Life Sciences: Its Historical Background

Life Sciences
The study of plants and animals began with early man’s concern for his health. He studied herbs for their medicinal value and learned certain things about his body from his primitive attempts at therapy. The Greeks took this simple body of knowledge and vastly enlarged and improved it, with emphasis on their medicine on sound natural science. Aristotle’s speculations about natural things led him to pioneer in botany, zoology and embryology.
Here are some of the noted Greeks who pioneered the field of Life Sciences.






Branches of Biology
Life sciences involve the scientific study of all living organisms such as microorganisms, plants, animals and human beings. The centerpiece of life sciences is biology.
What are the branches of biology which are deemed useful in studying living organisms?
Traditionally, biology has been divided into two major areas 1) Botany, the study of plants and 2) Zoology, the study of animals. However, most biological sciences study both plants and animals. All the many fields of biology are related to one another in some ways.
Ten main subdivisions of biology
Anatomy – the study of the structure of living things.
Physiology – the study of the normal functions of living things.
Pathology – the study of disease, generally in animals.
Biochemistry - the use of chemistry in the study of living things.
Taxonomy – the classification and naming of things.
Biophysics – the use of physics in the study of living things.
Biomathematics – the use of mathematics in the study of living things.
Biological Psychology – the use of biology in psychological studies.
Ecology – the study of relationships of living things to each other and to their environment.
Biological Earth Science – the use of earth sciences such as geography in the study of living things.
Highlights in Biology
- Anaximander, (611? – 54B.C.) a Greek philosopher who believed that man evolved from fish.
- Hippocrates, (460? – 377?) Father of Medicine.
- Andreas Vesalius, (1514 – 1564) a Belgian- born physician who became known as the Father of Anatomy.
- William Harvey, (1578 – 1657) an English doctor showed in 1628 that human blood circulates and later became known as the Father of Physiology.
- Anton Van Leeuwenhook, (1632 - 1723) a Dutch amateur scientist who discovered bacteria with his microscope.
- Robert Hooke, (1635 – 1703) an English scientist who described cells as tiny boxes.
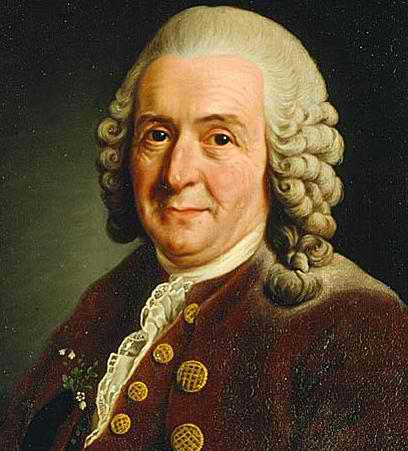
- Carolus Linnaeus, (1707 – 1778) a Swedish scientist who developed the system of binary nomenclature that biologists use today.
- Baron Cuvier, (1769 – 1832) a French naturalist who first compared the structures of the bodies of various animals with that of man.
- Mathias Schleiden (1804 – 1881) a German botanist and Theodor Schwann, (1810 – 1882) a German physiologist set forth the theory that cells make up all living organisms.
- Charles R. Darwin, (1809 – 1882) an English naturalist who proposed the Theory of Evolution that revolutionized biology.
- Gregor Johann Mendel, (1822 - 1884) an Austrian monk who discovered the Principles of Heredity.
- Louis Pasteur, (1822 – 1895) a French bacteriologist who proved that bacteria spread disease and developed vaccines for rabbits and anthrax.
- Louis Agassiz, (1807 – 1873) a U.S. naturalist who became known for his study of living and fossils fish.
- Asa Gray, (1810 – 1888) an American botanist who classified plants.
- Rudolf Virchow, (`1825 – 1902) established the science of Pathology.
- Thomas Hunt Morgan, (1866 – 1945) an American scientist who established the Gene Theory.
- Ivan Petrovich, (1849 - 1946 a Russian physiologist who showed how nerve controls the flow of digestive juices.
- Karl Landsteiner, (1868 – 1943) an American physiologist who discovered the main types of human blood.
- Albert B. Sabin, (1906 -) an American scientist who developed polio vaccines.
- Melvin Calvin, (1911 -) an American scientist who established the chemical pathway of C3 photosynthesis.
- James D. Watson, (1928 -) a U.S. biologist and Francis H.C. Crick, (1916 -) of England developed the model of DNA, the basic components of genes.
- Sir Alexander Fleming, a British biologist of 1900’s discovered penicillin.
- Barbara McClimteck, of U.S. established that genes could move from one location to another on chromosomes.
Questions for Study
- Why is the science of Biology considered the centerpiece of life sciences?
- List the ten main branches of Biology.
- Enumerate at least ten scientists responsible for the existence of Biology as a science.