The German Language Series: Part III - "Du" or "Sie", Basic Introductions, and Personal Pronouns

Du oder Sie?
In Germany, a person can address another with either du or Sie. Both words equate to “you” in the English language. Yet, du is used when referring to family, friends, fellow students, or children, while Sie is used in situations where there is not yet a sense of familiarity, such as when speaking to strangers or acquaintances.
With these distinctions in mind, here are some conversational basics. The first instance will depict a formalized meeting between two stranger, while the second scenario will be a conversation between friends.
Formal Conversation Basics
Vocabulary Included:
Herr: Sir
Frau: Ma’am
Guten Tag: Good day
Mein Name ist: My name is…
Ihr: your (formal)
Wie ist Ihr Name? : What is your name?
Woher kommen Sie? Where do you come from
Ich bin: I am
Und: and
Aus: From/ out of
Ich komme aus: I come from/ out of
______________________________________________________________
Remember, all personal pronouns in this conversations referring to “you” are formalized.
Herr H. : Guten Tag! Mein Name ist Norbert Hoffman. Und wie ist Ihr Name?
Frau K. : Hallo! Ich bin Sabrina Kappes.
Herr H. : Woher kommen Sie, Frau Kappes?
Frau K. : Aus München. Und Sie?
Herr H. : Ich komme aus Hamburg.
Informal Conversation Basics
Vocabulary Included:
Grüß dich: Hello to you
Wie geht’s dir? : How’s it going?
Nicht slecht: Not bad
Und du? : And you?
Sehr Gut: Very good
Danke: Thank you
Mir geht’s… : I’m doing… (As in “I’m doing well”)
Bis später dann: Till later, then
Tschüss: Bye
_______________________________________
Anna: Grüß dich. Wie geht’s dir?
Matthias: Nicht slecht, danke. Und du?
Anna: Mir geht’s sehr gut.
Matthias: Bis später dann!
Anna: Ja, tschüss!
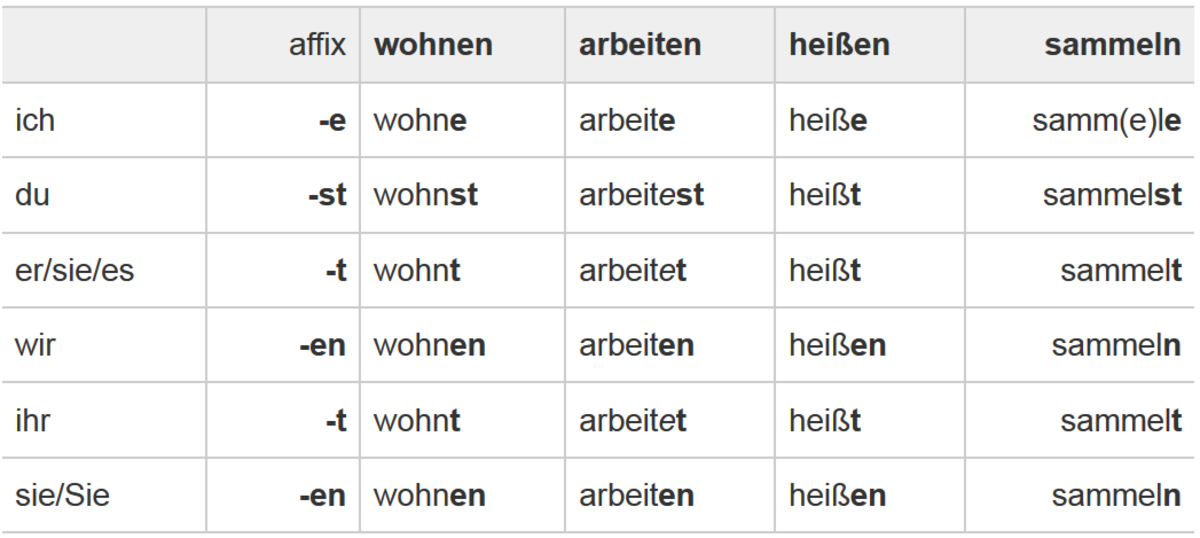
Plural:
First Person
-wir (we)
Second Person
-ihr (you all)
-Sie (formal)
Third Person
-sie (they)
Personal Pronouns
Learning a little grammar with basic phrases might help in understanding.
A fundamental of sentence structure is personal pronouns. Not only will these indicate the proper conjugation of verbs, but will also serve as objects of a sentence.
The following personal pronouns are in the nominative case. The only one that should be capitalized is the formal form of “you”.
Singular:
First Person
-ich (I)
Second Person
-du (you)
-Sie (formal ‘you’)
Third Person
-er (he)
-sie (she)
-es (it)