DCC (Digital Command Control) the best thing since sliced bread for model railroaders

DCC (Digital Command Control) what is it?
Digital Command Control systems are used to operate locomotives on a model railroad. When equipped with Digital Command Control, locomotives on the same electrical section of track can be independently controlled.A DCC command station, in combination with its booster, modulates the voltage on the track to encode digital messages while providing electric power.Each locomotive is equipped with a mobile DCC decoder that takes the signals from the track and, after rectification, routes power to the motor as requested. Power can also be routed to lights, smoke generators, and sound generators. A stationary decoder can be attached to the rails to allow control of turnouts, uncouplers, operating accessories (such as station announcements) and lights.The great advantage of using DCC over traditional DC systems is the simpler wiring needed to operate more than one locomotive at a time. Before, to operate more than one locomotive independently, the track had to be wired into separate "blocks" with switches selecting which controller powered which block of track. If an operator failed to switch control of a block before his locomotive entered, a short circuit or loss of control was possible. With DCC, many layouts can be wired as a single large block, and each operator can control his locomotive without worrying about crossing a block boundary.

Books about DCC (Digital Command Control) on Amazon

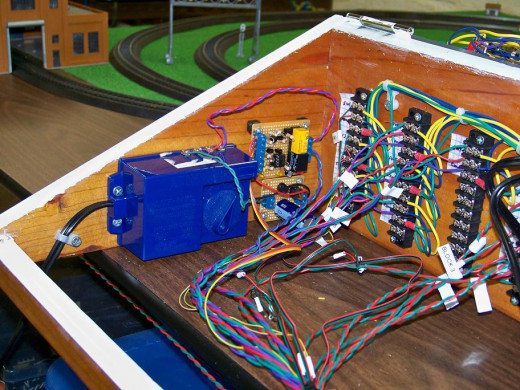
I used to be a DC (Direct Current) guy
I used to be a DC (Direct Current) guy, I used the traditional method of controlling my HO Scale locomotives by breaking my track layout into block sections. Each block section was electrically isolated from other block sections that could be controlled from the main control panel. By electrically isolating each block section I could indiviually control each locomotive running on each block section. This method worked, and was used for many years before the dawn of affordable DCC (Digitical Command Control) systems but it required a lot of throwing switches to control each electrical block. Plus it was not very realistic as your where essentially controlling the track not the locomotive itself. It also required a lot of electrical wiring as you can see from the picture.
Some Important Information
Before continuing I need to instill in you some important information:1. All DCC (Digital Command Control) systems, no matter what manufacturer, encode the exact same signal format on the track. This format was standardized by the NMRA the National Model Railroad Association which actively creates standards for the model railroad industry.2. Since the signal format on the track is the same for every manufacturer of DCC (Digital Command Control) systems per National Model Railroad Association standards, you can mix and match decoders manufacturer brands and they will all work with your Digital Command Control system. For example you could purchase a Digital Command Control system from Digitrax and purchase decoders from Atlas and these components will work together.3. You cannot mix and match DCC (Digital Command Control) systems. For example, a Digitrax DCC system will not be able to communicate with an Atlas DCC systems or the other way around. Each manufacturer of DCC systems uses its own protocol or communcation standard for communication between DCC components. The National Model Railroad Association is only concerned that the digital signal on the track is standardized.

My first DCC (Digital Command Control) system
I purchased the Zephyr Command Control System. This was a basic DCC (Digital Command Control) system offered by Digitrax. I purchased the Zephyr command control system because:1. This Zephyr Command Control System was inexpensive. 190.00 on Amazon. This is a major factor when you have a family and little funds.2. The Zephyr Command Control System is expandable. You can purchase other components to link your computer to the Zephyr Command Controls System. In addition, you can purchase a booster which will allow you to control more DCC decoder equipped locomotives. The Zephyr Command Control System has a limited 2.5 amp output which will probably allow you to control about 5 or 6 locomotives at one time.3. The Digitrax web site was professional, informative, and it instilled in me confidence in their products and support.4. The Zephyr Command Control System was "Made in the USA" how often do you see those words?
Installing a decoder in a DC (Direct Current) locomotive
Being on a small budget for my model railroad hobby, I decided to retrofit a DC (Direct Current) locomotive with a decoder. A basic Digitrax decoder (model DH123D) can be had for under $20 from most hobby stores and I already own several DC (Direct Current) locomotives. A good DCC equipped locomotive can be close to $100. Beware of the term "DCC Ready" this means that the locomotive is setup to accept a plug-in DCC decoder board but does not come equipped with one. The Digitrax DH123D comes with a detailed wiring diagram and instructions.
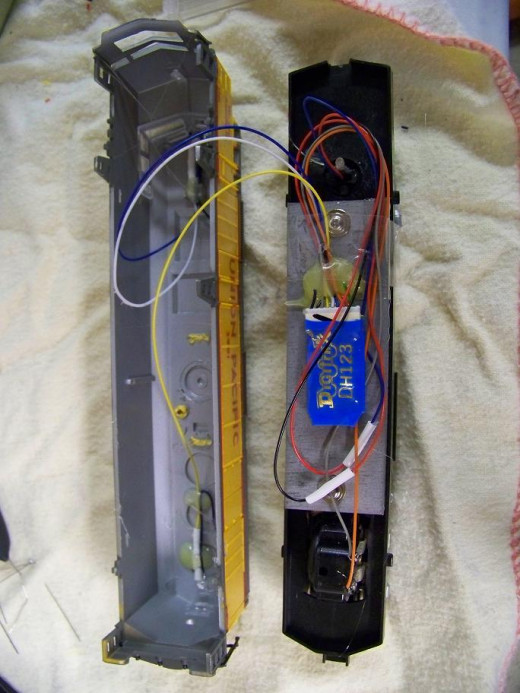
Installing a decoder in a DC (Direct Current) locomotive (Continued)
The Digitrax DH123D decoder wiring was pretty straight forward. All I did was follow the wiring diagram that came with the decoder. The DH123D decoder has outputs for controlling forward and reverse lighting so I hot glued LEDs (Light Emitting Diode) in the locomotive shell to be used for forward and reverse lights. Note: Unlike incandescent light bulbs, LEDs are polarity sensitive and they also need a 1K current limiting resistor wired in series with them. The DH123D decoder comes with a detachable wiring harness. I recommend disconnecting the decoder from the harness while soldering the harness wires in place. Once all of the wiring harness wires were soldered to the right connection I used a dab of hot glue to keep the wire harness in place. I then attached the DH123D decoder, it is the blue object in the picture labeled "DH123' in gold.
Digitrax Decoders for Sale on Amazon
I only purchase Digitrax Decoders for my layout since I use the Digitrax Zephyr Command Control system to run my layout. After all, how helpful will Digitrax support be if you have a problem with a locomotive that has another brand's decoder installed?

Testing the Zephr Command Control System
Note: You need to purchase or retrofit a locomotive with a DCC (Digital Command Control) decoder before testing. I chose to retrofit an old HO locomotive with an decoder for testing purposes. The decoder is an electronic part that is in each DCC (Digital Command Control) locomotive that allows the DCC (Digital Command Control) system to control each locomotive separately on the same track without having to electrically isolate the track sections into blocks like in a standard DC (Direct Current) system. You will notice I have two track sections in my test setup. The long track is for testing the DCC equipped locomotive, the short one is for programming the DCC decoder in each locomotive.

Testing the Zephr Command Control System (Continued)
In order to run several DCC (Digital Command Control) locomotives on the same track you need to assign a unique ID to each one of the locomotives. The Zephr Command Control System (like all Digital Command Control systems) superimposes a digital signal on the track along with the power to run the locomotive(s). In this digital signal there is an ID. Only the locomotive with the ID encoded in the digital signal will respond to the request made from the Zephr Command Control System. Digital signals encoded on the track may tell a locomotive with a specific ID to move forward, move in reverse, stop, change speed, turn on/off sounds or turn on/off lighting. The commands recognized from the Zephr Command Control System depends on the decoder installed in the locomotive. Some basic decoders only recognize signals to control direction or lighting while the more expensive decoders have the ability to play sounds through a small speaker installed in the locomotive. I like to put a small sticker on each decoder equipped locomotive to identify its ID number.

Programming a decoder equipped locomotive
By default, all Digitrax decoders have the ID number of 3 assigned to them. You need to change this to a unique ID number for each locomotive. If all locomotives have the same ID number of 3 you will not be able to control each decoder equipped locomotive separately and they will all respond to the same commands from the Digital Command Controller system. For the Digitrax Command Control System you program the ID by putting the decoder equipped locomotive on a separate programming track and enter the proper keystrokes on the Digitrax Command Control System to make this programming change. Note: There are many other parameters you can program into the decoder including custom speed tables and special lighting effects. Programming these parameters is out of the scope of this Squidoo Lens.
Running your locmotive on a DCC equipped layout
Not many modifications are needed to convert your DC block layout to a DCC (Digital Command Control) Layout. Simply disconnect your DC Transformer and connect your DCC System. Make sure all of your isolated electrical blocks are switched so that they received power and embedded digital signal from your DCC System. Never connect your DC Transformer and your DCC system to track at the same time. This could cause damage to your DCC system.. I am still in the testing phase so I have not yet attached my Zephyr Command Control DCC system to my DC block layout yet.
Conclusion
DCC (Digital Command Control) systems offer so much more flexibility in running your model railroad then the convention DC block system. With a DCC (Digital Command Control) system you are controlling the decoder equipped locomotive itself rather then controller power to the track where the desired locomotive you want to control is currently located. In addition, DCC (Digital Command Control) systems offer the ability to control lighting and sound that was never available under a conventional DC block layout system.The Zephyr Command Control system is a low-cost, expandable system that will allow you to get started in using DCC (Digital Command Control) to control your model railroad locomotives.










