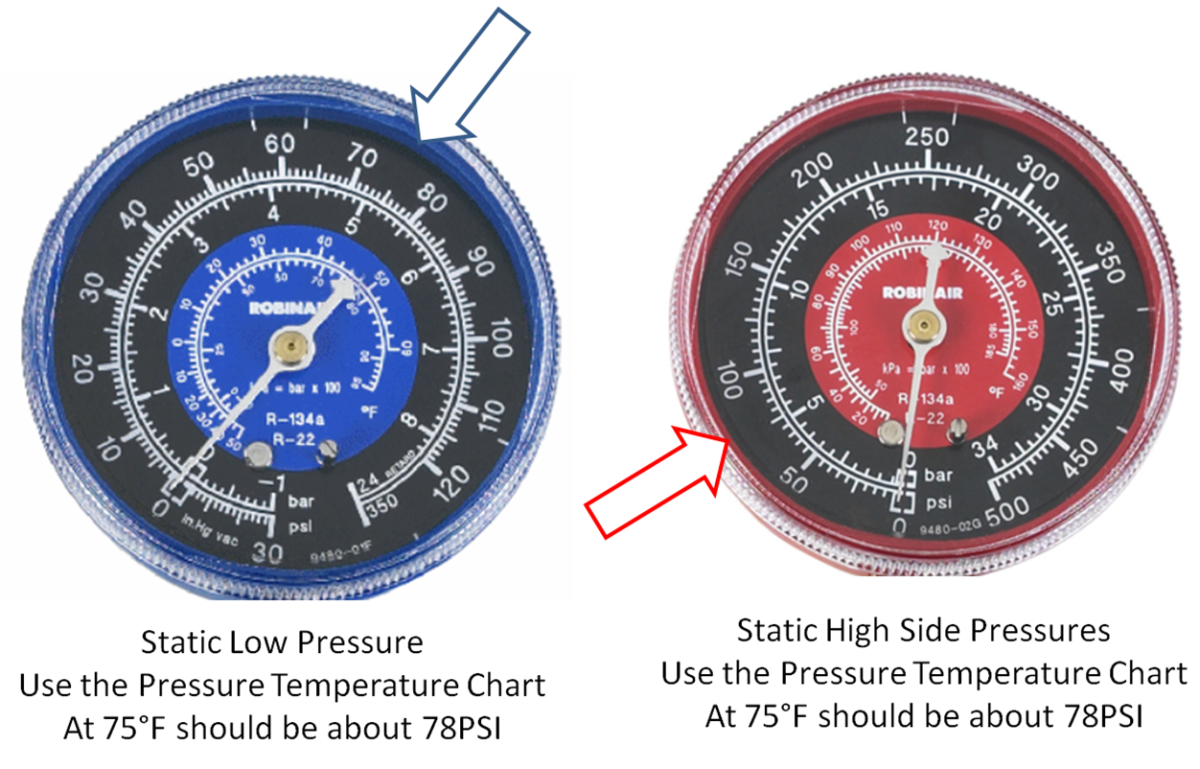
Refrigeration Cycle
INTRODUCTION
In general refrigeration is defined as any process of heat removal, more specifically, refrigeration is defined as that branch of science which deals with the process of reducing and maintaining the temperature of a space or material below the temperature of the surroundings.
To accomplish this, heat must be removed from the body being refrigerated and transferred to another body whose temperature is below that of the refrigerated body. Since the heat removed from the refrigerated body is transferred to another body, it is evident that refrigerating and heating are actually opposite end of the same process. Often only the described result distinguishes one from the other.
The working substance used in a refrigerator is called refrigerant. Generally speaking, a refrigerant is any body or substance which act as a cooling agent by absorbing heat from another body or substance. As a matter of convenience and economy it is not practical to permit the refrigerant vapor to escape to the outside and be lost by diffusion into the air. Therefore the refrigerant must be circulated in a cyclic process during a refrigeration process and must be uses again and again. Hence vapor compression cycle and vapor absorption cycle are the two most important cycles of refrigeration.