Why you look the way you do? Why you do the things you do?
Human Body
The Human Body
Why we look the way we do? Why we do the things we do like walking, running, feeling, seeing, hearing and a lot more intrigue us. The human body is a machine that does many things. To do these things, it needs many parts. All these parts together are what we are.
Human Skeleton
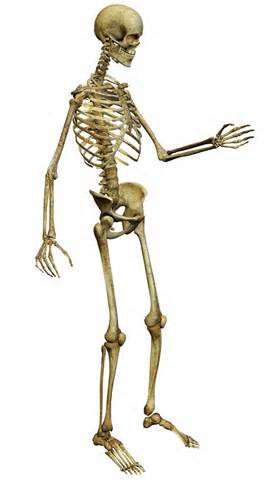
The Skeleton
Our body is composed of more than 200 bones and these make up our skeleton. The skeleton performs several functions: protection, support and keep the shapes of the body. The skull is the one protecting our brain, while the ribs protect the heart and the lungs. The skeleton also helps the body in keeping its shape and supports the soft parts of the body like the skin.
Muscles and Joints

Movements, Muscles and Bones
If your going to have a closer look at your body, you would notice that some part is moving all the time. Why? The muscles are the one making these movements possible. Now what makes your eyes blink? What about your tongue? The muscles are the one making your eyes blink and move the tongue. Muscles allow you to walk, jump, run, lift and throw. During sleep, muscles are still working through helping you to breathe.
Bones in your body form joints to allow you to move around. These are in found in your arms and legs.
What about your hands and feet?
To be able to carry out various tasks like writing, drawing and even lifting heavy objects you use your hands. On the other hand your feet help you walk, jump, stand and run. Why? These are all because of the bones, joints and muscles.
The Heart
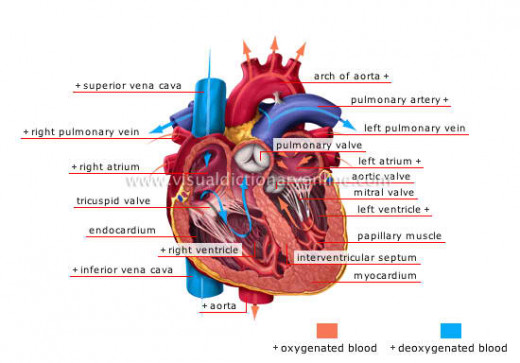
The Heart: The Pumping Organ
It is the pumping organ of the circulatory system. It is a hallow large muscle about the size of one’s fist. The heart lies under the breastbone in the center of the chest cavity. It is completely enclosed by a thin tough membrane called pericardium, which protects the heart from rubbing against the lungs and wall of the chest. The inside of pericardium acts as a smooth lining that secretes a slippery liquid. The heart beats smoothly and with little friction and against the moistened lining of the pericardium. An adult’s heart is about 3 inches (13 cm.) long, 3 ½ inches (9 cm.) wide and 2 ½ inches (6.4 cm.) thick. The septum divides the heart into right and left portions. The right portion of the heart receives and distributes the non-oxygenated blood, while the left portion is concerned with the reception and distribution of arterial or oxygenated blood. The heart has two chambers, one above the other and the other on each side of the septum. The upper chamber on each side is called an atrium. The thin – walled atria collect the blood flowing from the heart into the veins. Below each atrium is another chamber called the ventricles. The two ventricles pump the blood into the arteries. The walls of the ventricles are made of thick strong muscles. The right ventricle pumps the right blood only to the lungs, but the left ventricle pumps blood into the entire body. The left ventricle has walls three times as thick strong muscles.
Structures of the Respiratory System
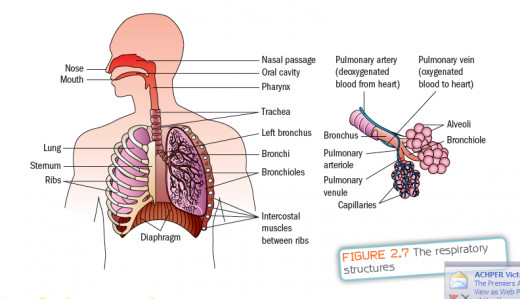
Breathing
For you to be able to live, your body needs a constant supply of oxygen and nutrients. The oxygenation of blood in the lungs, the use of oxygen and production of carbon dioxide by the tissues and the removal of carbon dioxide from the blood in the lungs is called respiration.
Structures of the Respiratory System
NoseNose is the only externally visible part of the respiratory system. The air enters the nose through the external nares or nostrils. The interior of the nose consists of the nasal cavity is divided by a midline called nasal septum. The mucus lining the nasal cavity rests on blood-rich connective tissue that is well supplied with mucous glands. Dust and other foreign particles are filtered from the air by the hairs at the entrance of the channels and by cilia along the epithelial lining.
Pharynx
From the nasal cavities, air moves into the throat or pharynx, which is the entrance to both the respiratory tract and the digestive tract. The throat cavity is connected with the larynx leading to the lungs and with the esophagus (leading to the stomach).
Larynx (voice box)
The larynx consists of muscles and cartilages bound in elastic connective tissue. Part of the cartilage is attached to and supports the epiglottis a flap like structure that points upward and allows air to enter the larynx during breathing. The epiglottis sometimes referred to as the "guardian of the airways" protects the superior opening of the larynx. When food is swallowed, the epiglottis helps prevent the food from going down the wrong tube.
The larynx contains two true vocal cords used to produce the sounds of speech. This ability of the vocal folds to vibrate allows us to speak. The slit like passageway between the vocal folds is called glottis. Air forced through the glottis gives rise to sound waves. The stronger the air pressure on the vocal cords, the louder the sound produced. The greater muscle tensions on the cords, the higher the sound.
Trachea or windpipe:
Air from the larynx moves into the windpipe or trachea. It is 4 inches (10-12 cm) long. The trachea branches into two main airways called bronchi. After the main bronchi enter the lungs, they divide into two branches, and then the branches divide again many more times down to the smallest airways, the bronchioles.
Lung
Lung is an organ of external respiration (breathing) present in human beings. It is vital in maintaining life and acts as an exchange point where oxygen from the air is substituted for carbon dioxide in the blood that flows through the lung. The blood carries the oxygen to all parts of body and brings carbon dioxide back to the lungs. Lungs are large pyramid shaped organs weighing about 21/2 lbs. They are made up of masses of spongy tissue suspended in the chest cavity. They extend upward behind the collarbone, and rest on the powerful muscular diaphragm that separates the chest and abdominal cavities. The esophagus, the heart and the large blood vessels lie in the middle area, the mediastinum of the chest, between the two lungs. Each lung is divided into lobes: the left lung has two lobes and the right lung has three.
Amazing Senses
You are able to hear, feel, see, taste and smell things around you because of your amazing senses. With the touch sensors all over your skin you are able to identify what is cold, rough or even smooth.
To be able to learn about the world you are into you use your eyes. The pupil is the small black hole in the middle of your eye where light enters. This light travels to a special part called retina. from here, signals are sent to your brain. Your brain do the sorting of signals into the pictures that you are to see.
Sounds as invisible waves travel your ears through the eardrum and to your brain.
Your tongue has taste sensors too for you to be able to taste food and drink.
Digestive System
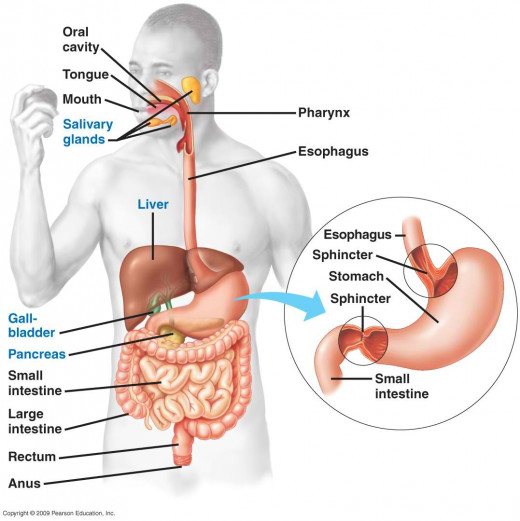
Digestive System
Digestion is the process by which food is broken down into smaller particles or molecules for use in the human body. This breakdown makes it possible for the smaller digestive particles to pass through the intestinal wall into the bloodstream. The simple digested food particles in the bloodstream are distributed to nourish all parts of the body. Digestion takes place in almost all parts of the alimentary canal where the food mixes with substances called enzymes, which speed up chemical reactions of the food. Fats, proteins and carbohydrates in foods are made up of very complex molecules and must be digested or broken down. When digestion is completed, starches and complex sugars are broken down into simple sugars, fats are digested into fatty acids and glycerin, and proteins are digested into amino acids. Simple sugars, fatty acids, glycerin and amino acids are digested foods, which can be absorbed into the blood stream.
You need to take in food for you to grow and be provided with energy. To stay healthy your body needs variety of food, exercises and sleep.
Miracles of Life
There are still so many amazing things we can say about our human body. .. from the union of the egg and sperm cell to zygote, fetus and the newborn baby. Its is now for you to answer:
Why you look the way you do? Why you do the things you do?
And I hope as you finished reading my hub , you would be enlightened about your body, value and respect not only your own body but other’s too.