What Is Demand-Side Economics?
The demand side economics may be also known as the "Keynesian Economics", named after John Maynard Keynes and his ideas to stimulate growth after the great depression.
The demand side economics has its bases on the aggregate demand, it is believed that in order to stimulate the economy it is advantageous to stimulate the aggregate demand. The idea that the free market will find the equilibrium is not accepted as the main reason for a balanced economy.
The idea behind the Keynesian Economics is that the Government should be responsible to stimulate the aggregate demand in order to achieve full employment and price stabilization, normally at a cost of a deficit in the government budget.
In this hub I will try to explain the concepts behind the demand-side economics. Explaining how economic growth can be achieved according to the demand-side theories, what is the aggregate demand and why is it so important, how taxes can influence the future of the economy and what is the relation between the European crisis and the demand-side economics.
Formula for the GDP
GDP = Private Consumption (C) + Gross Investment (I) + Government Spending (G) + (Exports (X) - Imports (M))
Economic growth can be achieved by increasing C,I,G,X or/and decreasing M.
Economic Growth
It is not clear and unanimous how a country can achieve economic growth, or at least which measures can guarantee that in the next year the economy will grow.
In order to have economic growth, the country has to increase the quantity of goods and services sold, according to the demand-side economics, if they are not sold, there is no economic growth since there is no money flowing. In order to have the products and services sold there are three big clients:
- Private Consumption, people and companies buying home produced goods and services.
- Exports, companies and people from other countries buying the tradable goods.
- Government intervention, the government can invest in the economy, but it may have costs on the long run.
For some countries there is also the solution of tourism or foreign investments, having money flowing to the country from the foreign tourists or foreign investors, but that may not be an easy measure to guarantee the desired economic growth.
Government influencing Economic Growth
According to Keynes the government should help the economy during times of recession, if private companies are not investing, then the Government should take place in the economy with interventionist policies, forgetting about the Laissez-Faire, that should be adopted when the economy is well.
The GDP is influenced directly by Government Spending (G), if G increases, so does the GDP and economic growth can be achieved. However the government should be careful because in the long run the government cannot accumulate deficits.

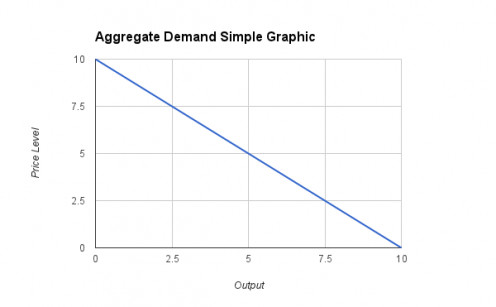
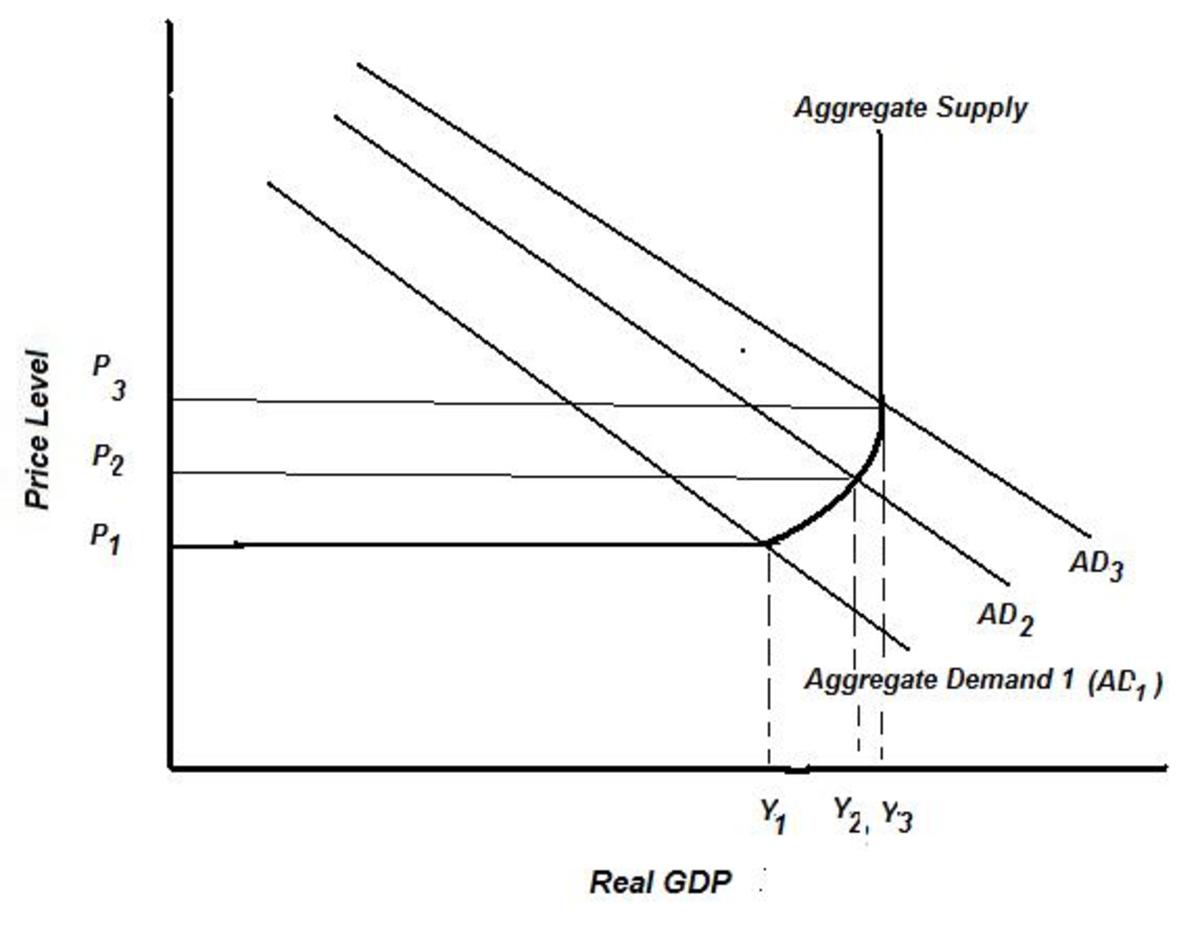
Aggregate Demand
The definition for aggregate demand (AD) is the total demand for final goods and services in the economy at a given time and price.
Like the GDP, there is a simple formula to know the AD:
- AD = Consumption + Investment + Government Spending + (Exports - Imports)
- AD = C + I + G + (X-M)
As you can see in the graphic, if the price level is 10, there is no aggregate demand, there is no interest in buying anything, but if the price level is around 0, everything can be sold. In order to find an equilibrium, it is needed the supply-side.
Similarities between AD and GDP
AD = C + I + G + (X-M)
GDP = C + I + G + (X-M)
According the Demand-side economics, the GDP is defined by the Aggregate Demand, that is why GDP cane be increased by influencing demand.
The difference is the way they quantified. GDP is a number in a given time at a price level. The aggregate demand can be showed in a graphic as a curve with different price levels for different outputs.


Taxes over Rich
According to the demand-side policies, the riches should be taxed, and the government should redistribute the money to increase the aggregate demand.
This measure would influence the flow of money, taking from the rich and giving to the poor.
However, if the economy is "over-heated" with great inflation, then the rich should benefit from a tax cut, in order to decrease the velocity of money in the economy.
This would lead to less money in circulation, lowering the inflation and having the economy at a sustainable growth rate.
How a tax break can affect the Government Revenue.
- The Laffer Curve
The best way to understand what happens to government revenues when there are changes in taxes is probably by understanding the Laffer Curve.
Can a tax break guarantee economic growth?
According the AD formula, the short term effect of a tax break is an increase in C. However G, X & M.
- After a tax break and in order to have a budget balance, G has to be decreased.
- An increase in consumption can lead to an increase in foreign produced good, increasing M, or a increase in home produced goods, decreasing the exports, I.
So as a short term policy, a tax break can positively affect economic growth, but in the long run it is not assured that the economy will get back on track.
Velocity of the money by the Poor and Rich
According to Keynes, the money in the hands of the poor has a greater velocity than in the hands of the rich. That happens because the poor needs to spend money to buy goods, so they normally spend as much as they have.
The rich can maintain their wealth and are not always spending their money in the economy. Since they have everything they want, they will only spend some of their money, leaving part of the money out of circulation, out of the economy.

Visual explanation of the European Crisis
The European Crisis
Most governments in Europe are now facing a difficult economic situation, mostly because of debt accumulated through the years.
Before 2007 some countries were having good levels of economic growth but with deficits, so when the debt crisis appeared, it was difficult to have a budget surplus and facing economic struggle.
Now that, according to the Keynesian Economics, the government should invest to support the aggregate demand, the governments of these countries do not have enough money for everything and they are facing the problem of over-debt.
Another problem is that other governments of the European Union, tired of the money being spent in ridiculous ways now want severe measures of austerity, causing the aggregate demand to fall.
According to the formula above, if there is a fall in G, and in C (due to higher taxes), the solution is an increase in I and/or X, but investments and exports do not depend directly on the government, so the direct influence of the government is causing a fall in the Aggregate Demand and in the GDP.
The solution to the European crisis according to the Demand-side Economics
According to the theories of Keynes, the solution to have economic growth was to stimulate the economy,
- Reduce the interest rate, this way people and companies will be less interest in savings, and they will be more interested in spending the money, increasing demand.
- Government investment in infrastructure, increasing government spending and creating new jobs (normally jobs for the poorest). More jobs mean more consumption, and with such investments, companies will also be interest to invest.

Want to know who was John Maynard Keynes?
- John Maynard Keynes
Today, June the 5th, in 1883, John Maynard Keynes is born in Sussex. He grows to be a professorial man with a round face, thin hair, a mouth as big as Carly Simon's, eclectic interests, and a towering reputation as a political economist.
More about Keynes
How debt can help an economy
- The Debt Benefits
There are many points of view when you want more information about the benefits of debt. There may be debt benefits for Government, investors, firms and others. Debt can be good to the Economy.