Teaching ESL – The Past Tenses
Are you teaching the past tenses to your ESL class?
This hub looks at the usage and form of:
- past simple
- past continuous
- past perfect simple
- past perfect continuous
It's perfect for revision of the past tenses just before a text.
The Past Simple

The Past Simple
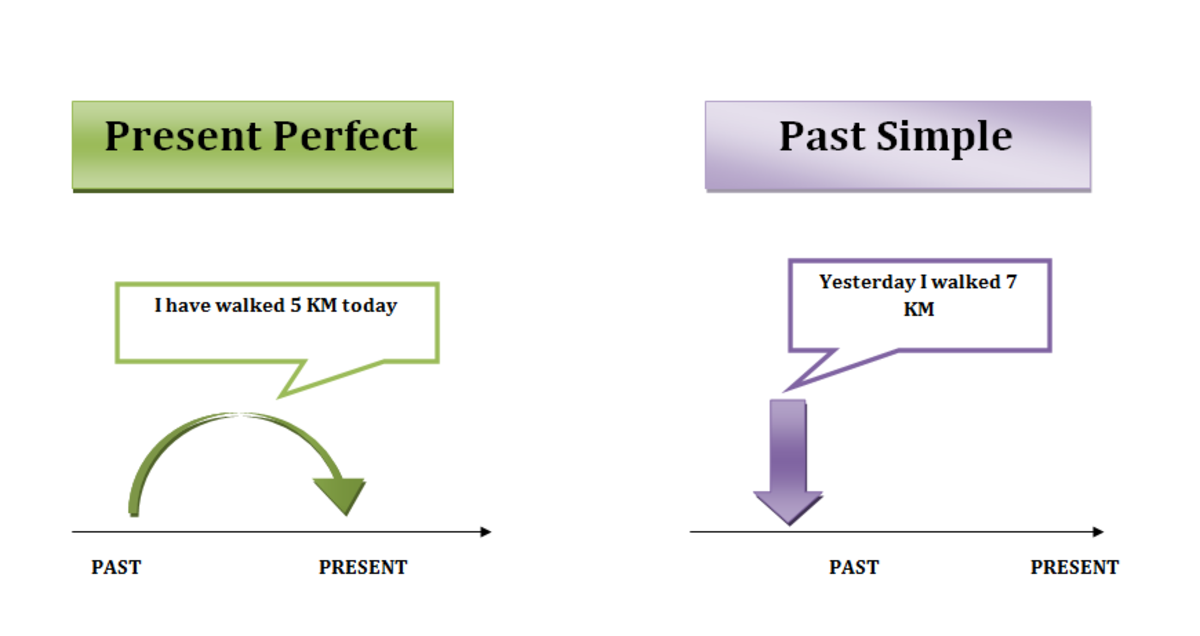
You use the past simple when the time period is finished. You use it to refer to an individual event, state or action or a series of events, states or actions that take place in the past.
If you see keywords like these: 1985, last January, yesterday, last month, ago, when…etc., you can safely assume the action is completed and the past simple is the correct tense to use.
- I had the flu again last week, I think it’s the same flu Mary had about 2 weeks ago.
- We slept for 12 hours yesterday.
- I was angry with you for not doing the project.
*Remember – the verbs do not change for the third person singular. The only verbs that change are the irregular ones in the affirmative form. A lot of important verbs are irregular and unfortunately there are no rules to follow, you just have to learn them.
The Past Simple
Affirmative
| Negative
| Interrogative
|
|---|---|---|
I went
| I didn't go
| Did I go?
|
You went
| You didn't go
| Did you go?
|
He went
| He didn't go
| Did he go?
|
She went
| She didn't go
| Did she go?
|
It went
| It didn't go
| Did it go?
|
We went
| We didn't go
| Did we go?
|
They went
| They didn't go
| Did they go?
|
You can contract the auxiliary verb: Did not - Didn't
The Past Continuous

The Past Continuous
It is used to describe an action that was in progress at a point in the past.
- What were you doing last night around midnight?
- I was sleeping.
The Interrupted Past – You use this when you are talking about a shorter action that occurred within a longer action in the past. The short action ‘interrupts’ what was ongoing. The past continuous is used to describe the longer action, the past simple to describe the short action.
- While I was having breakfast, a policeman came to the door.
The past continuous is also used to describe a gradual development of an action.
- The waves were becoming more and more treacherous.
It is often used to ‘set the scene’ in a narrative.
- Karen was smiling. She had never been so excited.
The Past Continuous
Affirmative
| Negative
| Interrogative
|
|---|---|---|
I was eating
| I wasn't eating
| Was I eating?
|
You were eating
| You weren't eating
| Were you eating?
|
She was eating
| She wasn't eating
| Was she eating?
|
He was eating
| He wasn't eating
| Was he eating?
|
It was eating
| It wasn't eating
| Was it eating?
|
We were eating
| We weren't eating
| Were we eating?
|
They were eating
| They weren't eating
| Were they eating?
|
Remember to contract the verb To Be: Were not / Was not - Weren't / Wasn't
The Present Perfect Simple

The Present Perfect Simple
The present perfect is a tense that connects the past to the present and the time period is unfinished.
- I’ve written 3 articles today (today is not finished, I might write more).
Something that started in the past still has an influence or a relationship with the present.
- She’s forgotten where she parked the car (she still can’t find the car).
It is not necessary to give information about the time period.
- We’ve been to California.
We also use the present perfect to express something that happened only recently.
- I’ve given up smoking.
Present Perfect Vs Past Simple
When a conversation is started in the present perfect, the vast majority of the time the conversation will revert into the past simple because people will usually ask a question or talk about a specific time period:
- A. Have you ever seen a volcano eruption?
- B. Why, yes I have.
- A. Really? When did you see one?
- B. I saw one when I went to Iceland.
- A. When did you go to Iceland?…etc.
For more on the differences between these 2 tenses visit this hub.
The Present Perfect Simple
Affirmative
| Negative
| Interrogative
|
|---|---|---|
I have seen
| I have not seen
| Have I seen?
|
You have seen
| You have not seen
| Have you seen?
|
He has seen
| He has not seen
| Has he seen?
|
She has seen
| She has not seen
| Has she seen?
|
It has seen
| It has not seen
| Has it seen?
|
We have seen
| We have not seen
| Have we seen?
|
They have seen
| They have not seen
| Have they seen?
|
Remember you can contract the verb:
have / has / have not / has not - 've / 's / haven't / hasn't
The Past Perfect Simple

The Past Perfect Simple
We use this when we talk about an event that happened before another event in the past:
- By the time I arrived the party had already started.
The starting point of the story is the past simple ‘when I arrived’ but the earlier action was that ‘the party had started’.
We don’t use it because one event preceded another, but to clarify the sequence of events. You can quite often use the past simple to explain things, but if you want to provide more information then use the past perfect simple.
We often use the past perfect in clauses connected by a conjunction (that, before, after, when, because, so, and) to a clause with the past simple in it.
- When I arrived the meeting had finished.
- They decided to get the bus because the car had broken down.
The Past Perfect
Affirmative
| Negative
| Interrogative
|
|---|---|---|
I had flown
| I had not flown
| Had I flown?
|
You had flown
| You had not fown
| Had you flown?
|
She had flown
| She had not flown
| Had she flown?
|
He had flown
| He had not flown
| Had he flown?
|
It had flown
| It had not flown
| Had it flown?
|
We had flown
| We had not flown
| Had we flown?
|
They had flown
| They had not flown
| Had they flown?
|
Remember to contract the verb when speaking:
Had not - Hadn't
The Present Perfect Continuous

The Past Perfect Continuous
We use this when we want to describe things that had been going on in the past and continuing for some time, but does not continue to the present. It stops at some point in the past or has recently finished:
- She had been working hard all day and finally finished the report around 8.
We often use the past perfect continuous with expressions like for or since to illustrate how long something lasted.
- He had been drink driving for years before he was caught.
- They had been working with that company since the 80s.
The Past Perfect Continuous
Affirmative
| Negative
| Interrogative
|
|---|---|---|
I had been doing
| I had not been doing
| Had I been doing?
|
You had been doing
| You had not been doing
| Had you been doing?
|
He had been doing
| He had not been doing
| Had he been doing?
|
She had been doing
| She had not been doing
| Had she been doing?
|
It had been doing
| It had not been doing
| Had it been doing?
|
We had been doing
| We had not been doing
| Had we been doing?
|
They had been doing
| They had not been doing
| Had they been doing?
|
Remember to contract the negative when speaking: Had not - hadn't
More Teaching Hubs
© 2013 Muttface