What are the Signs and Symptoms of Leukemia (AML)?
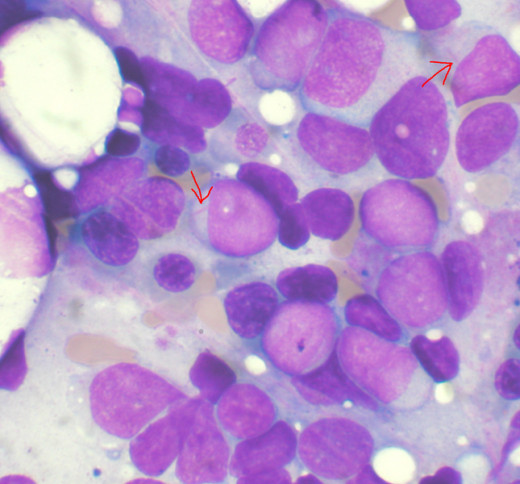
Bone Marrow Aspirate showing Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Several blasts have Auer rods.
What is Leukemia?
Leukemia is an uncontrollable growth of developing blood cells (blast cells). As they undergo a cancerous change they don’t grow into mature blood cells and are not capable of performing the functions of the mature blood cells.
Based on the origin and the nature, Leukemia can be grouped as
- Acute Myeloid Leukemia
- Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
- Chronic Myeloid Leukemia and
- Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia
In this hub we will see in detail about Acute Myeloid Leukemia.
Leukemias (AML, CML vs. ALL, CLL)
What is Acute Myeloid Leukemia?
Our blood cells are formed in the bone marrow. There are two main types of stem cell lines in the bone marrow; myeloid stem cell line and lymphoid stem cell Line. Red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets originate in the Myeloid Stem Cell Line and immune cells like B-cells and T –cells originate in the lymphoid stem cell line. Acute Myeloid Leukemia affects the growth of blast cells in myeloid stem line. These patients bone marrow will be filled with immature myeloid blast cells which in turn results in less number of mature red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets. Thus people with Acute Myeloid Leukemia become susceptible to anemia, recurrent infections, easy bruising and fatigability.
As you know red blood cells contain hemoglobin which is the oxygen carrying compound in the blood. Different tissues of our body get oxygen with the help of hemoglobin. So anemia which is a reduction in hemoglobin makes the person fatigued.
White blood cells are essential for our body’s immunity and a reduction in the number of white blood cells make the person susceptible to infections.
Likewise platelets play an important role in the formation of blood clots and the prevention of continuous bleeding if the body is injured. A reduction in the number of platelets will make the person susceptible to easy bruisability and bleeding tendencies.
As the disease advances there will be accumulation of immature blast cells in organs like spleen and liver.
What are the Risk Factors for Acute Myeloid Leukemia?
The exact cause for Acute Myeloid Leukemia is not known. The risk factors can be
- Exposure to ionizing radiation: Large doses of ionizing radiation can put people at risk for developing Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Those who have received large doses of ionizing radiation as a part of their treatment (radiation therapy) for another cancer come under this category.
- Exposure to certain chemicals: benzene exposure over a period of time may put people at risk for developing Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Certain chemotherapeutic drugs are also known to cause Acute Myeloid Leukemia.
- Smoking increases the chance of development of Acute Myeloid Leukemia
- Some genetic factors are also believed to play a role in the development of Acute Myeloid Leukemia
MegaFood Blood Builder 90 Tablets
What are the Signs and Symptoms of Acute Myeloid Leukemia?
As discussed earlier the bone marrow of a patient with Acute Myeloid Leukemia is filled with immature blood cells. As a result the number of all types of mature blood cells will be low.
- Anemia: It results from the decrease in number of red blood cells. Patients will have fatigue (tiredness) and weakness. They may feel giddy especially when they get up from sitting or lying down positions. Patients may also feel breathless with increased activity.
- Increased Frequency of Infections: This is because of the reduction in number of white blood cells. It can be skin infections, respiratory infections or urinary tract infections.
- Easy bruisability: This is because of the low platelet count. There can be nose bleeds, excessive bleeding during menstruation prolonged bleeding from cuts and wounds.
What are the Treatment Options available for Acute Myeloid Leukemia?
Chemotherapy: is the main treatment for treating Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Chemotherapy uses a combination of drugs given in cycles with rest periods in between. Acute Myeloid Leukemia is rapidly progressive and hence the treatment should be started as early as possible. Chemotherapeutic drugs target the rapidly multiplying cancer cells. They can also cause damage to the rapidly multiplying other cells of the body like bone marrow, gastrointestinal mucosa and hair follicles and may result in various side effects.
Chemotherapy for Acute Myeloid Leukemia is divided into
- Induction therapy: which aim to reduce the proportion of immature blast cells in the bone marrow to less than 5 percent, bring about absence of blast cells from the circulation and to bring back the blood cell counts to normal
- Consolidation therapy: aimed at maintaining the remission phase and prevention of relapse (reappearance of leukemia).
Summary
Acute Myeloid Leukemia is a type of blood cancer for which the most important treatment option is chemotherapy. The prognosis or the course of the disease depends on various factors like age of the patient, previous treatment for cancers and the genetic predisposition of the patient.