The Electricity Guy: The Components

Controlling the Circuits
In this entry of 'The Electricity Guy' we will take a look at some of the devices used to control electricity within a circuit.
Each of these components has a specific purpose and each is represented by a schematic symbol.
There are a lot of different types of components that can be used, but for simplicity this article will look at only the most common ones. Transformers are not covered in this article as they were covered in 'Completing the Circuit'.
The Core of All That Is Electronic
Transistors and Integrated Circuits
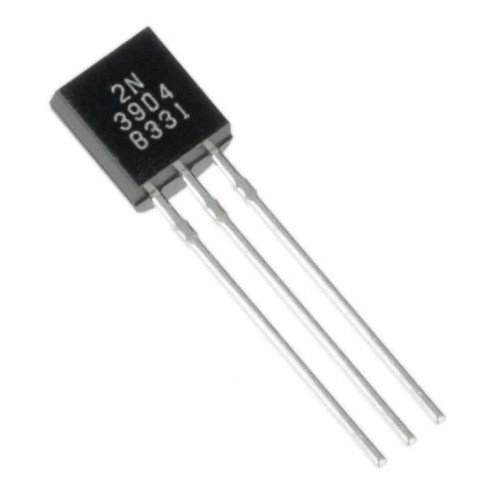
The transistor is the base of everything electronic.
One single transistor is all that is needed to make a signal amplifier.
What a transistor does is that it uses a small amount of electricity to control a larger amount. Before transistors, vacuum tubes were used to do this.
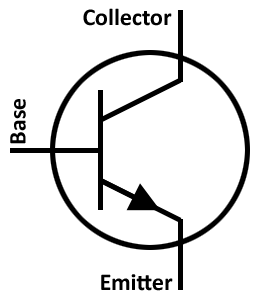
There are many different types of transistors, but the basic one consists of three parts. The emitter, collector, and base.
The emitter is the input and the collector is the output. The base controls the electricity travelling from the emitter to the collector.
This is your basic amplifier. The amount of current supplied to the base directly affects the amount going through the transistor. This is exactly how an amplifier works.
The base of the transistor is controlled by other components in the circuit. In the case of an audio amplifier, for example, a variable resistor (discussed later) may be used to control the amount of current going to the base. This in turn controls the amount of current allowed through the transistor. This is how a volume control works.
In some cases, many tiny transistors may be packaged together into a single package (chip). This is called an integrated circuit.


Rectifying the Situation
Didoes, Light Emitting Diodes, and Bridge Rectifiers
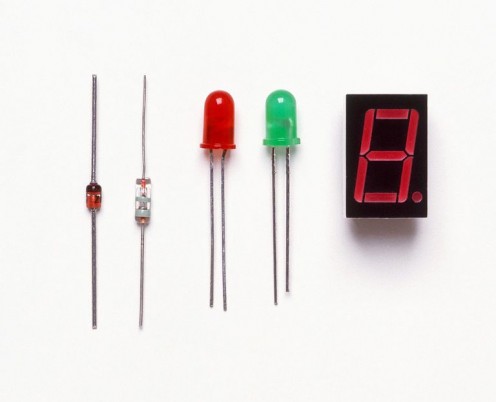
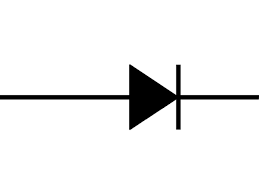
The job of a diode is very simple. It allows electricity to travel only in one direction.
There are many different types of diodes including ones that give off light.
For simplicity, I will not go into discussing all of the different types.
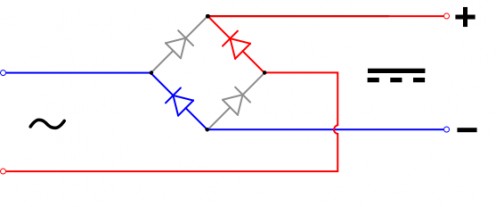
Diodes are commonly used in power supplies for electronics to convert AC into DC. Although one will do the job, there is still a lot of leakage in the reverse direction to cause problems in an electronic circuit. Therefore, in these cases many diodes are used in conjunction with capacitors (discussed later). This is called a bridge rectifier. A bridge rectifier with the transformer together is called a power supply.
There are also diodes that give off light, These are called light emitting diodes (LED). There are different types of these as well. Generally the construction and type of materials used in an LED will determine what color is produced when a current is applied. There are even muti-color LEDs.
At one time the LED was used only as an indicator on a control panel, but it has seen a lot of growth lately. They are now used in TV screens and as a lighting source.
LED as a lighting source is very efficient since almost all of the energy used by an LED is used to produce light.
Capacitance
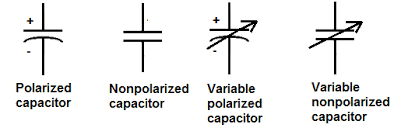
Capacitors and Variable Capacitors
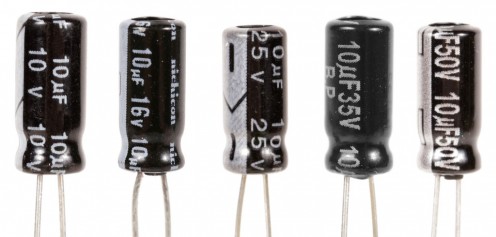
A capacitor is most commonly used as an electrical filter.
It stores a charge for a short amount of time, and then when fully charged it will release the entire charge back into the circuit.
Like other components there are different types of capacitors. Again, to keep things simple, I will not go into discussing the different types.
However, capacitors have a maximum voltage rating. They also have a capacitance rating. The capacitance rating is measured in microfarads. A higher microfarad rating means that the capacitor will hold a bigger charge before discharging.
There are also variable capacitors. These can have their microfarad rating adjusted. The most common use of these is in radio tuners.

Putting Up Some Resistance
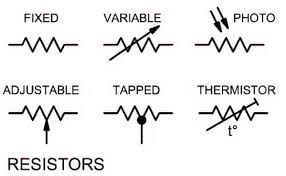
Resistors, Variable Resistors, Potentiometers, and Rheostats
The job of a resistor is to do exactly what the name implies. It resists the flow of electricity to a particular part of the circuit. The most common application for this is to drop voltage in a DC circuit. Since a transformer will not work within a DC circuit, a resistor is used instead.
There are different sizes of resistors measured in watts. The smallest is a 1/8 watt, used in very low current applications. The highest wattage used in most electronics applications is 10 watts. However, there are also giant resistors used in industrial applications.
Another measurement used for a resistor is, obviously, resistance. Measured in ohms.
Larger resistors have the resistance value printed on them. However, smaller ones don't have room for printing, so they use a color code.
There a five stripes on each resistor. The first four indicate the value in ohms, and the fifth indicates the tolerance (%).
Here is how to read the resistor stripes:
..................First/Second/Third Stripe......Fourth Stripe........Fifth Stripe
BLACK.........................0.................................x1......................--
BROWN.......................1............................... x10 ...................1%
RED..............................2..............................x100...................2%
ORANGE......................3............................ x1000...................--
YELLOW.......................4............................x10000..................--
GREEN.........................5...........................x100000.................--
BLUE.............................6..........................x1000000................--
VIOLET..........................7.................................--.......................--
GREY.............................8.................................--.......................--
WHITE...........................9..................................--..................... --
SILVER..........................--..................................--................... 10%
GOLD.............................--..................................--......................5%
Some resistors have a tap off of the middle so that the same fixed resistor can provide two different resistance values. These are called tapped resistors.
In addition to fixed resistors that have a resistance that can not be changed, there are also variable resistors. These can be controlled by moving a contact (called a wiper) along the resistor strip.
This type of resistor is commonly used as a volume control but is used for other applications as well.
Other names for these types of resistors are potentiometer and rheostat. Although there are slight differences between them, for the purpose of this article, they are all variable resistors.
Finally there are thermoresistors and photoresistors.
These two types do the same as a variable resistor, but are controlled by heat and light, respectively.


Summary
That about covers all of the basic components and give you a better understanding of what happens inside some common electronics.
I will go into more detail about each component in future articles.
That is all for this entry.
More electricity and electronics articles from "The Electricity Guy" coming soon.
Look for electronics hobbies articles including Arduino projects as well.