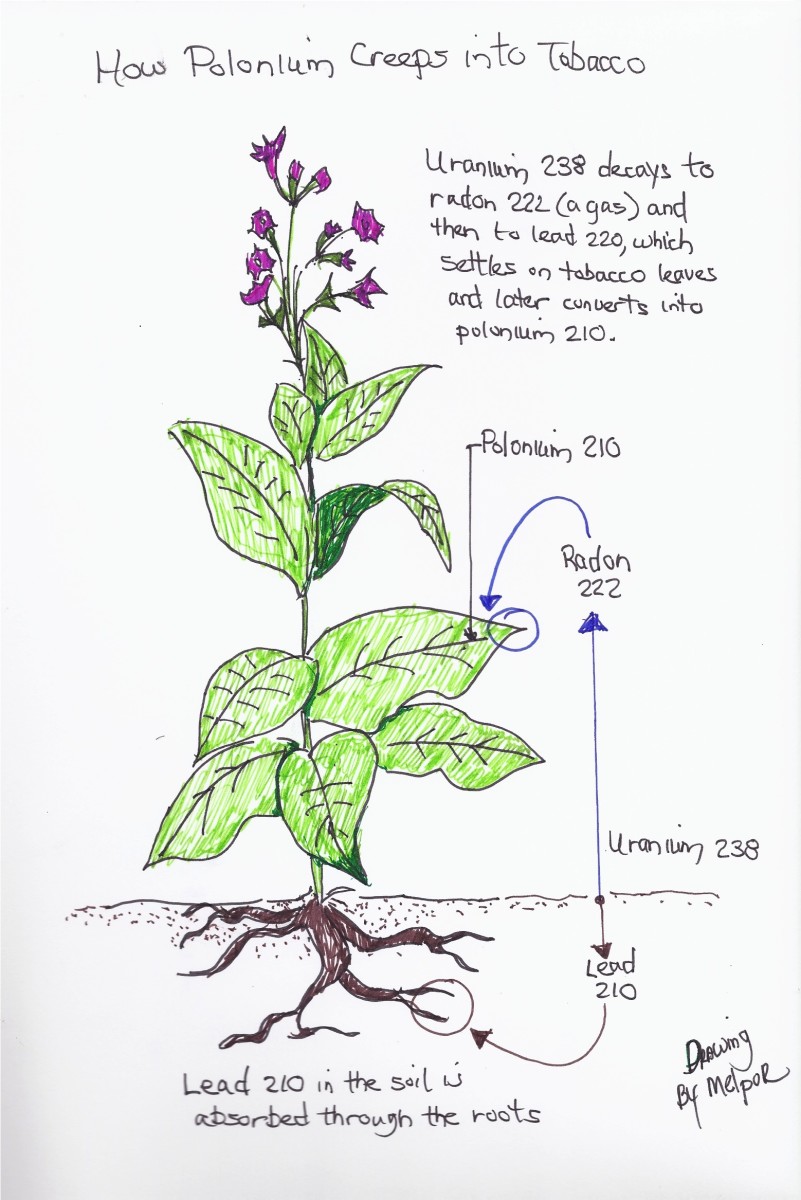
Link Between Smoking and Schizophrenia - A Study
A lot has already been said about the dangers of smoking. There is a sufficient evidence base, as well as a lot of scientific research on how tobacco consumption affects our body. However, almost all previous studies have focused mainly on the study of the respiratory and cardiovascular systems. But new data obtained by scientists from the UK suggests that tobacco smoke can carry a much greater danger than we thought.

How smoking affects the body
A new study published on the website of the University of Bristol suggests that smoking tobacco can increase the risk of developing depression and schizophrenia. Scientists came to this conclusion together with their colleagues from the Bristol Biomedical Research Center (BRC) and the local Department of Epidemiology.
It is well known that the bad habit of smoking is much more common among people with mental illnesses - especially in patients with depression and schizophrenia. However, most of the studies that examined this relationship did not help to figure out what is the root cause in this case. Does a mental illness increase the likelihood of smoking, or is smoking itself a risk factor for mental illness?
To find out, the team applied an analytical approach called Mendelian randomization. This method allows us to draw conclusions about causal relationships, based on genetic variants and predispositions that can be the cause of pathology. For this, the mapping of human genes is necessary, and scientists had such information. After analyzing data from 462,690 people of European descent (among whom were 8% of smokers and 22% of former smokers), experts concluded that smoking tobacco increases the risk of depression and schizophrenia.
People with mental illnesses are often overlooked as part of their smoking reduction programs, says lead contributor Dr. Robin Wootton. "But our work shows that we must make every effort to prevent smoking and encourage smoking cessation due to negative consequences for both physical and mental health."
All people whose data were used for the experiment were divided into 3 categories - non-smokers, smokers, and those who quit smoking. As a result, it turned out that the second and third groups had signs of depression (and in some cases, schizophrenia) 2.2 times more often than those who did not smoke at all. At the same time, interestingly, the duration of tobacco use did not play a special role.
According to scientists, even after a short period of tobacco abuse, after some time, people showed signs of anxiety disorder. The opposite picture, when the violation of mental balance led to the use of tobacco, was practically not observed. So if you suddenly smoke - abruptly quit this habit and replace it with something useful. For example, following me and reading my articles.
Of course, this study is primarily based on statistical data, but the researchers themselves emphasize that there is definitely a relationship between the psychological sphere and smoking. This work encourages scientists to begin a full-scale study on the effects of tobacco smoke products on the development of mental disorders, which experts plan to do soon.