Theory of Set; A Brief Note (Elementary Level)

Introduction
The theory of sets was developed by a German mathematician Georg Cantor. The set theory plays a vital role in today’s many branches of mathematics, economics etc. In theory sets are used to define the concept of relations and functions. This hub briefly explains the set theory and related concepts.
What is a Set ?
By definition a set is one which contains many objects. These objects are called ‘elements of a set’.
For example
1) Even number 0 to 10. That is, 2,4,6,8
2) People of a country or a state
How to Represent a Set?
Suppose a set with the elements of natural numbers 1 to 10. The set can be represented with in braces { }. And further we can give a name for the set, suppose ‘N’. So the set can be represented as given below.
N = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10}
Here ‘N’ is the set and 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10 are the elements which can be denoted by E.
Some Concepts of Set
Following are the some concepts related to the set theory.
Two methods of Representing a Set
Generally there are two methods to present a set.
1- Roster or tabular method
I the above example the set ‘N’ represented as tabular method. That is, N = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10}
2- Set builder method
It is another method of representing a set. By this method the above set can be represented as given below.
N = {x/ x natural numbers between 1 to 10}
Finite and Infinite Sets
If the elements of a set are finite, it is a finite set.
For example – N= {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10}
Infinite set is one the elements are infinite.
For Example – N= {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7,….. }
Equal Sets
Suppose consider two sets below,
A = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6} and
B = {6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1}
Here the elements of set A are the same elements of set B. So, it will equal, it is called equal sets where set A = set B.
Null Set
Null set or empty set is a set, in which there are no any elements. It can be represented as { }. {0} is not a null set.
Singleton Set
If a set contain only a single element, it is called singleton set.
For example = { }, {0}, {17}
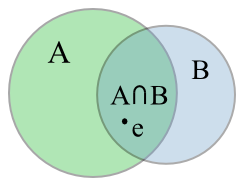
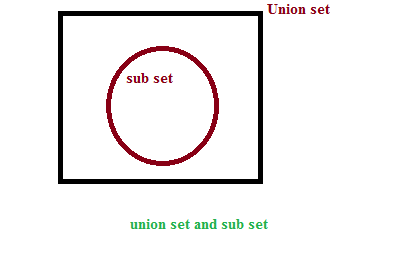
Union Set and Sub Set
Suppose consider set A= {a, b, c, d, e}, B = {a, d, e} and C= {b, c, e}.
Here A is the union set (u) and B and C are the sub sets. Because, few elements in set ‘A’ are included in the elements of set B and set C.
Union set and Subset can be represented in Venn diagram as showing below.
Power Set
Power set of a set is the all possible subset of that set.
For example; A= {1, 2, 3}
Subsets (P) = {},{1},2},{3},{1,2},{1,3}{2,3},{1,2,3}
Here the number of elements of set A are 3 and its subsets are 8. Note that {} will be a subset of all sets. The number of subsets (power set) of a set can be calculated by raising the number of elements to 2.
For example, A= {a, b, c, d}
Since in the set A contain 4 elements total subsets (power set) will be 2*2*2*2 = 16 or 2^4 = 16.
Two Major Set Operations
Mainly, there are two operations can be seen in set theory. They are Union operation and intersection operation.
I) Union Operation
To find union of two sets, we have to join all the elements of two sets. But the elements never repeat.
For example;
A= {a, b, c, d, e, f}
B= {a, c, f, h, j, m}
Here Union of the set A and set B
Becomes AUB = {A, B, C, D, E, F, H, J, M}
II) Intersection Operation
To find intersection of two sets we have to take common elements in both sets. It is denoted by inverse ‘U’
For example;
A = {a, b, c, d, e, f} and B = {a, c, e, f}
Then A intersection B = {a, c, e, f}
Compliment of a Set
Compliment of a set contain elements outside the set or in universal set. It is denoted by A.
Suppose consider U= {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10}
And A = {1, 3, 7, 9, 10}
Then A= {2, 4, 5, 6, 8}
Differences of Two Sets
It is the difference between two sets.
For example;
A = {1, 3, 5, 7, 9} and B = {2, 3, 6, 7, 9}
A - B = {1, 5}
B - A = {2, 6}