Steps to the Scientific Method of Research
What is the Scientific Method?
The scientific method of research involves identifying a problem, collecting data, forming a hypothesis based on that data, and testing that hypothesis. According to Frank Wolfs from the University of Rochester:
"The scientific method is the process by which scientists, collectively and over time, endeavor to construct an accurate (that is, reliable, consistent and non-arbitrary) representation of the world."
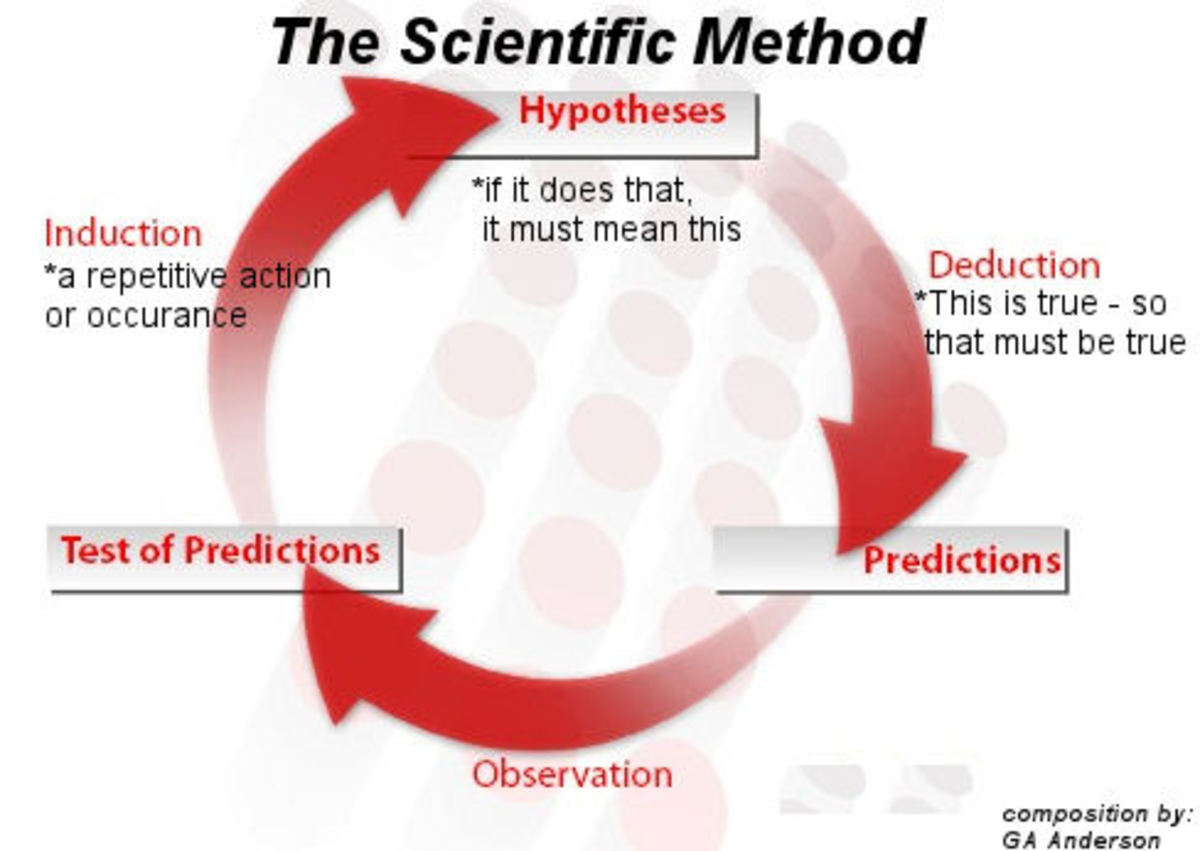
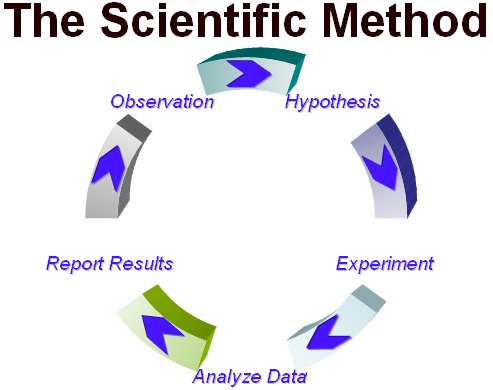
Basic Steps of the Scientific Method of Research
- Ask a question: Ask about the who, what why, when, where and how about something you observe. This method of observation must be something that can be measured.
- Research: You don't want to just go from asking a question to just testing it without knowing the best ways to test it. Knowing background information on your observations is the best way to start before diving into a hypothesis and then testing it.
- Construct a hypothesis: A hypothesis is basically an educated guess. Think of it this way: "If ____ (I do this), then ____ (this) will happen." Again, make sure it is something measurable, preferably with numbers.
- Test hypothesis with an experiment: The experiment needs to only change one factor at a time to make it a fair assessment about whether or not your hypothesis is true. Make sure to repeat it to ensure that your results are valid.
- Analyze the results and make a conclusion: Look at the results of your experiment and see if your hypothesis is proven to be true or not. At this point, if they're partially or completely false, you may start back from scratch with a new hypothesis.
- Report your results (if the hypothesis was true, partially true, or false): It is important to share your results in a presentation or other any other variety of ways to others. Professional scientists do this all the time with reports or at meetings.
- Rethink hypothesis (if the results from the original one are false or only partially true)
Common Mistakes
Scientific theories should be able to be tested by anyone so if anyone does your same experiment or one of their own, they should be able to get the same results or else you probably made a mistake somewhere.
Some people can't get passed their bias and formulate tests for their hypothesis that are not completely fair. They also can't get passed what they believe is logic and believe that testing is redundant. With the scientific method of research, you must always test your hypothesis and do so as unbiased as possible.
Some may also ignore any errors in their experiment without acknowledging or exploring them further. This leads to some believing that their errors were actually some sort of phenomena, which is later proven to be false. This also can prevent the scientist from seeing a new discovery they may have just come across.
The most important aspect of the scientific method of research is its unbiased look at information in order to better understand the universe. Remembering this when going through proving or disproving your own hypothesis is essential to keeping accurate information.