The Negative Effects of Fish Consumption: Why Fish Matter

What is a Pescatarian?
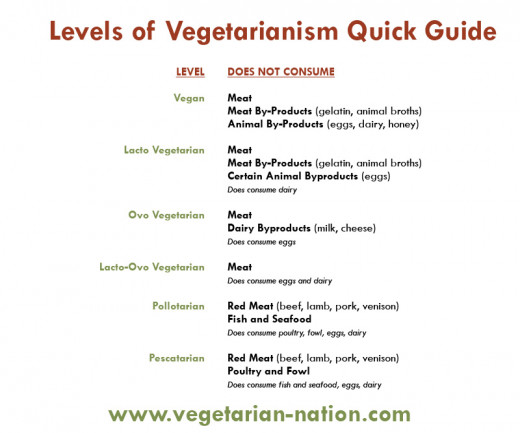
A person’s stance on the consumption of meat is an extremely individualized ideal; therefore, various types of meat limiting diets have arisen in society. Vegans, lacto-ovo vegetarians and pescatarians comprise the majority of the sub sets of animal product limiters. Pescatarians consume fish; however, this diet avoids all other animal flesh such as cattle. The question arises as to why there exists such a diet, more specifically, why a practicing pescatarian avoiding meat for ethical reasons would support the consumption of fish.
The basis of pescatarianism has likely emerged due to a lack of information, the incomprehensibility of the lives of fish and the absence of stringent policy making on an international scale. With recent research on sustainability, overfishing, health concerns and the moral issues involved in aquaculture and the commercial fishing industry, there is little argument to support the pescatarian diet; therefore, any true vegetarian should morally avoid the consumption of fish in its entirety. At the same time, society as a whole should limit their consumption of fish.
Vegetarians are the most commonly known animal product limiters – avoiding fish, meat and dairy products. To answer the question behind the rationale of a pescatarian diet, one must look to the source – practicing animal product limiters. In a study comparing varying types of these limiters, Haverstock and Forgays determined that out of a group of 247 animal product limiters, a higher percentage of vegetarians were concerned with animal rights than that of a pescatarian, while the pescatarians were more concerned with health, environmental and political concerns than the vegetarians. The motives supporting pescatarianism are numerous and scattered – health, environmental and moral – these are the same arguments, however, against the lifestyle.

Health Concerns of Fish Consumption
A well-known reason to avoid meat, yet consume fish, lies in the healthy nutrients found in marine animals. High amounts of protein, vitamin D, selenium, iodine and omega 3 fatty acids are found in fish and have been accepted as common knowledge as support for fish consumption. The omega 3 fatty acid remains vital in metabolism and contains a necessary amino acid that the human body does not naturally contain.
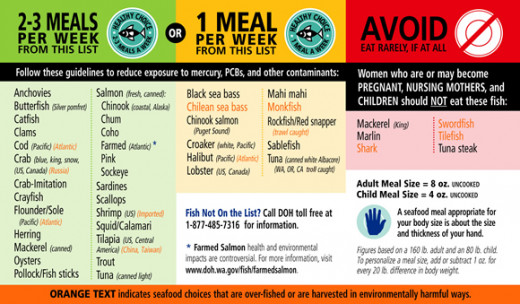
At the same time, pescatarians avoid meat as a result of the potentially harmful risks of the high amounts of saturated fat found in cattle flesh. Pollution, however, can have an adverse effect on the quality of fish, negating the pescatarians’ health reasoning. Despite the Clean Water Act of 1972, some countries continue to illegally dump waste into the ocean because they have no known alternative. This waste and sewage “sludge” contaminates the marine ecosystem, leading to hazardous pollutions in fish populations. Mercury, PCB’s, metals and pharmaceuticals found in fish are associated with neurodevelopment and cancer risk. As commercial fishing and aquaculture continue to grow consumers must understand the quality and source of the fish to determine its potentially harmful contaminants.
The mislabeling of fish products further complicates the health risks associated with fish consumption. Merchants strive to make a profit, unfortunately this leads to illegal overfishing and therefore mislabeling. In 1997 The National Seafood Inspection Laboratory discovered that 37% of fish and 13% of other seafood were incorrectly labeled. This can cause harmful health effects. In the US alone seafood causes 18–20% of the food borne illnesses afflicted by 76 million Americans in a single year. Fish manufacturing is a faulty political system which can place the opportunity for money ahead of the health of the consumer. Pescatarians who consume fish for necessary nutrients can easily find these same nutrients in vitamins; at the same time, they would avoid the risk of potentially harmful contaminants in the fish as a result of pollution and mislabeling.

Environmental Concerns of Fish Consumption
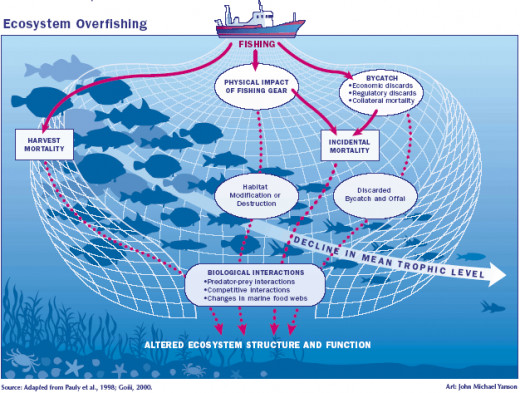
While cattle meat production contributes to global warming through its large carbon footprint, fish production also has adverse effects on the environment that cannot be ignored. Overfishing and illegal fishing have resulted in the endangerment of numerous fish species and marine wildlife. The National Marine Fisheries Service (NMFS) works to monitor the endangerment of marine wildlife to stop the extinction of fish species; however, illegal, unreported and unregulated fishing leads to possible extinction of many marine animals. There are approximately 2,100 species listed as endangered on the NMSF list including yellow fish tuna and several species of salmon found in the United States.
Little was known about the impact of fishing until the 1930s when scientists were able to statistically prove that fishing could harm fish populations. Even with several failed political attempts to curb commercial fishing, the world seemed to turn their backs to the environmental impacts of overfishing. As terrestrial creatures, society has viewed the ocean as an infinite resource opposed to an ecosystem that should be protected. The world continues to overlook this vast resource as overfishing still continues.
A lack of absolute global policy regulation has also contributed to illegal fishing. At the same time, ignorance breeds poor lifestyle choices – society remains unaware of the illegal activities involved in the fish served on their dinner plate. A true animal product limiter concerned about the environment would practice a strict vegetarian diet, avoiding consumption of not only land animals but marine animals as well.
Do Fish Experience Pain?
While pescatarians and non-vegetarians alike may be unable to comprehend the morality of fish manufacturing there is new evidence to show possible pain perception in marine animals, especially that of vertebrates. In Lynn Sneddon’s journal, “Pain Perception in Fish: Evidence and Implications for the Use of Fish” she examines the definition of pain and the anatomical and behavioral attributes of fish in examining this pain. She concludes that fish contain nociceptors which can detect potentially harmful stimuli, and that these nociceptors are similar in structure to that of mammals. Similarly, an experiment measuring brain activity using MRI scans on fish demonstrated activity in the higher thinking portions of the brain when presented with harmful stimuli. Sneddon articulates that “rather than considering fish to be incapable of pain because they have a different brain structure to humans, authors have proposed that the pain experience may simply be in a rudimentary form compared with human pain. Therefore fish do experience pain, it’s just more primitive in nature”. While there is still question and controversy over perception of pain in fish, there remains little globally enforced legislation protecting fish from harm in commercial handling


So, why do we continue to eat fish?
As humans, we acknowledge the inherently sinful act of slaughtering another human; therefore, it should also be inherently sinful to slaughter an animal “unless there is some morally relevant difference between humans and animals” according to philosopher John Hill. This difference has been reduced to the basis of experience – scientists often look to the development of the neo cortex, responsible for thought processing and higher intelligence, to determine the ethicality of meat consumption and proper animal treatment. Animals served on the dinner plate are close, neurologically, to that of humans. In this instance, there is little difference between humans and the animals humans consume.
The question now arises as to the difference between the terrestrial animal and the marine animal. An explanation for this is inherent in the location of the animals – land and sea. Humans, land creatures, are capable of relating to mammals like themselves, while they are unable to relate to a creature swimming in the ocean with gills, such as a cod. To many, the ocean is an abstract entity, an unknown abyss which houses incomprehensible obscure creatures. For this reason, a salmon or trout may not be ranked equivalently on the societal imaginary ethical scale with cattle. As Ken Montaigne states in a National Geographic piece, “If the giant bluefin lived on land, its size, speed, and epic migrations would ensure its legendary status, with tourists flocking to photograph it in national parks. But because it lives in the sea, its majesty—comparable to that of a lion—lies largely beyond comprehension”. The world has struggled to comprehend the majesty of aquatic life. An international uproar on the protection of ocean animals did not occur until the late 1960’s before which society only viewed marine life as a commodity.
Today, there is still a lack of an enforced international policy regarding commercial fishing, while at the same time, there is little focus on the ethical concerns of fish consumption. The ocean constitutes 70% of the world’s makeup making it an integral and necessary aspect of human survival. The barrier separating land and sea must be broken in order for society to ascertain the detrimental effects of fish consumption.
.Whether willingly or forcefully, many children have been dragged along with their father for a Saturday afternoon of fishing– here they experience the pensive process of waiting and the anticipation as the rod begins to fling itself forward, bending over into the water’s edge. Then finally, that moment when the floundering fish is reeled in, struggling with the hook in its mouth as it attempts to take its last breath out of water. The hook is removed and the fish continues to flail on dry land, seeking the refuge of the salt water. Slowly the life drains out of the fish, its movements become few and scattered until they end entirely. Two fingers are placed inside the gills and the fish is carried home; that same fish, just a few hours later, is served on a set of dinner plates and engulfed.
This could be a pescatarian – a fish consumer who does not eat meat. The reasoning behind this diet is inadequate in supporting the claim of a pescatarian diet. While fish may provide key omega 3 fatty acids, adverse health effects are plausible due to pollution and mislabeling. At the same time, environmental factors that influence land animals exist at the ocean level as well. Many species are overfished due to illegal, unreported and unregulated fishing. Most importantly, a conclusion regarding pain perception in fish is still widely unknown. New evidence demonstrates an activation of the genes involved in higher intelligence when fish are presented with noxious stimuli.
Ignorance, a lack of policy making and incomprehensibility has enabled this diet to gain popularity and has placed the value of fish on a lower level to that of terrestrial animals. The ocean covers 70% of the world and 95% of this great mass has yet to be investigated. The ocean is not an exploitable resource that can be expended for its commodities – it is an integral part of this earth that must be preserved, maintained and investigated. The consumption of fish is contributing to the detrimental effects on the millions of aquatic animals living in the wondrous sea; for this reason, a pescatarian diet lacks the integrity of a true vegetarian lifestyle. Next time that salmon, cod or lobster is placed in front of you, think twice before indulging in these soon to be rare creatures.









