The Unanswered Conundrum: What Are Dark Matter and Dark Energy?

Mankind has never stopped wondering what the world around them is made up of. Their curiosity about their existence, the seen and unseen have tended them to explore the world inside the atoms and the world beyond the earth. The ancient Greeks believed that there were four elements that everything was made up of: earth, water, air, and fire. Soon they perceived that the idea was err. On the hand, everything about us is either matter or energy. Matter means objects which have mass. And energy is used to describe how much potential a physical system has to change. In physics, energy is a property of matter. It can be transferred between objects, and converted in form. Even mass can be transformed into energy, as Einstein reckoned. The universe was previously thought be made up of only baryonic matters. But the concept went awry when, around thirty years ago, astronomers found there had been ever more evidence accumulating that suggested there was something in the universe that we could not see, perhaps some new form of matter.
Dark Matters are Really Dark:
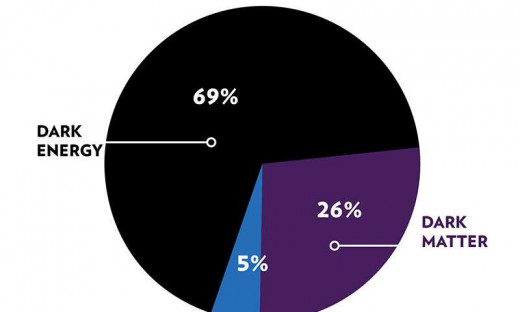
Should we question about the structure of the universe, we can easily get along with the electrons, the protons and the neutrons. These visible and 'normal' particles, which made up the planets, galaxies and the clusters of stars, and called baryonic matter because its mass is combined mass of baryons e.g. electrons, protons and neutrons. To the scientists' surprise, studies concerning the rotation of spiral galaxies in the 1920s showed that the rotation of the stars at the edge is about the same as that of stars close to the galactic centre, defying Newtonian Mechanics which suggests if a galaxy contained only the visible mass we perceive, the rotational speed of the centre would drop off with the distance at the edge. So, the galaxies must have more matter than what we see. Thus the idea of dark matter emerged. Dark matter does not interact with the electromagnetic force. Since it does not absorb, reflect or emit light, it is extremely hard to spot. Researchers have been able to infer the existence of dark matter only from the gravitational effect it seems to have on the visible matter. Some of the dark matter like burnt of stars and dim interstellar reside as a part of the galaxy, and it is referred as normal dark matter. However, according to many calculations, the normal dark matter is a small part of the total dark matter and the rest is called non-baryonic dark matter. While we know that protons and neutrons are baryons, the dark matter cannot consist of them. And the only known member of nonbaryonic matter is the neutrinos. Neutrinos have a very smaller mass than that of protons and neutrons. But the number of neutrinos in the universe is huge thus the mass of them is large enough to make the difference and to account for nonbaryonic dark matter. Dark matter candidates arise frequently in theories that suggest physics beyond the Standard Model, such as supersymmetry and extra dimensions. One theory suggests the existence of a "Hidden Valley", a parallel world made of dark matter. The dark matter consists of 27% of the total matter of the universe while the visible baryonic matter contributes only 5%. So, its gravitational effects are necessary to explain the rotation of galaxies, the motions of clusters, and the largest scale-structure in the entire Universe. But we know very little about this mysterious object of the universe.
The Universe is Expanding:
Until 1931, Albert Einstein believed the universe to be static. But American physicist Edwin Hubble proved Einstein's notion of stationary universe wrong by determining that the universe is expanding, which is a direct outcome of his studies related to the distance supernovae. But dramatically enough, when two independent teams of astrophysicists in 1990 observed the distant supernova to deduce the expansion rate of the universe, they found, to their surprise, the rate is 'increasing' rather than decreasing, meaning the expansion of the universe wasn't slowing down, it was speeding up! Therefore, they concluded that something must be counteracting gravity and they called it Dark energy. The dark energy makes up nearly three-fourths of the universe, yet the scientists know very little about it. Both dark matter and dark energy are related to the gravitational effect in the large scale of the universe and both are little understood.
A bit about Gravity
According to Newton's model of gravity, Gravity is the force that attracts two bodies toward each other, the force that causes apples to fall toward the ground and the moon to orbit the earth. The more massive an object is, the stronger its gravitational pull. And the shorter the distance between the objects, the larger the magnitude of force (e.g. The pull). Newton uncovered the science behind the motion of a body falling freely at earth and the motion of the moon. Newton's model successfully define different phenomena of our classical world, for instants a body at free-fall and the gravitational pull between two balls kept at a distance. But Newton's model fails to explain the orbit of Mercury.
Every planet orbits the Sun in an ellipse, as Kepler noticed a century before Newton. Surprisingly, Mercury and Mars are noticeably more elliptical, with their closest approach to the Sun differing significantly from their greatest distance. It is of many aspects where newton's model breaks down.
To resolve the complication arose in Newton's model, Albert Einstein came up with his model of gravity. In newton's world, one-dimensional time and three-dimensional space are two independent quantities. But Einstein's world, these two entities are entangled and, together, create space-time. He showed that, in his theory of general relativity, gravity is not a force, instead is due to the curvature of space-time caused by the uneven disturbance of mass, be it a planet or star. According to Einstein's general relativity (GR), the gravitational pull has a direct effect on time. That means, a clock on the surface of the earth ticks slower than a clock situated on the top of a building, at the same time a clock on a satellite ticks a few dozen microseconds faster than that clock on Earth.
Although currently available theories have been enormously successful in describing in classical scale, we still do not fully understand gravity on either the cosmological scale or quantum scale. Hubble's discoveries suggested that the universe must have begun with a big bang, which was later proved by Penrose and Hawkings. However, at the singularity, one could no longer ignore the small scale effects of quantum mechanics. To understand the universe from the theory of extremely vast (GR) to the theory of extremely small (QM), the physicists are seeking for a single quantum theory of gravity. Quantum gravity could uncover the mystery of the universe.
The Dark Matter's Showtime:
Yet, Einstein's model of gravity fits precisely to describe the motion of massive objects like planetary movement and motion of galaxies and the clusters of stars. In 1917, Einstein represented a relativistic model of the universe called stationary universe and it was a pure blooper. Until 1931, he believed the universe to be homogenous, static, spatially curved. However, this interpretation had one major problem: If gravitation was the only active force, his universe would collapse – an issue Einstein addressed by introducing the cosmological constant. In his theory of general relativity, Einstein included a cosmological constant to account for the stationary universe scientists thought existed. The constant suggested the vacuum energy density, which is dynamic, meaning it is changing, unlike other constants. It provided a way of balancing the gravitational contraction caused by matter. He was the first to understand that space was not simply empty, space can have its energy. He also understood that more space could emerge into existence. But American physicist Edwin Hubble helped astronomers see that we live in an expanding universe, one in which every galaxy is moving away from every other. Astronomers observed that the light of distant galaxies was shifted toward the red end of the light spectrum. This redshift was interpreted as a sign that the galaxies are moving away from us. This suggested that the universe was expanding and Einstein abandoned his model of a static universe. Dark energy can be interpreted by the cosmological constant but only if it doesn't just balance gravity to keep a static universe but has negative pressure to cause the expansion to accelerate up.

Most physicists believe that dark matter consists of new, undiscovered subatomic particles, but some believe that it could be related to an unknown fundamental force. Some theorize that dark energy is an intrinsic property of space-time rather than a usual matter that is the source of space-time curvature. Universe is filled with a changing energy field, known as "quintessence." Quintessence is a scalar field, it differs from the cosmological constant explanation of dark since it is dynamic and changes over time, unlike other constants that do not change. Some physicists speculate that a form of dark energy called quintessence could be a fifth force.
The properties of the unknown quantity are still up for grabs. The scientists have used their knowledge of big bang to the modern-day large scale structure of galaxies and predicted that Dark matter and dark energy may rip apart everything in the universe billions year of years from now. We still are unsure how and what are the factors that govern the universe precisely. Someday CERN’s Large Hadron Collider will probably uncover the truth! Uncertainty is the beauty of science and the universe.
© 2020 Yusrat Sadia Nailat