonded!
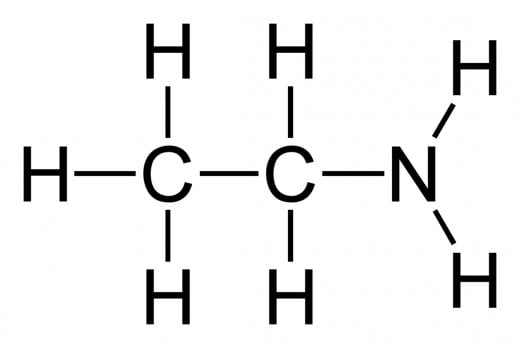
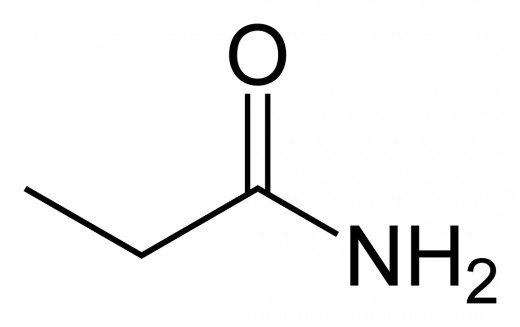
Amines and Amides: Both involve a amine group (R - NH2) attached to a carbon. An amide also has a oxygen double bonded to the same carbon. Amides can only exist on terminal carbons.
To name the amine, identify the main carbon chain, drop the ending, and add -amine. Remember to specify on which carbon the amine group is bond to, should the main hydrocarbon chain contain 3 or more carbons!
To name the amide, identify the main carbon chain, drop the ending, and add -amide.
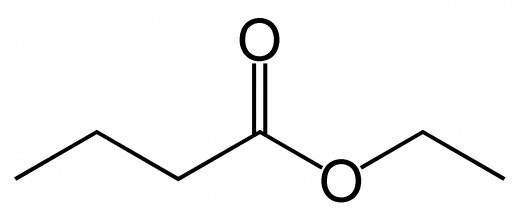
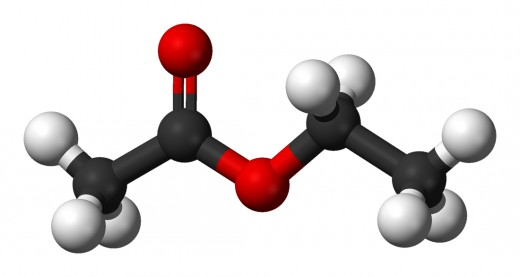
Esters: The result of 'esterfication' reaction between a carboxylic acid and an alcohol (R1 - COOH - R2).
The alcohol part is named first. This is the chain that is attached via an oxygen, to a carbon that has a oxygen bound through it via a double bond. The carboxylic acid part is the chain which has a carbon that has a double bonded oxygen as well as a oxygen bonded to another chain.
The alcohol part is treated as an alkyl (-yl). The carboxylic acid part is named by dropping the end and adding -oate.
The picture on top of this hub is that of ethyl ethanoate, an ester!
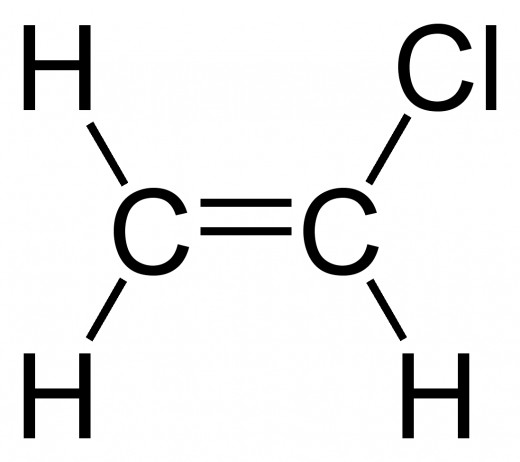
Halides: Hydrocarbon chains with halogens attached to them (- X).
As always, find the longest hydrocarbon chain. Then find which carbon the halogen is bonded to (should the hydrocarbon chain be longer than 3 carbons). Then simply add 'Halogeno-' (e.g. 'Chloro-' or 'Bromo-')