Profit and Loss Account in Study of Economics
It is always the interest of the business to earn profit. This is the underlying reason why business has been motivated to invest and expand on specific production of goods and services. However, the profit of the business is the result of incentive and reward for taking risk to sell a particular product in the market. The high risk business may assume to have high reward or even loss if the business fall short of selling the product.
Generally, the financial profitability is measured by simple illustration that
PROFIT = REVENUE-COSTS
A. Revenue
The sales of goods and services in the market are usually the revenue or income of the firm. The productivity of the enterprise relies so much on higher revenue in order to meet the financial expenses in the operation of the business.
- Revenue provides financial variables as to the cost of sales and gross profits on a given goods or services produce in the market.
B. Costs
The production costs of the firm provide financial information as to the expenses on the operation of the business. The costs of the marketing operations must always be lower than the revenue in order to earn profit. It is not only the operation costs (production costs such as administrative, marketing and overhead cost) but also the interest, tax and dividends are included in the costs.
- Operating Cost provides financial variables as to the production cost of sales, marketing and distribution, finance and administration, and other overheads including depreciation. The sum of these variables is the Total Operating Costs.
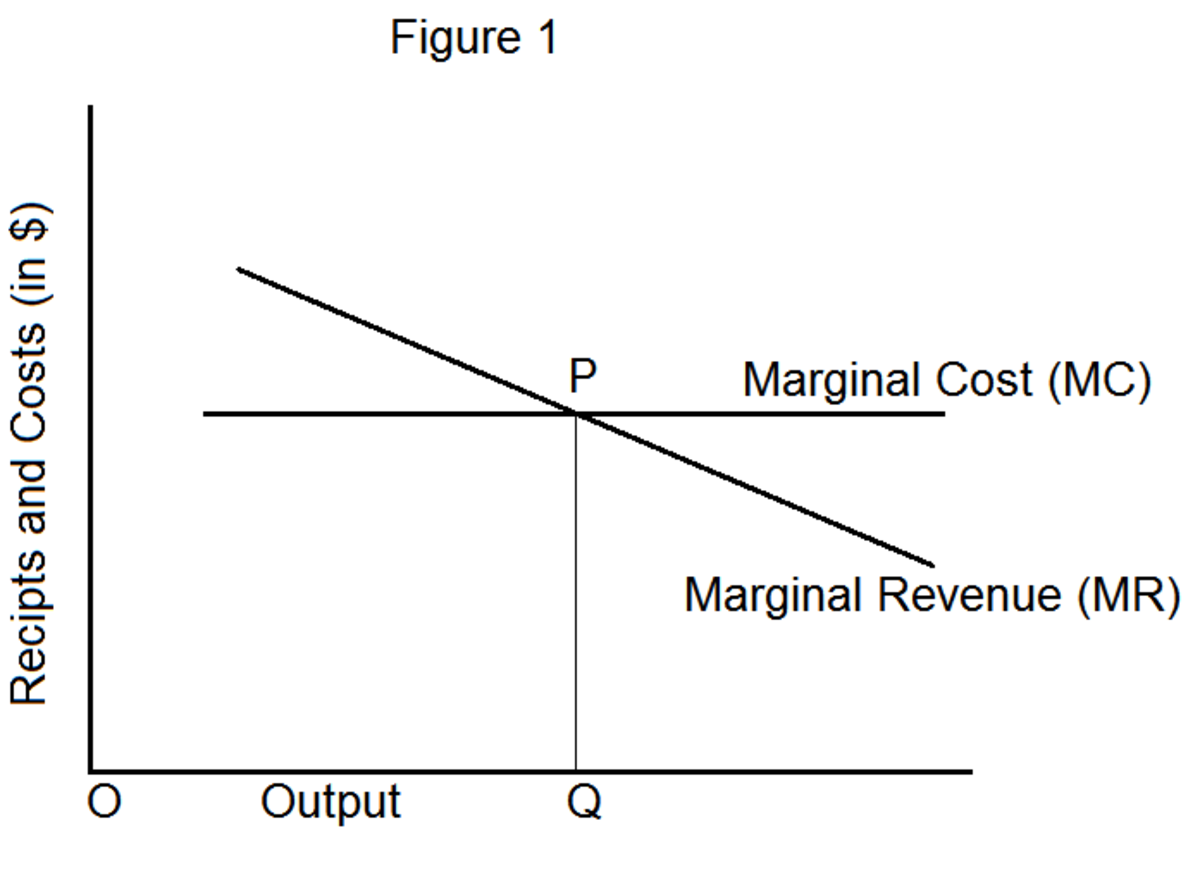
- Operating Profit is computed by the Gross Profit and deducted by the Operating Costs. While Operating Margin Cost is computed based on the Operating Profit and divide it to the Revenue.
- Other deductions in the operation of a firm include interests, taxes, and dividends in order to get the retained profit Simple Illustration of the Profit and Loss Accounting
The task of accounting is to gather relevant data to monitor the financial profitability on the operation of the business. This is done by recording the financial data (Book Keeping) finding out the result through the profit and loss account. For example, a firm has the following financial data:
P’000 P’000
Revenue 150,000 100,000
Cost of Sales 90,000 55,000
Gross Profit 60,000 45,000
Gross Profit Margin/Revenue 40 % 45 %
Operating Costs
Sales, Marketing and Distribution 20,000 18,000
Financial and Administrative Costs 9,000 6,000
Other Overhead Production Costs 8,000 7,000
Depreciation 3,500 3,200
Total Operating Costs 40,500 34,200
Operating Profit 19,500 10,800
(Gross Profit less Operating Costs)
Operating Profit Margin 13.00 % 10.80 %
( Operating Profit/Revenue)
Interest (300) (250)
Profit Before Tax 19,500 10,550
Taxation (310) (150)
Profit After Tax 18,890 10,400
Dividends 5,000 3,400
RETAINED PROFITS 13,890 7,000
There are 3 parts in the monitoring profit: (1) the trading account; (2) the profit and loss proper ;and (3) the appropriation account.
- The Trading Account. The ‘trading’ means the buying of raw materials to process it for a finished product and selling them to particular market. Likewise, the “money in” is the revenue and “money out” is the costs of the business. (i.e. Gross Profit)
- The Profit and Loss Proper. These are the income received from investment and starts with the Gross Profit. The costs and revenues are added including any other activities not directly related to trading.
- The Appropriation Account. This account presents how profit is appropriated in the profit and loss account.