10 Common Fitness Supplements And Their Purposes

Reminder:
These are all called supplements for a reason. None of the things listed below are needed in order to exercise and get results. Most of the time, a balanced diet and exercise work just as well!
Do not take any supplements, pursue any workout program, or try any diet without first consulting a doctor or physician.

1. Branched-chain Amino Acids
What it Does:
Branched-Chain Amino Acids (called BCAAs) are basically the amino acids (the building blocks of protein) needed to build muscle. The amino acids are: leucine, isoleucine, and valine. Those are the amino acids the body does not make itself, therefore they have to be ingested from other sources.
BCAAs help someone have a better workout by fueling the muscles and preserving the stores of glycogen (muscle fuel)
When to Take it:
They can be taken any time, even during the workout.
Who Should Take it:
Anyone who wants to enhance the workout and aide in muscle recovery after the workout.

2. Protein Powder
What it Does:
Increases the intake of protein, which is necessary to repair muscles after working out.
When to Take it:
Right after a workout is the best time, but they can be consumed any time
Who Should Take it:
Anyone who struggles to reach their quota of protein for the day, or who wants a little protein boost after a workout.
Note:
There are many different kinds of protein powders out there, and they each do different things. From whey isolate, concentrate, or hydroslysate, to casein protein, it can be quite confusing to know which one to purchase. Below are the different types of protein powder and the benefits of each one.
Whey Isolate:
High amounts of pure protein (around 90%); virtually lactose-free, carbohydrate-free, fat-free, and cholesterol-free; more expensive but overall better for the body; suggested for athletes who suffer from lactose intolerance
Whey Concentrate:
Higher amounts of carbohydrates, fat, and cholesterol than the isolate; cheaper than whey isolate; 29%-89% protein per pound; contains BCCAs and glutamine
Whey Hydrolysate:
The amino acid bonds are broken, allowing the protein to be absorbed by the body more quickly. They cost more than regular whey concentrate.
Casein:
A slow-digesting dairy protein. Often taken before bed because it is broken down slowly. Similar to whey in that it helps build muscle.
Pea Protein:
High in BCAAs and low in carbohydrates. Made from dried and powdered peas. Completely plant-based, and usually used as an alternative to whey proteins for people with intolerance to dairy.

3. Multivitamin & Multi-mineral Supplements
What it Does:
Supplements the body with a variety of vitamins and minerals possibly missing from the diet. The nutrients often vary by brand, so read the label and do some research.
When to Take it:
Most people take them in the morning with breakfast
Who Should Take it:
Anyone wanting to supplement their diet with essential nutrients

4. Creatine
What it Does:
Increases the body's ability to make energy at a faster rate. It is naturally occurring in the body and in the foods people eat, such as meat. It offers more fuel to the muscles, allowing for muscle growth. It does cause weight gain due to water retention.
When to Take it:
2 -5 mg in a protein drink is suffice. Can be taken before or after the workout, depending on when someone drinks a protein shake.
Who Should Take it:
Anyone who wants to supplement their efforts in the gym.

5. Fish/Krill Oil
What it Does:
High in the essential Omega-3 Fatty Acids, which help in the prevention of heart disease and can even aide in lowering blood pressure. Krill oil has also been said to be beneficial in helping arthritis symptoms as well as premenstrual syndrome symptoms.
When to Take it:
Daily along with the other vitamins. Any time during the day, though most take it in the morning.
Who Should Take it:
Anyone wanting to supplement their diet, especially if it lacks in fish and/or other kinds of seafood.

6. L - Carnitine
What it Does:
In the most basic scientific version, L-Carnitine helps transport fatty acids to the mitochondria in cells. Simply put, it is a nutrient (made in the body with the help of Vitamin C) that helps with making energy. It also aides in aging as it keeps cells healthy.
It is often taken to aid in weight-loss but can benefit recovery post-workout, increase muscle oxygen supply (which stops that muscle burn and keep the muscles from tiring faster), and boosts red blood cell production, which transports oxygen through the body faster.
When to Take it:
Mixed in with a pre-workout drink, such as a protein shake.
Who Should Take it:
Anyone suffering from a deficiency of the nutrient, or someone looking to get the most from a workout.

7. Glutamine
What it Does:
Glutamine helps reduce muscle soreness after a workout and can help boost the immune system
When to Take it:
Glutamine can be taken 2 or 3 times a day - before the workout, after the workout, and before bed
Who Should Take it:

8. Pre-Workout
What it Does:
Pre-workout has caffeine in it, which helps wake the body up and get it ready for an intense workout. Pre-workout can make people feel jittery, most athletes mentioning a "buzz" in their body after consuming it, so use with caution.
When to Take it:
As the name suggests, pre-workout is taken before a workout to keep a person from feeling tired during the workout
Who Should Take it:
Anyone who wants to workout, but feels they need an energy boost before going

9. Beta Alanine
What it Does:
Used for improving an athlete's performance, building muscle mass, and improving the overall physical functions of the elderly.
When to Take it:
Take 2 to 5 grams before a workout
Who Should Take it:
Anyone looking to make the most of their time in the gym or someone wanting to supplement their muscle growth. Also, the elderly can benefit from small amounts taken daily, though it is also made by the body and therefore not necessary.
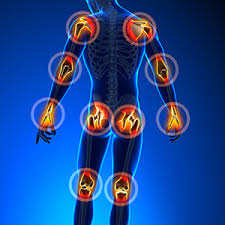
10. Glucosamine
What it Does:
Glucosamine is a supplement specifically designed to support joint health and help joint pain from arthritis.
When to Take it:
2-3 times a day; can be taken with a meal as this prevents an upset stomach
Who Should Take it:
Anyone suffering from osteoarthritis, or anyone looking to keep their joints in top health.
© 2018 Caitlyn Booth