Crohns Disease Symptoms
What is Crohn's Disease?
Crohn's Disease is a type of inflammatory bowel disease that causes inflammation of the digestive tract. It can affect any area of the gastrointestinal tract from mouth to anus, but it most commonly affects the lower part of the small intestine, called the ileum.
An estimated 500,000 Americans suffer from Crohn's disease. It affects men and women equally and seems to run in some families. About 20% of people diagnosed with Crohns disease have a blood relative with some form of inflammatory bowel disease, most often a brother or sister and sometimes a parent or child.
Crohn's disease is not contagious and can occur in people of all age groups, but it is more often diagnosed in people between the ages of 20 and 30.
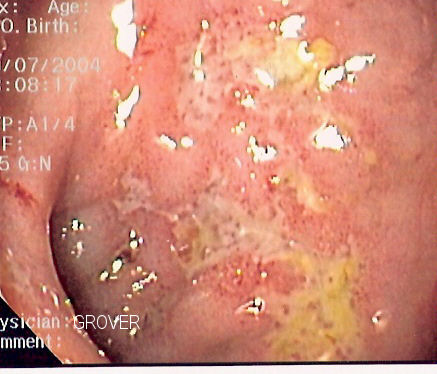
Crohn's Disease symptoms
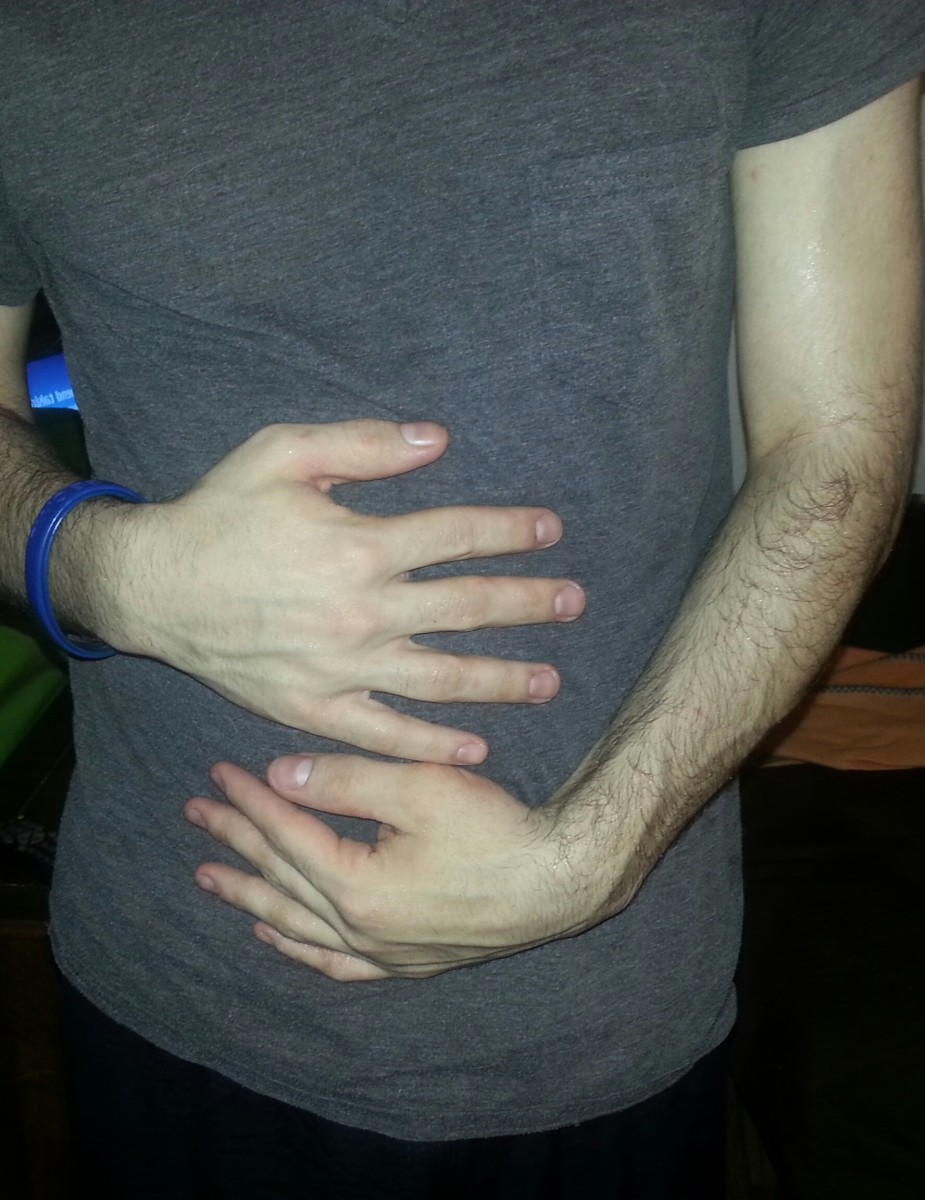
The most common presenting features of Crohn's Disease are chronic diarrhea, which may, or may not, be bloody, abdominal pain, often in the lower right area, and fever. Some may also complain of loss of appetite and fatigue.
The main symptoms include:
- Abdominal pain and cramping
- Diarrhea
- Loss of appetite
- Weight loss
- Rectal bleeding
- Fever
There may also be other extraintestinal symptoms that usually become more common as the disease progresses. These symptoms can vary widely among individuals:
- Arthritis
- Mouth ulcers
- Eye inflammation
- Skin problems
- Night sweats
- Anemia
- Hemorrhoids
Crohn's disease can also cause some neurological complications (reportedly in up to 15% of patients). The most common of these are seizures, stroke, myopathy, peripheral neuropathy, headache and depression.
Many people with Crohn's disease have symptoms for years prior to the diagnosis. The usual onset is between 15 and 30 years of age, with no difference between men and women. The condition may go undiagnosed for years because symptoms usually develop gradually.
Depending on the severity of Crohns Disease symptoms, there are several treatment options available including prescription medications and nutritional supplements. The objective of the treatment is to correct nutritional deficiencies, control inflammation, and relieve crohns disease symptoms like diarrhea, abdominal pain, and rectal bleeding. Treatment may also include surgery.
Since there is no cure for Crohn's disease, the primary goals of treatment are to:
- induce remissions
- maintain remissions
- improve the quality of life