Charcot foot as a complication of diabetic neuropathy

Diabetes mellitus is a leading global metabolic disorder
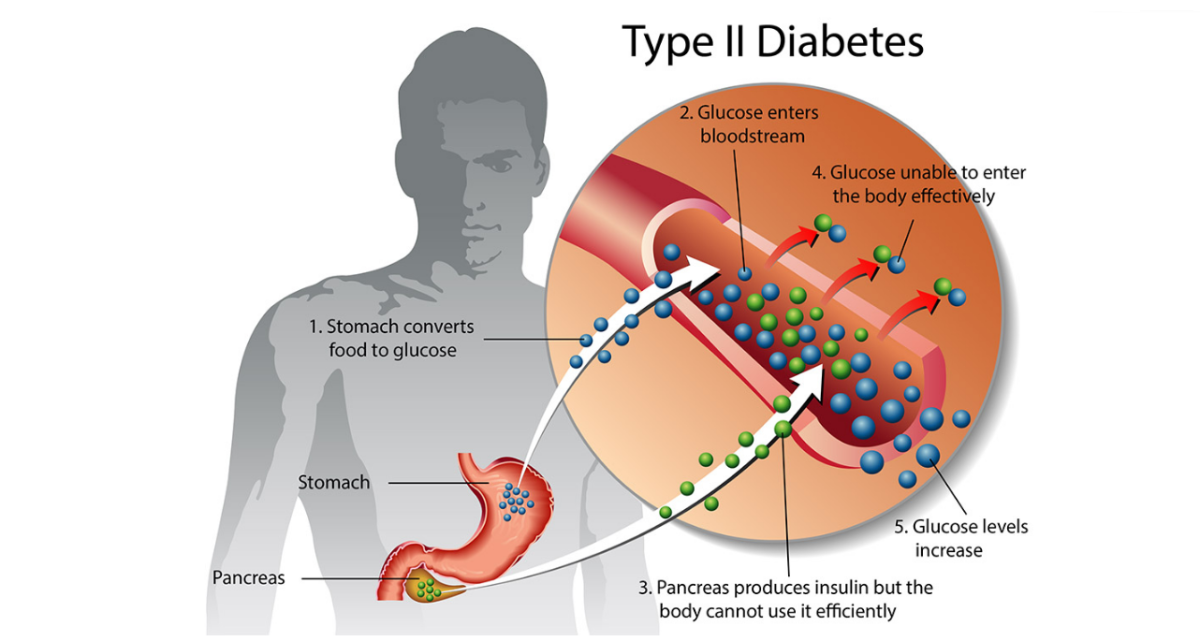
Diabetes mellitus is a leading global metabolic disorder accompanied by the overwhelming burden of its associated complications. Hyperglycaemia-induced endothelial damage or endothelial dysfunction serves as the primary instigator for the development of microvascular disease. Diabetic neuropathy represents the majority of microvascular sequelae and is the renowned perpetrator of a variety of foot complications, namely the Charcot foot (CF). CF is a debilitating medical emergency which is often mismanaged either due to a delayed diagnosis or lack of clinical expertise in the management of CF. Often, misdiagnosis during the acute stages of CF leads to irreversible and persistent joint destruction which may be refractory to medical or surgical treatment. Timely intervention with offloading measures is crucial during acute CF in ceasing active bone resorption. Current anti-resorptive agents may be considered as adjunctive therapy in combination with offloading. Novel agents are underway that will enable bone formation and suppress bone resorption.
Foot problems are common causes of disability in diabetic patients
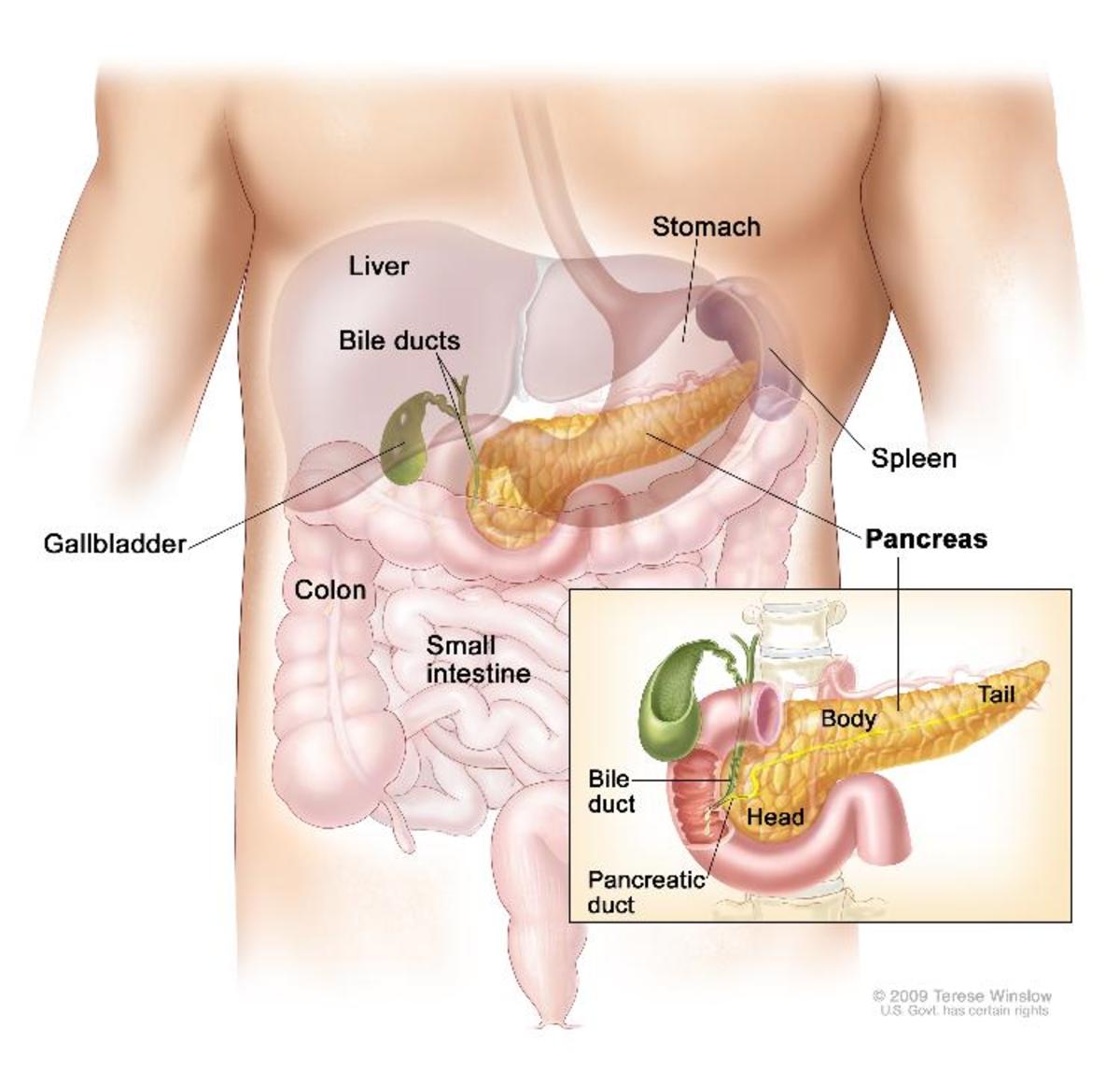
Foot problems are common causes of disability in diabetic patients with as many as 25% expected to develop severe foot or leg problems during their lifetimes. Although skin ulceration is the most frequent problem, bones may also be involved in two different clinical conditions: osteomyelitis and Charcot osteoarthropathy. Osteomyelitis causes complications in up to one third of diabetic foot infections and is due to direct contamination from a soft-tissue ulcer. Osteoarthropathy Charcot foot is a chronic and progressive disease of the bone and joints. Both osteomyelitis and Charcot joint are conditions with an increased risk of lower limb amputation, both may have a successful outcome when recognized and treated in the early stages. The major diagnostic difficulty is in distinguishing bone infection (osteomyelitis) from non-infectious neuropathic bony disorders as in osteoarthropathy Charcot foot. An additional difficulty is found when a bone infection superimposes a Charcot osteopathy. This condition, which can be clinically suspected when foot ulceration appears in Charcot foot, needs to be diagnosed because it implies a different therapeutic strategy.

Foot ulceration and Charcot neuroarthropathy
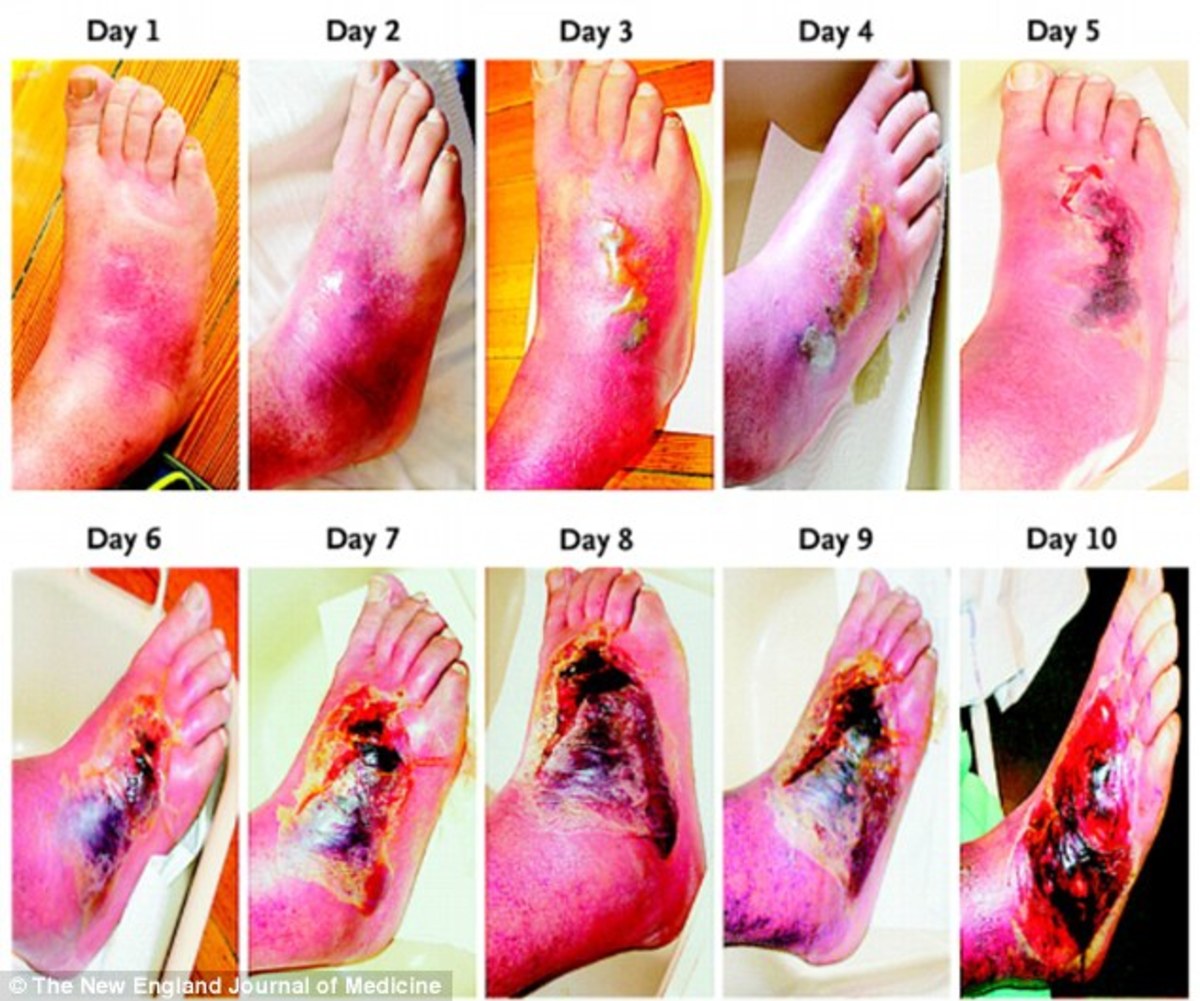
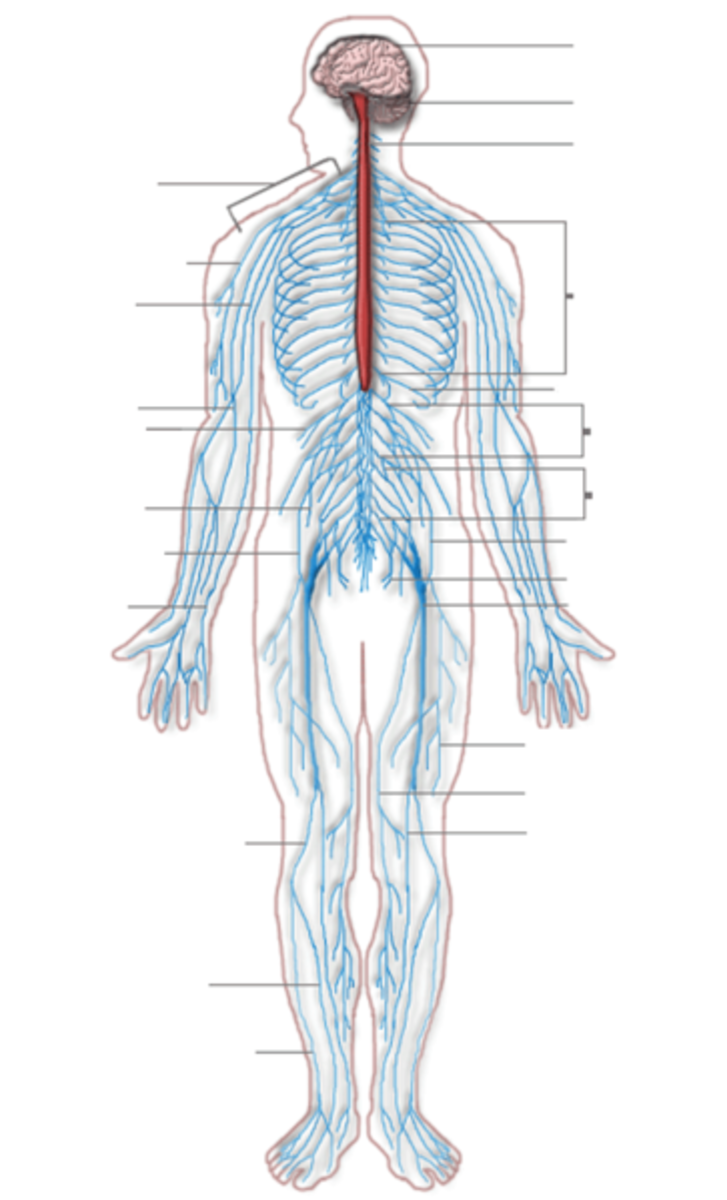
Foot ulceration and Charcot neuroarthropathy (CN) are well recognized and documented late sequelae of diabetic peripheral, somatic, and sympathetic autonomic neuropathy. The neuropathic foot, however, does not ulcerate spontaneously: it is a combination of loss of sensation due to neuropathy together with other factors such as foot deformity and external trauma that results in ulceration and indeed CN. The commonest trauma leading to foot ulcers in the neuropathic foot in Western countries is from inappropriate footwear. Much of the management of the insensate foot in diabetes has been learned from leprosy which similarly gives rise to insensitive foot ulceration. No expensive equipment is required to identify the high risk foot and recently developed tests such as the Ipswich Touch Test and the Vibratip have been shown to be useful in identifying the high risk foot. A comprehensive screening program, together with education of high risk patients, should help to reduce the all too high incidence of ulceration in diabetes. More recently another very high risk group has been identified, namely patients on dialysis, who are at extremely high risk of developing foot ulceration; this should be preventable. The most important feature in management of neuropathic foot ulceration is offloading as patients can easily walk on active foot ulcers due to the loss of pain sensation. Infection should be treated aggressively and if there is any evidence of peripheral vascular disease, arteriography and appropriate surgical management is also indicated. CN often presents with a unilateral hot, swollen foot and any patient presenting with these features known to have neuropathy should be treated as a Charcot until this is proven otherwise. Most important in the management of acute CN is offloading, often in a total contact cast.
In people with diabetes mellitus
In people with diabetes mellitus, the Charcot foot is a specific manifestation of peripheral neuropathy that may involve autonomic neuropathy with high blood flow to the foot, leading to increased bone resorption. It may also involve peripheral somatic polyneuropathy with loss of protective sensation and high risk of unrecognized acute or chronic minor trauma. In both cases, there is excess local inflammatory response to foot injury, resulting in local osteoporosis. In the Charcot foot, the acute and chronic phases have been described. The former is characterized by local erythema, edema, and marked temperature elevation, while pain is not a prominent symptom. In the latter, signs of inflammation gradually recede and deformities may develop, increasing the risk of foot ulceration. The most common anatomical classification describes five patterns, according to the localization of bone and joint pathology. This review article aims to provide a brief overview of the diabetic Charcot foot in terms of etiology, pathophysiology, and classification.
OBJECTIVES
OBJECTIVES: To outline the epidemiological profile of diabetic patients with Charcot arthropathy affecting the midfoot alone or extending from the midfoot to the hindfoot; To assess the results from the treatment that these patients undergo, according to a preestablished protocol, over the medium term. METHODS: We retrospectively evaluated 88 patients (110 extremities) with Charcot arthropathy of the midfoot. The minimum follow-up period was 12 months. We included 45 patients with Charcot arthropathy affecting the tarsal-metatarsal joints (51%); 20 patients in whom the talonavicular, calcaneocuboid and subtalar joints were affected (23%); and 23 patients in whom both the midfoot and hindfoot were affected (26%), as described by Brodsky and Trepman. We defined the treatment as successful when a functional foot was preserved; and unsuccessful when the foot was amputated. RESULTS: From treating Charcot arthropathy primarily involving the midfoot were satisfactory in the cases of 75 patients (85%) treated according to our protocol. For the patients with severe lesions affecting both the midfoot and the hindfoot, a greater number of complex operations (i.e. arthrodesis) were needed in order to obtain the same overall rate of satisfactory results. The osteoarticular lesions originating in the midfoot probably extended progressively to the hindfoot because of delayed diagnosis with inadequate early treatment. CONCLUSION: It was possible to preserve a functional extremity in 85% of the patients. Severe lesions involving the midfoot and extending to the hindfoot required a greater number of surgical procedures to treat them.

Autonomic function was studied in three groups of insulin-dependent diabetic patients. Heart rate changes during deep breathing and on standing were significantly less in 28 patients with a recent history of foot ulceration compared with 40 patients with peripheral neuropathy but without ulceration (p<0.001) and 54 patients without neuropathy (p<0.001). Sympathetic function was assessed in 36 of these patients from peripheral arterial diastolic flow patterns obtained by Doppler ultrasound measurements and expressed as the pulsatility index (PI). Patients with a history of ulceration (n = 10) showed considerably increased diastolic flow (Pl = 4.28 ± 0.53, mean ± S.E.M.) compared with 12 neuropathic patients with no history of ulceration (Pl = 7.80 ± 0.68, p<0.002) and 14 patients without neuropathy (Pl = 9.55 ± 0.89, p<0.002). Severely abnormal autonomic function occurs in association with neuropathic foot ulceration, but patients without ulcers have lesser degrees of autonomic neuropathy, thus a causal relationship has not been established.

Charcot neuropathic osteoarthropathy
Charcot neuropathic osteoarthropathy is commonly known as ‘Charcot foot’. It is a serious foot complication of diabetes mellitus that can frequently lead to foot ulceration, gangrene, hospital admission and foot amputation. A multidisciplinary approach to the management of Charcot foot is taken involving medical and allied health professionals. The management approach may also differ between different countries. To date, there is no systematic review of the literature undertaken to identify the clinical effectiveness of non-operative interventions in the treatment of acute Charcot foot. Objective The objective of this review was to identify the effectiveness of non-surgical interventions with reducing lesions, ulceration, the rate of surgical intervention, reducing hospital admissions and improve the quality of life of subjects with Charcot foot. Search strategy A comprehensive search strategy was undertaken on databases available from University of South Australia from their inception to November 2006. Selection criteria Randomised controlled trials or clinical controlled trials were primarily sought. Critical appraisal of study quality and data extraction was undertaken using Joanna Briggs Institute instruments. Review Manager software was used to calculate comparative statistics. Results This review identified 11 trials and five trials were included in the review. Three trials involved the use of bisphosphonate, a pharmacological agent. Two experimental treatments were also included, evaluating palliative radiology and magnetic fields. No trials were found using immobilisation and off-loading interventions for acute Charcot foot. The overall methodological quality score of the five studies was moderate. Owing to heterogeneous data, meta-analysis could not be performed. The trials did not report on reducing lesions, ulceration, rate of surgical intervention, hospital admissions and the quality of life of subjects with Charcot foot. The trials evaluating bisphosphonates reported greater reduction in foot temperature and disease activity for intervention subjects compared with controls. Another outcome of this review indicated additional beneficial effects of bisphosphonates in reducing pain and discomfort. The trial evaluating palliative radiotherapy found no difference between groups on any outcome. A significant reduction in the amount of deformity and reduced healing time to consolidation was found after treatment in the group receiving magnetic therapy treatment. Discussion There is a lack of clinical trials evaluating the effectiveness of non-operative interventions for the management of Charcot foot (immobilisation, removable cast walkers, advice/dispensing of footwear and prescribing of orthotics). Bisphosphonates may be useful adjuncts to standard management of Charcot foot by improved healing demonstrated by a reduction in disease activity indicated by skin temperature and bone destruction. Magnetic therapy may reduce deformity, joint destruction and improve mobility. Conclusion There is a lack of evidence supporting the use of pharmacological or non-surgical interventions with reducing lesions, ulceration, rate of surgical intervention, hospital admissions and improving the quality of life of subjects with Charcot foot. Bisphosphonates may improve the healing of Charcot foot by reducing skin temperature and disease activity of Charcot foot, when applied in addition to standard interventions to control the position and shape of the foot.