Plastics

Introduction
Plastics are a group of materials, either synthetic or naturally occurring, that may be shaped when soft and then hardened to retain the given shape. It is a type of material that is a household name and has several real-life applications. Hence, it will be intriguing to find out how plastics are being made.
Resources for Plastics
After crude oil is being extracted by drilling wells, it is being transported to an oil refinery whereby it undergoes fractional distillation (FD). To put it simply, during this process, crude oil is firstly heated to form vapour which will enter FD column. In this column, the vapour will cool and be separated into different products based on the boiling point in each section. This means that the product formed in the higher section will have lower boiling point than those in lower section.
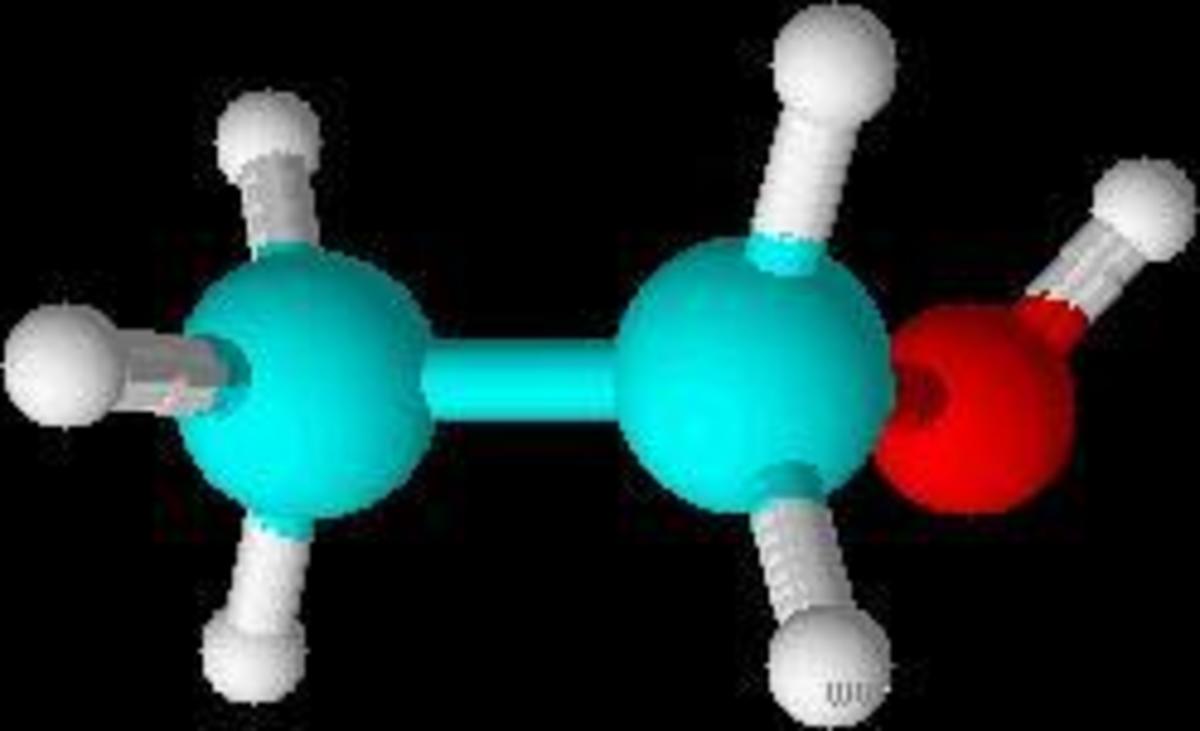
Introduction to Addition Polymerisation
To fully understand how a huge polymer in plastics are made from several monomers through addition polymerisation, we will use the monomer that is shown in the picture (Chloroethene) as an example to illustrate the entire process.
Step 1 and 2
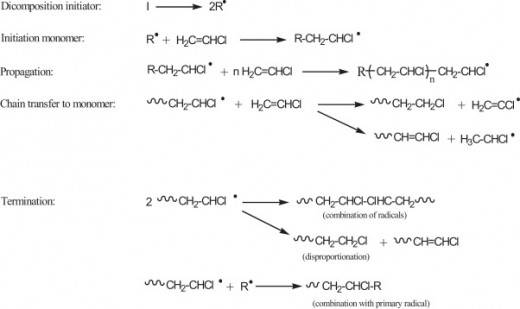
Before we can begin the addition polymerisation, we will need a radical. In this case, we will use iodine as an example.
Firstly, the UV radiation will provide the energy to break the bond between 2 iodine atoms. As a result, each of the bonded electrons will be transferred to each atom to form 2 radicals known as R· (we will use this to represent iodine radicals)
Secondly, the initiation step will occur. During this process, the initiator radical (R·) will be added to the monomer (chloroethene) to form a new radical having the unpaired electron on a carbon atom, as illustrated in the above picture.
Last 2 steps of the process
The third step of the addition polymerisation is the propagation step whereby a monomer adds onto the polymer chain and each new monomer unit creates an active site for the next attachment. This step continues until all the chloroethene has been used.
The final step of this process is the termination step whereby 2 chains of molecules are combined. The structure enclosed in brackets, ―[CH2―CH2―]n is the repeating unit of the polymer chain. The number of repeating units, n, varies according to the length of the polymer chain or, in other words, the molecular weight.
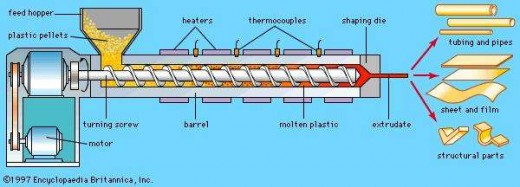
Applications of Plastics
At this point, we have fully understood how crude oil is being extracted to produce plastics.
Before we move on to Part 2 of Plastics, let us talk about the applications of plastics. In our mind, when we are asked about the applications of plastics, we can easily name a few, ranging from plastic bags to plastic containers and water bottles. However, do you know how these products are being formed?
To find out more information on this topic, stay tuned to Part 2 of plastics (link attached below) whereby we will be discussing more theoretical topics such as the differences between synthetic plastics and naturally-occurring plastics, advantages and disadvantages of plastics as well as both industrial and individual level of recycling plastics.
Part 2 of plastics
- Plastics Part 2
In part 2 of plastics, we will first answer the question before moving on to topics such as the differences between synthetic plastics and naturally-occurring plastics, the advantages and disadvantages of plastics as well as the industrial and indivi