Human Senses

How many do we have?
Most people focus on "the 5 senses" whenever the human senses are discussed. The truth is that we have quite a few more than 5 senses. The five senses sight, touch, taste, hearing, and smell are just the most recognizable and easily explained senses. Humans have quite a bit more than those 5. Some are obvious once you think about it, like temperature. Others are a bit less well known, like vestibular sense.
New senses are still being discovered by scientists from time to time, and it is a very interesting field of study.
Lets learn more about the less well known human senses.
Temperature
Hot/Cold
Your sense of temperature is very important. If you did not have a sense of hot or cold, you might go out on a cold day and suffer from hypothermia. You would have no way to sense that it is simply too cold to be out without proper attire, and could eventually die.
Conversely, no sense of heat would be a problem as well. You might go outside in sweltering heat and become hyperthermic, which can also kill you.
The senses of hot and cold are actually two separate senses, and have separate receptors for each.
All humans are different, and this helps explain why if two people are in the same room, one person can feel hot, while the other can feel warm.
Interestingly, scientists have found cold sensing receptors in the spine, which can explain how a "shiver" can go through your spine.
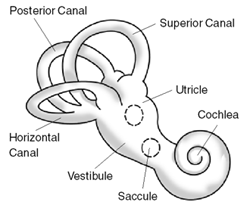
Vestibular Sense
The sense of where you are, movement, and head orientation. This sense is incredibly important for balance. Think of times when you have had an ear infection. If you became dizzy, this may have been due to problems with your vestibular sense.
Sometimes, people suffer from vertigo. This can be due to calculi (very small stones) in your ear wreaking havoc with your vestibular sense.
My wife has a particular rough time with her vestibular sense, and can easily become unbalanced and fall.
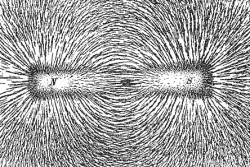
Magnetoception
Magnetoception has to do with detecting magnetic fields, especially to orient yourself and direction.
While not nearly as sensitive to magnetic fields as Homing Pigeons, humans have been shown to have a response to magnetism. An early study showed that after volunteers were disoriented, and then asked what direction they were facing, they were more likely to have an incorrect response if a magnet was near their head.
Further studies how explicitly shown that magnets cause a response visible on an EEG.
Proprioception
This is a sense that helps you determine where your bodyparts are. This is also one of the most easily fooled senses.
I once saw a police officer doing a sobriety check. A motorcyclist had been involved in a crash and was suspected to be intoxicated. One of the officer's instructions to the motorcyclist was to tilt his head back and touch his nose alternatively with each hand. He had quite a bit of trouble standing up, and wobbled just with his head back, never mind being able to touch his nose successfully.
Alcohol is well known to effect the central nervous system, and therefore proprioception.
Another interesting trick is called the Pinocchio Illusion which involves touching your nose with your finger, closing your eyes, and having someone stimulate your biceps. It makes you feel that your nose is growing!

Synesthesia
Synesthesia is an interesting phenomenon that is kind of an association of two senses. In the example shown, the person with synesthesia is perceiving letters and associating colors with them.
Other combinations of synesthesia are possible. A person might associate the color black with a cough, for example. There are many examples and each person experiencing synesthesia is different.
There are more...
Science is still discovering more senses. Some other well known ones are sense of pressure, pain, time, stretch receptors, chemoreceptors, and many more!