- HubPages»
- Education and Science»
- History & Archaeology»
- History of the Americas
Ten of The Worse Earthquakes in U.S. History
1964 Map of The Great Alaska Earthquake

The Ten Worse Earthquakes in U.S. History
Here is the list according to the USGS:
1. 1964 Great Alaska Earthquake 9.2
2. 1700 Cadadia Subduction Zone, Alaska 9.0
3. 1965 Rat Island, Alaska February 3, 1965, 8.7
4. 1957 Andrian Island, Alaska, March 9, 1957, 8.6
5. 1938 Shumigan Islands November 10, 1938, 8.1
6. 1946 Uninak Island, Alaska, April 1, 1946, 8.1
7. 1899 Yakutat Bat, Alaska September 10, 1899, 8.0
8. 2002 Denali Fault, Alaska November 3, 2002, 7.9
9. 1987 Gulf of Alaska November 17 7.9
10 AndreanofIslands, Alaska 7.9
The 1964 Alaska Earthquake
An earthquake is caused by a sudden slip on a fault. The tectonic plates are always moving, sometimes getting stuck at the edges because of friction.
On the average, there is a magnitude of 7 or higher in or offshore every one yo two years and a magnitude of 8 or higher every twelve years. So we may be long over-due for "the big one."
This 1964 earthquake struck Prince William Sound on March 27, 1964, at 5:36 P.M. lasting 4.5 minutes and was the most powerful recorded earthquake in U.S. history. It is also the second-largest next to a magnitude 9.5 in Chile, 1960.
Of note is the fact that we can never have an earthquake of 10 or higher. It simply can't happen because the magnitude is related to the length of the fault on which it occurs. No-faults long enough for a magnitude of ten are known to exist, and, if it did, it would extend around much of the planet.
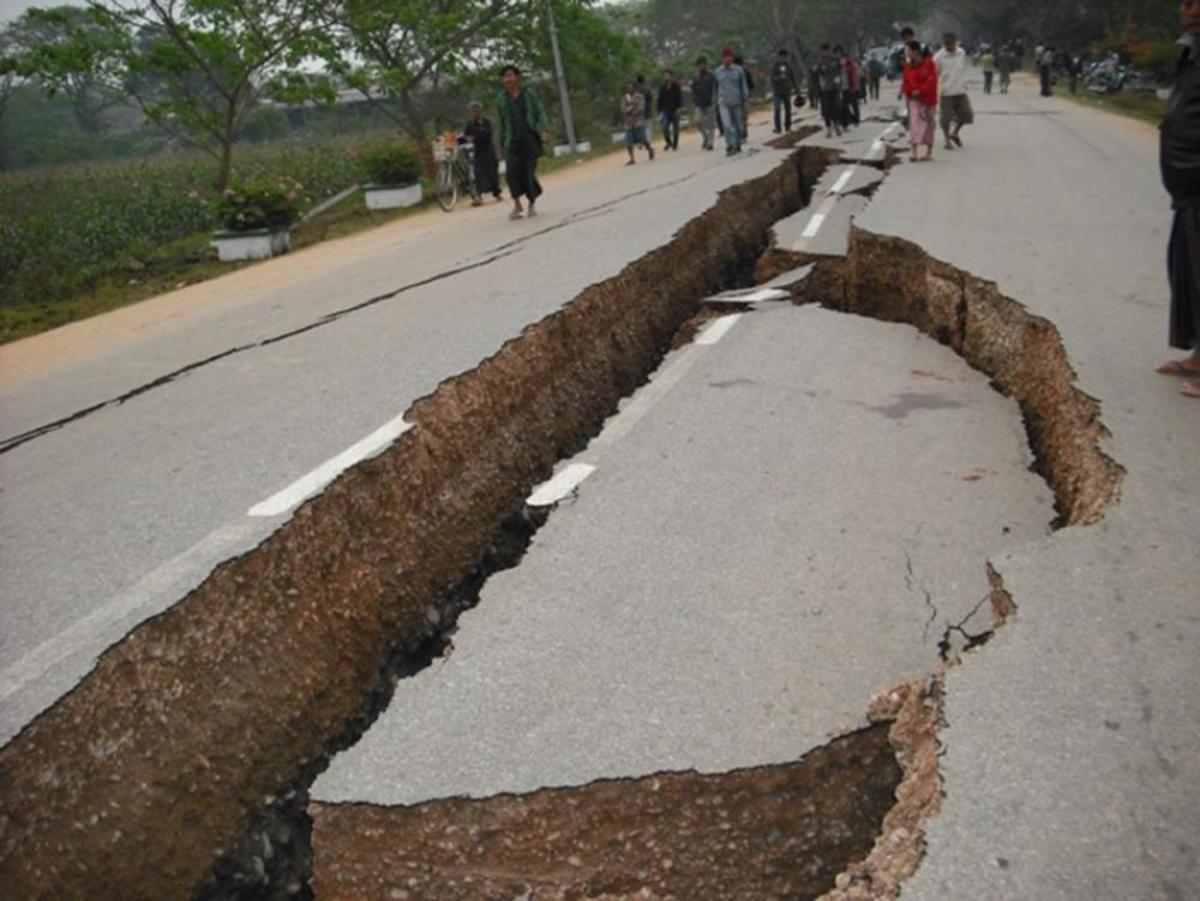
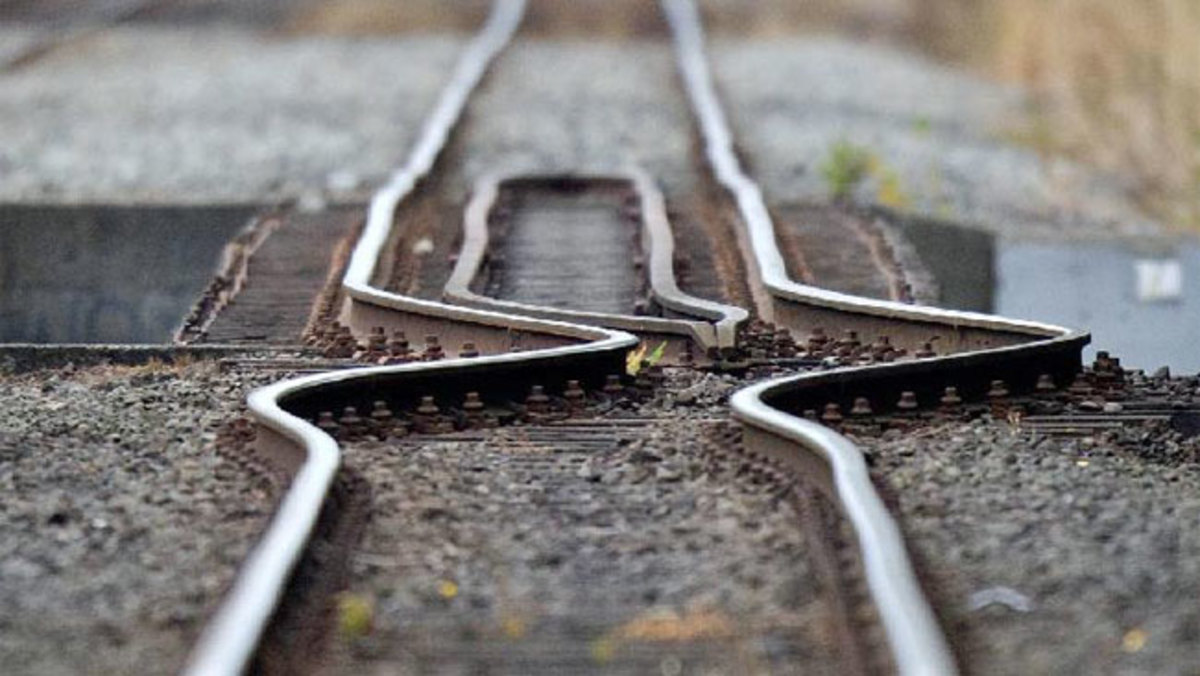
This earthquake unleashed tsunamis, fissures, avalanches, and landslides. In some areas, the earth was raised as high as thirty feet. The following day, eleven aftershocks were felt measuring 6.0. Even though 139 lives were lost, only fifteen were the direct result of the earthquake. Most deaths were attributed to tsunamis. Among natural disasters, tsunamis are the closest to being unsurvivable.
Many areas of Anchorage and Juneau had to be totally redeveloped. Even the Space Needle in Oregon swayed during the earthquake. Waterways as far away as the coasts of Texas and Louisianna were affected.
In downtown Anchorage, the quake caused streets to crack, blowing cars into the air. Parts of the city dropped, leaving deep holes. At the airport, the control tower collapsed, killing the controller. The entire town was nothing but chunks of dirt, rock, snow, and ice. Forty-five miles north, the SS Chena, a 400' freighter, was in port in Cordova, Valdez, and saw the town of Valdez burst into flames, and the docks were on fire. In the village of Choenga, an eight-nine foot wave killed twenty-three of the seventy-five residents.
Over time, the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers spent 110 million dollars on salvage, rescue and rehabilitation operations. The code name for them was "Operation Helping Hands."
Devastation in Anchorage



Oil Tanks Exploding, Anchorage

Effects of Disasters
After any disaster, there will be so many problems. You won't be able to travel because of roads; your utilities will be cut off, water will be scarce or contaminated. Food will be challenging to get and keep, and medical help may not be accessible. Organizations like the Red Cross and Disaster Relief may not be able to gain access for a while. It is suggested that two weeks of water be stored, along with canned goods and medical supplies. It is essential to be prepared for any disaster, no matter where you live.
We can't stop natural disasters. They can strike anywhere or anytime. We can only try to stop the damage by building stronger houses and buildings and on solid ground. {planting trees to prevent erosion and landslides.
Floods and drought kill more Americans over time than other disasters.