Orion Spacecraft
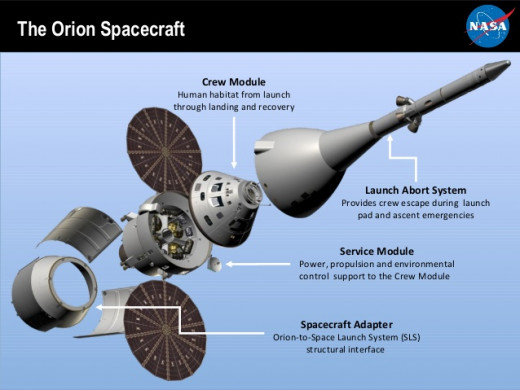
Orion is the one of the most famous spacecraft in NASA research center. It is also called as multipurpose crew exploration vehicle (MPCV). It can be comfortable to travel a crew of upto 6 members astronauts into the space (outermost atmosphere of earth). It is developing by NASA for launch on the space system since 2004 . Orion, the multipurpose crew vehicle was announced by NASA on May 24, 2011. It is bigger than Apollo spacecraft.
Orion is intended to facilities exploration of human beings on to the Mars planet.
Crew Exploration vehicle (CEV) was announced by George W. Bush of US president in the year of January 14, 2004 as a part of vision for space exploration. The crew exploration vehicle was partly a reaction to the space accident. The CEV effectively replaced the conceptual Orbital space plan
It normally consists of four parts they are:
- Launch abort system
- Crew module
- Service module
- Space craft adapter
Mass properties:
Gross weight (liftoff) : 15,571 lbs
Dry mass : 9849 lbs
Propellant (liquid fuel): 5722 lbs
Orion Launch abort system:
The Orion launch abort system is the top most part of Orion vehicle which is above the crew module to safety in the event of an emergency during launch or climb to orbit and it protects the crew module from dangerous atmospheric loads and Heating, motors etc...
Orion Launch abort system consists of four parts:
- Altitude control motor
- Jettison’s motor
- Launch abort motor
- Fillet
- Ogive fairing
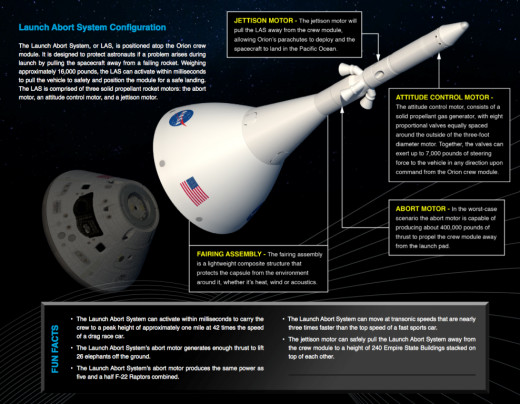
Altitude control motor:
It is top part of the launch abort system and it controls the crew module of controlling Flight path when it changed by the jettison’s motor and it away from the it steering in the event of emergency. It was tested in the December 2009 by ATK’S Facility in Elkton, Maryland.
Jettison’s motor:
It is below the attitude control motor it is also called as the solid rocket motor and it separated the crew module and launch abort system. The static test was conducted by the Aero jet corporation in Sacramento, California and it is totally completed in the year of April 2008
Abort motor:
It is below the jettison’s motor and it provides half million pounds of thrust to lift crew module and it is pulling the crew module away safety while emergency event on launch pad. It was completed in the November 2008by 5.5seconds ground test firing at the abort motor
Mass properties:
Dry mass : 19351 lbs
Propellant : 300 lbs
Oxygen/nitrogen/water: 77lbs
Landing weight : 18939 lbs
Gross weight : 19650(lunar)/21,400 lbs (ISS)
Crew module:
The Crew module is the one of the most important part of multipurpose crew vehicle (Orion). It comfortable to travel the 6 astronauts into the space and it also carries reusable transportation of research instrument consumables and services as the docking port for crew transfer. It is the only part which reaches the earth after each mission.
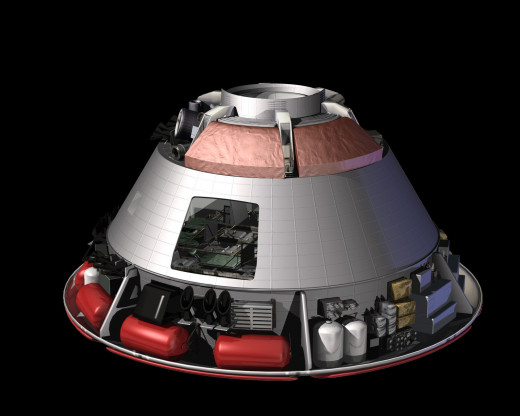

Mass properties:
Oxygen/nitrogen/ water: 694 lbs (lunar)
Propellant weight : 17,433 lbs (lunar)
Gross weight : 27,198 lbs (lunar)
Service module:
It is below the crew module which supports it from Launch through separation prior to re-entry. It provides the in-space propulsion capability for orbital transfer, attitude Control, and high altitude ascent aborts and water, oxygen, and stores electrical power while on-orbit, and It maintains the vehicle system temperature. This module can also transport unpressurized cargo and Scientific pay loads.
Space craft adapter:
It is the end part of the crew vehicle which protects the service module and for launches crew exploration vehicle (CEV)
Testing of crew exploration vehicle (CEV):
The test of vehicle is begins in March 2009 took place in controlled water environment, it is testing near Kenndy space center
Environmental testing:
The environment testing of Orion is started from 2007 to 2011 by NASA at Glenn Research Center in Sandusky at Ohio.
Launch abort system testing(LAS):
The first Orion launch abort test was successfully completed on November 20, 2008 and the LAS motor provide 2200kms of thrust in case an emergency situation .her eyes on the launch pad on during the first 91kms of the rocket climbs to orbit
The full scale of launch abort system was testing is began from March 2009 to May 10, 2010 and it was successfully executed by NASA at White sand, New Mexico. During the launch abort system testing, they used three solid fuel rockets motors. They are Jettison’s motor, Attitude control motor, and the main thrust motor
Exploration flight test-1:
The flight test -1 is conducted on December 5th 2014 and the Orion capsule was launched by delta-4 heavy rocket
After completion of the test at splashed down in Pacific Ocean about 4.5hrs later and the two orbit flight was NASA first launch of a vehicle to travel human being more than hundred miles into the space

© 2015 KALYAN CHAKRAVARTHY THADAKA