Social Psychology Exam
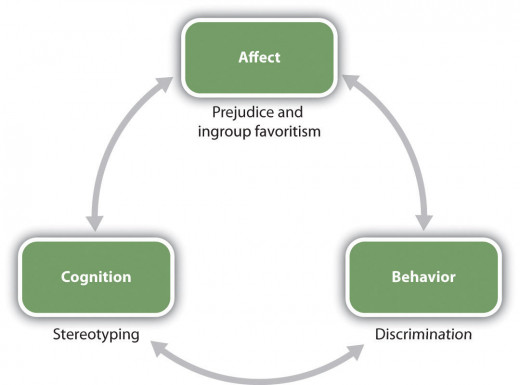
Q: Describe ABCs of social psychology.
A: The ABC’s of Social Psychology are the simple definition of social psychology; they are the three areas that work together to create human experience. The A part of the ABC’s of social psychology stands for social affect. Affect is mainly social and it is about how people emotionally respond in reference to themselves, events, other people, and any issues they many encounter. Affect is also about the positive and negative feelings that people experience all the time in the background of their lives. Affect can help people to function efficiently, but it can be harmful if it gets out of control. The B section refers to social behavior; this part is about social exchange and social rewards. This section is about the goods, services, and emotions that people give to other people, as well as the positive and negative outcomes the people receives for their behavior such as: attention, financial support, guilt, love, and feelings of frustration. The C represents social cognition meaning mental activity in relation to social activities that teach people how to understand and predict the behavior of other themselves and other people. One aspect of cognition is the active interpretation of events and the different ways other people perceive the same event. Attitudes and schemas and how they allow people to make snap judgments of other people both correctly and incorrectly are another aspect of social cognition.
Q: Provide some examples of cultural differences in expressing emotions
A: Different cultures express emotions in different ways. For instance people who live in warm climates close to the equator tend to use more nonverbal communication than people who live in colder climates farther from the equator. Also people who live in warmer climates are more likely to touch other people during conversation than people who live in colder climates. In Latin American cultures people use eye contact to display emotion while in Japanese cultures people avoid eye contact whenever possible. In Dutch cultures people use facial expressions to express emotion while people in Japanese cultures people express emotion through their tone of voice. People from collectivist cultures tend to avoid expressing negative emotions in public in order to fit in and get along with everyone else. In individualist cultures people tend to emphasize the importance of individual autonomy and power and, as such, people from individualist cultures tend to focus less on controlling and masking emotions than other cultures. Expressing affection by hugging, kissing, or holding hands in public is considered wrong and sometime illegal in some cultures such as: China, India, Indonesia, and Middle East cultures. While in American, European, Canadian, and Brazilian cultures affection in public is allowed and even encouraged. Emotions are expressed in many different ways in many different cultures; in some cultures certain emotional expressions can cause a person to be fined or imprisoned.
Q: Explain the relationship between self-awareness and self-consciousness.
A: Self-awareness is the extent to which people fix their attention on their own self-concept. Self-consciousness is a form a self-awareness that occurs when people feel they are being observed and judged by the public. When a person’s self-awareness is increased they often become self-conscious. For instance, if a person is performing a role in a play and the person suddenly becomes aware that the whole audience is watching him or her, the person then becomes more self-conscious. An increased self-awareness leads to self-consciousness.
Q: Compare and contrast Bait and switch technique and low-ball technique.
A: The Bait and switch technique and the low-ball technique are both very similar and only slightly different attitudes-follow-behavior idea that are very popular among salespeople. The bait-and-switch technique is a persuasion attempt that occurs when a person is offered one product at a low price only later to find that the low price is not available. This technique is often used by retailers and dealerships both intentionally and unintentionally. For instance a person sees an ad online that a store is selling bicycles for $25, but when the person arrives at the store there are no bikes at that price available then the person is more willing to purchase a more expensive bike because he or she already committed themselves to purchasing a bicycle. The store may have run out of the bikes unintentionally, purposely stocked a very limited number of the cheaper bikes, or never stocked any of the less expensive bikes to begin with. The low-ball technique is a persuasion attempt that occurs when a persuader promises a person something they desire in order to get the person to picture themselves engaging in the desired behavior, the persuader then explains that their offer is not actually possible. An example of this technique would be if a TV salesperson promised a customer a low price on a brand new Smart TV in order to get the customer to imagine themselves purchasing the TV. Once the customer has committed him or herself to purchasing the TV the salesperson would then tell the customer that they cannot actually sell the TV at that price. In this situation the TV salesperson is attempting to get their customer to purchase the TV at a higher price by getting the customer to have already committed him or herself to purchasing the TV. Both techniques involve the seller getting the buyer to imagine themselves owning the product and then committing to purchase the product only for the buyer to discover that the item they want is not available at the price that they were promised. The two techniques are different in that the low-ball technique is an intentional deception while the bait-and-switch technique is not always intentionally deceptive, sometimes a store or dealership simply run out of the product that was advertised as a low price.
Have you ever made the fundamental attribution error?
Q: What is fundamental attribution error? Explain with an example.
A: The fundamental attribution error occurs when people overestimate the role of person factors and overlook the impact of a situation. An example of a person making a fundamental attribution error would be if a high school student turned and said hello to a fellow student and that student gave an unfriendly hello back. The student might react by deciding that the other student is a jerk and a mean person. This would be a fundamental attribution error because the student would be making a judgment on the other student without knowing what the other person’s situation; the other student may have just flunked an important test, recently lost a family member or maybe the student just got dumped by their boyfriend/girlfriend. Situational factors can just as important as person factors because the student might not have acted the same way if he or she was not in a bad situation.
Q: What is social influence? How does it cause conformity?
A: Social influence is occurs when an individual’s actions, thoughts, and reactions are influenced by groups or other people. Social influence comes in many forms such as: peer pressure, persuasion, and marketing. Social influence can cause conformity because people want to be accepted socially and to do that they have to conform to the norms of society and any groups they are a member of.

Q: When does groupthink occur within a group
A: Groupthink happens within a group when the group makes a poor judgment as an outcome of a defective group process and strong conformity pressures.
Q: Differentiate between stereotypes and prejudices
A: Stereotypes are when people falsely believe that all people with specific characteristic are the same. For instance a Stereotype would be that Black Americans are good at sports. Prejudices are an unfair and illogical feeling of dislike for a person or a group because race, sex, religion, etc. A prejudice would be if a person hated all Black Americans because of their skin color or their race.

Q: Explain the impact of social norms on prejudices.
A: Social norms can cause and sustain prejudices. Social norms are behaviors considered appropriate within a social group. A social group can develop a prejudice and that prejudice can grow within a group until it becomes a social norm in the group. For instance, a church group might dislike a different religion and that dislike might eventually become a prejudice. Over time the prejudice could become a social norm in the church group to the extent that any new members would conform to the church’s social norms and prejudices.
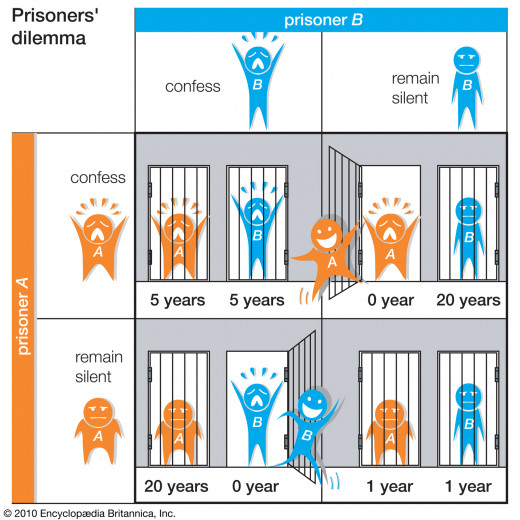
Q: Explain the prisoner’s dilemma game.
A: The prisoner’s dilemma game is a laboratory simulation that represents a social dilemma where the goals of the individual compete with the goals of another individual or a group of individuals depending on the simulation. The goal of the game is to determine how people react when faced with balancing their own interests with the interests of others. In this game each individual will benefit the most if they act for their own immediate self-interests and yet everyone else will be worse off; if the individual acts in everyone’s self-interests than everyone benefits to a lesser degree. One example of a prisoner’s dilemma could take place at the exit of a crowded parking lot; each individual needs to decide if they will rush the exit or cooperate with everyone and take their turn to reach the exit. If an individual rushes the exit they could get out before everyone else, but they could cause a traffic jam that will cause it to take longer for everyone else to exit the parking lot.