Out of One Blood

From one blood, God made all nations of men. This is stated in the holy Bible. Acts 17:26. This spiritual and historical book focused on the one physical attribute we all possess. Are we one blood? Medically the composition of blood is basically the same for all people groups. We need blood in order to live regardless of our nationality or culture. This is the only reason why we are 'one blood'. There are however, different blood types or groups for individuals.
Our blood is the life giving liquid that flows through our body. Actually it's our body's largest tissue. It consists of cells (red and white), plasma (our blood's water) and platelets - rounded cell fragments that contain no nucleus. It's purpose is to keep us alive by transporting oxygen, minerals, etc through out our body. Blood also controls body temperature and aids in the releasing of metabolic waste products through the liver. Blood is so important in keeping us alive that it needs to be replaced. Knowing our correct type will aid in this process.
Let's take a look at blood groups and our blood's four (4) main components.
Blood Groups
Blood groups
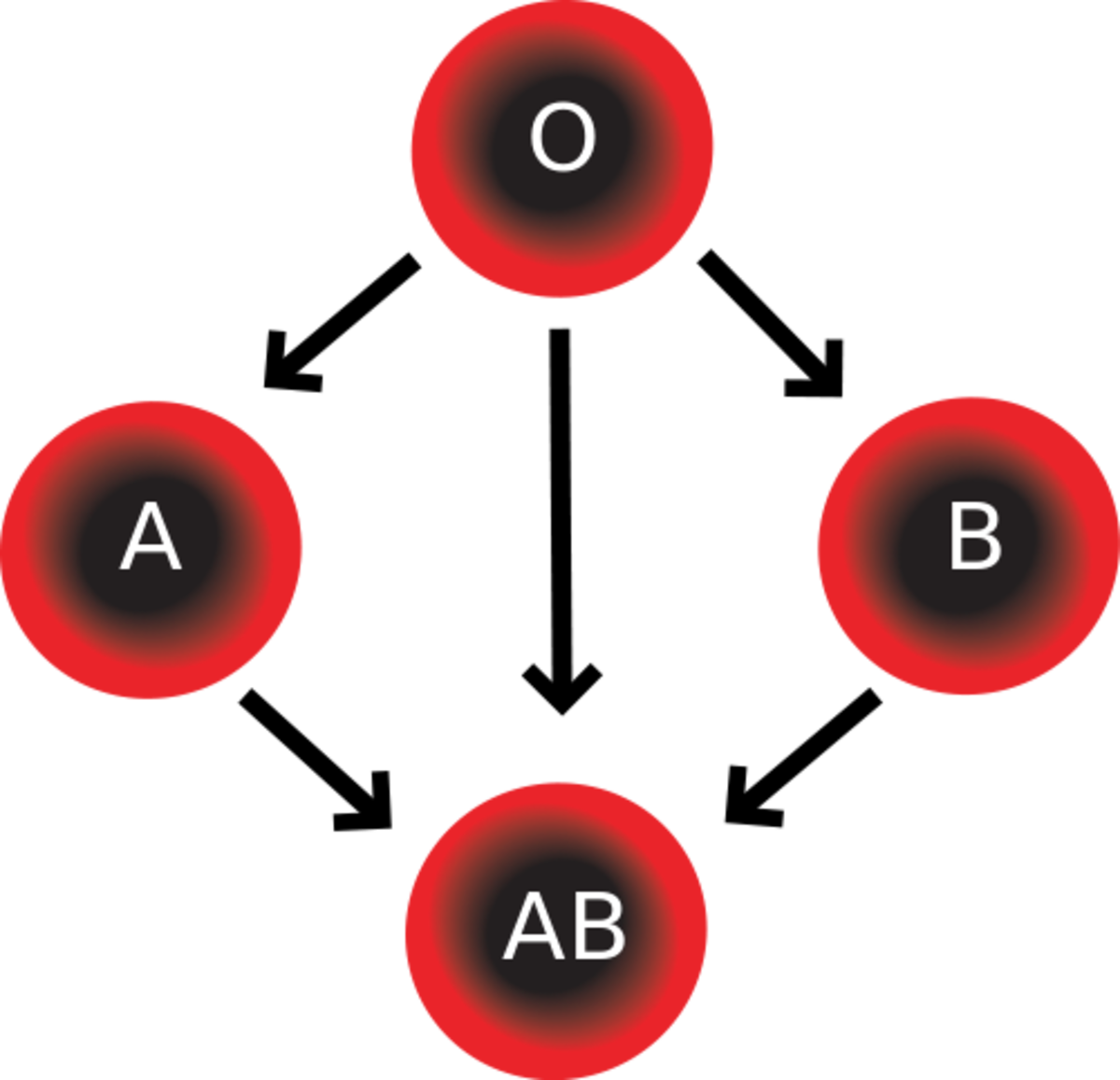
The whole blood in the body of an individual is divided into four (4) basic types or groups. They are:
- A - contains A antigen and B antibody.
- B - contains B antigen and A antibody.
- AB - contains both antigen and neither antibody.
- O - contains neither antigen but both antibody.
These type or group classifications have a lot to do with the protein found in the red blood cells specifically. These proteins bind antibodies or the immunity factor to the cells. Antibodies are responsible for the disease fighting ability in the blood. Viruses and bacteria that appear are attacked when they enter into the bloodstream. The antigen present in the red blood cell is there to protect us from illness. The antibody that is developed in the white blood cell immunizes us from harm caused by viruses and bacteria. It is important to match a persons correct blood type when it comes to giving blood in order to replace missing components. A wrong match may result in death. Correct typing and cross matching is a must when determining blood type. Recent studies have also shown the effect of blood groups on the metabolic rates of individuals.
The importance of the RH factor
There is a protein that is located on the red blood cells of individuals. It is the RH factor. Most of us are RH - (RH negative). This means that we lack the protein. Those of us who have RH is RH + (Positive). When an RH negative mother is pregnant with an Rh positive child, there is a chance that her blood will mix with that of her baby. The antigens from her blood will attack the child causing hemolytic disease in the baby. Hemolytic disease is an anemic reaction in the fetus or newborn. This will ultimately cause death for the baby because his red blood cells aren't able to produce enough antibodies to protect him from this anemia. Bilirubin, the result of this inability of the under developed red cells in bone marrow to correct anemia is not released from the baby's system. Therefore the organs of the developing child will break down. Fluid builds in organs and tissues. The heart will also fail. This will cause a still birth (death).
Blood testing is done during pregnancy to determine whether or not an RH negative mother is carrying an Rh positive child. She is given an injection of RH immune globulin (RHIg) during the 28th week of pregnancy and also 72 hours after giving birth to sensitize her. This injection will help her to carry her newborn to term and guard against her blood attacking her own child. Subsequent pregnancies and births aren't in danger if this problem is taken care of when first discovered. In the event of the unborn child's red blood cells being destroyed by the RH antibodies from the mother, an intrauterine blood transfusion is given to the unborn child to save his or her life.
Blood Groups
Type
| Cell
| Plasma
|
|---|---|---|
Type A
| A antigen
| B antibody
|
Type B
| B antigen
| A antibody
|
Type AB
| Has both A and B antigen
| Doesn't have A or B
|
Type O
| Neither A or B antigen
| Has both A and B
|
Blood's 4 main components.
Within whole blood there are 4 main components:
- Red cells - makes up 40 to 50% of our bodies' blood volume.
- White cells - makes up 1% blood volume in healthy people. Responsible for immunity.
- Platelets - these cell fragments aid in clotting the blood.
- Plasma - the water in the blood that carries red and white cells and also platelets.
Blood Components
Whole blood is given to people today to replace blood loss during surgeries or after accidents. Blood components are given today to recipients with certain illnesses. In the case of cancer a blood transfusion may be given to replace the iron that is lost. Cancer based anemia (iron poor blood) is brought about when good or healthy blood cells as well as bad or unhealthy cells are destroyed by chemotherapy as it fights cancer. This patient needs new red blood cells (a component) in order to supply much needed iron.
Before someone receives a blood transfusion, he is pricked by a needle in the finger or blood is drawn from a vein. This blood is tested for his blood type as well as any positive or negative RH factors. These factors are determined in order to have the right kind of blood transfused. The new blood will be attacked by the person's immune system if the wrong blood type is transfused. When this happens the patient will get sick and possibly die.
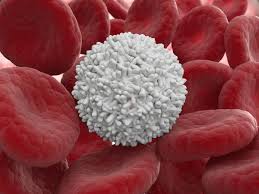
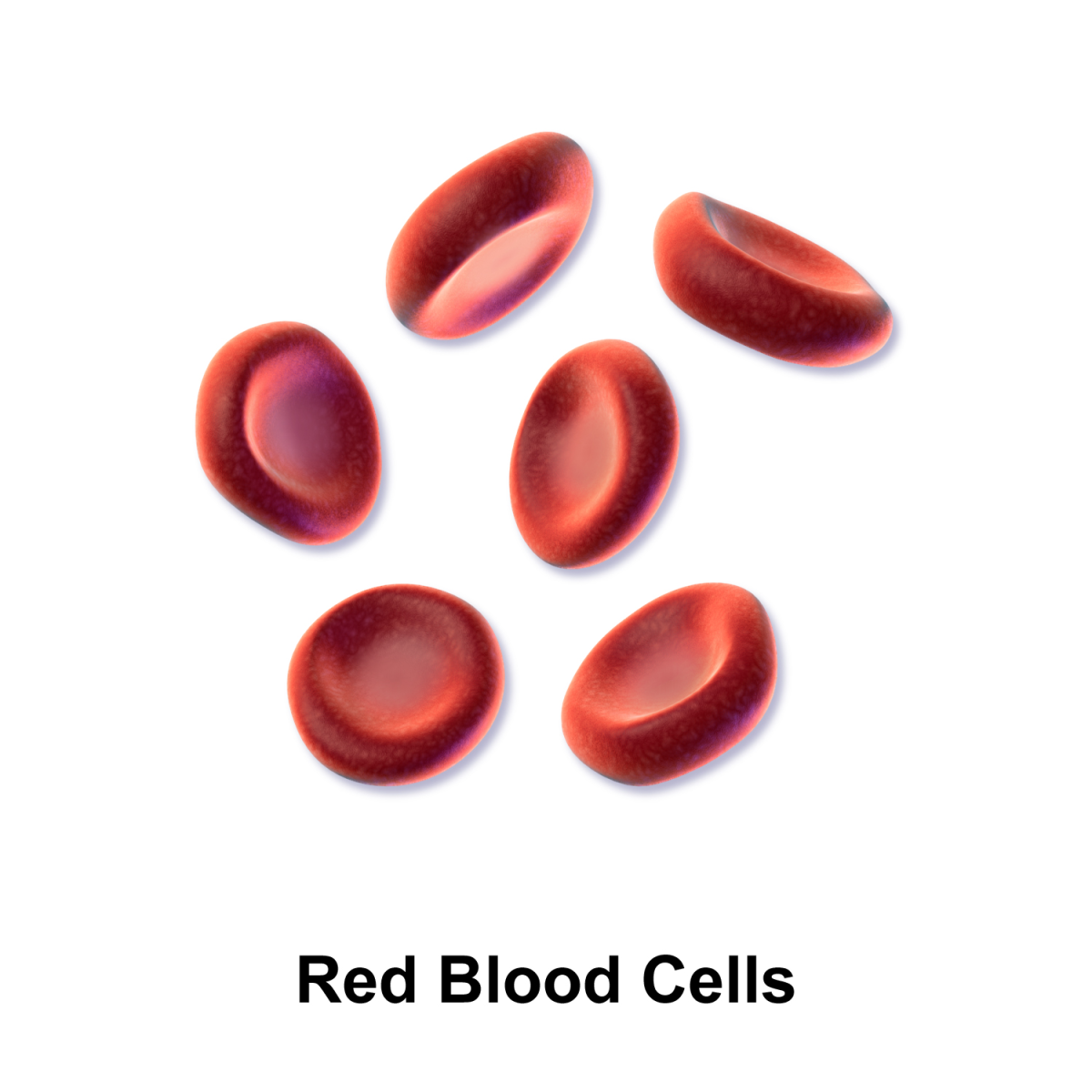
Red Blood Cells
A single drop of blood contains millions of red blood cells. These cells transfer 95% oxygen or carbon dioxide into our lungs and is releases it into the air. Carbon dioxide is then released from the lungs into the air.
White Blood Cells
White blood cells are important in fighting infections in the body. An over abundance of these cells are a symptom of cancer. This type of cancer is called Leukemia. These blood cells do not die, they just continue to develop more and more causing an imbalance in the body thus interfering with the function of the normal cells in the blood. Leukemia also affects the bone marrow where all blood cells are produced.
Platelets
Platelets are the rounded red cells that do not have a neucleus, or central portion within. They are also called cell fragments. These cells are capable of clotting in order to stop blood loss. We would bleed to death if it weren't for these cells.
Plasma
The water contained in our blood that carries nutrients throughout the body and metabolic wastes from our bodies. This water is about 55% of the total blood makeup. The blood cells themselves; red cells, white cells and platelets make up the other 45% of what is known as whole blood.
This is just some of the information available about the blood in our bodies and how it works and what it does.
- Human Blood: Blood Components
- Human Blood: Rh Blood Types
- What are Some Rare Blood Types? (with pictures)
Watch this slide show of rare blood types. There are several rare blood types, including B-, O-, and the rarest blood type, AB-. Most people with rare blood types...
- Hemolytic Disease of the Newborn - Online Medical Encyclopedia - University of Rochester Medical Cen
- Intrauterine fetal blood transfusion for Rh disease
An intrauterine transfusion provides blood to an Rh - positive fetus when fetal red blood cells are being destroyed by Rh antibodies.A blood transfusion is given to replace fetal red blood cells that are being destroyed by the Rh - sensitized mother'