Dementia - Cognitive Decline
Dementia Facts
Dementia is a term for conditions and diseases that are characterized by a decline in a person’s language, memory, problem-solving skill and all other types of thinking skills. Dementia makes performing everyday activities very difficult and sometimes impossible. The most common cause of dementia is Alzheimer’s disease.
Alzheimer’s disease results in problems with the memory, behavior, judgment, attention, thinking, mood and abstract thinking.
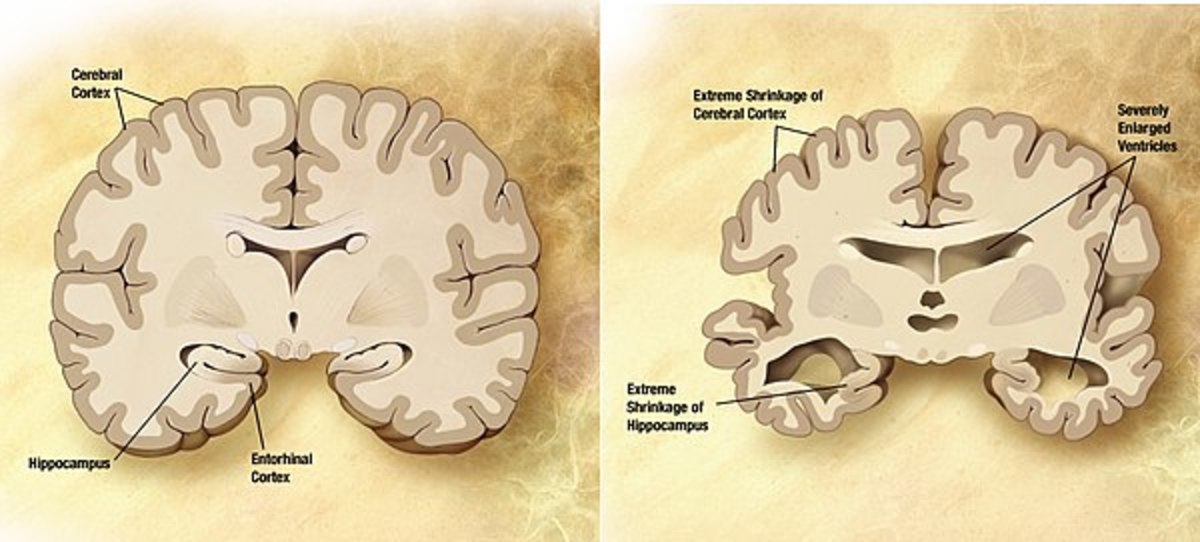
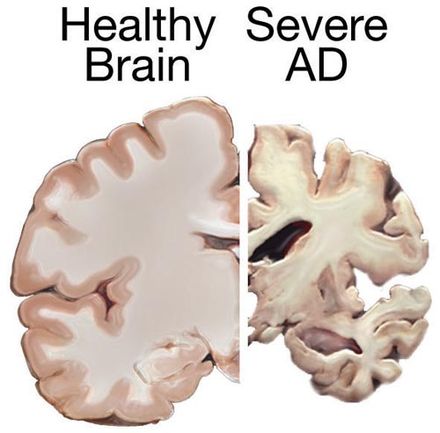
The brain has neurons that communicate and connect at the synapses, which is the place neurotransmitters carry information between cells. The process is interrupted with Alzheimer’s disease, which will destroy the synapses and kill the neurons, damaging the brain’s communication network. There is no cure and these symptoms will get worse over time. Chronic stress accelerates cognitive decline and impairs memory function.
Alzheimer’s Disease Signs and Symptoms
There are some early signs of this disease, which increase over time and they include:
- Loss of concentration - A person may lose their ability to even complete an easy project.
- Forgetfulness - There may be unopened mail lying around and bills not paid.
- Language problems - A person may lose their train of thought in the middle of a sentence.
- Confusion about time and place
- Loss of insight - A person may not understand even simple concepts.
- Impaired judgment - This person may participate in risky behavior.
- Mood and behavioral changes - Their personality may be quite different and they may wander away from home when the disease progresses.
- Apathy and depression - They may lose interest in foods or not change clothing without being prompted and depression may be a serious problem
In addition to the behavior affected by brain changes there are other problems as well. Feelings of confusion or fear are not uncommon. Other illnesses can complicate medical issues for the patient with dementia, which may include new medications, pain, constipation, lack of sleep, problems with seeing or hearing.
There are studies that show people who are experiencing cognitive impairment are sometimes deficient in essential vitamins and nutrients. Scientists have found out that specific nutrients play an essential role in the brain’s cellular activity.
Late stages include a patient turning increasingly inward and needing assistance with almost all of their personal care. They typically need twenty-four hour assistance.

Other Types of Dementia
In addition to Alzheimer’s disease there are several other types of dementia and they include:
- Vascular dementia is the second most common type of dementia, which is caused by a lack of blood flow to the brain and it can be caused by atherosclerotic disease or a stroke.
- Lewy body dementia is due to protein deposits in nerve cells, which interrupt chemical messages in the brain causing disorientation and memory loss.
- Advanced Parkison’s disease patients may develop dementia and they have trouble with judgment and reasoning, plus they may have hallucinations.
- Frontotemporal dementia is a dementia that affects the front and side parts of the brain that control language and behavior, (Pick’s disease).
- Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease is very rare, and the symptoms vary with patients typically dying within a year of their diagnosis.
- Wernicke’s disease or encephalopathy, caused by a lack of vitamin B1, which leads to bleeding in the lower brain areas.
- Mixed dementia refers to a patient with more than one type of dementia. The combination of vascular dementia and Alzheimer’s disease is the most common type.
- Normal pressure hydrocephalus (NPH) causes the brain to build up excess fluid in the ventricles and this disorder accounts for five percent of dementia cases.
- Huntington’s disease, a genetic disorder, causes dementia. Two types exist: juvenile and adult onset (starting in a person in their 30s or 40s), which can lead to dementia.
Recognizing The Early Stages of Dementia
Diagnosing Dementia
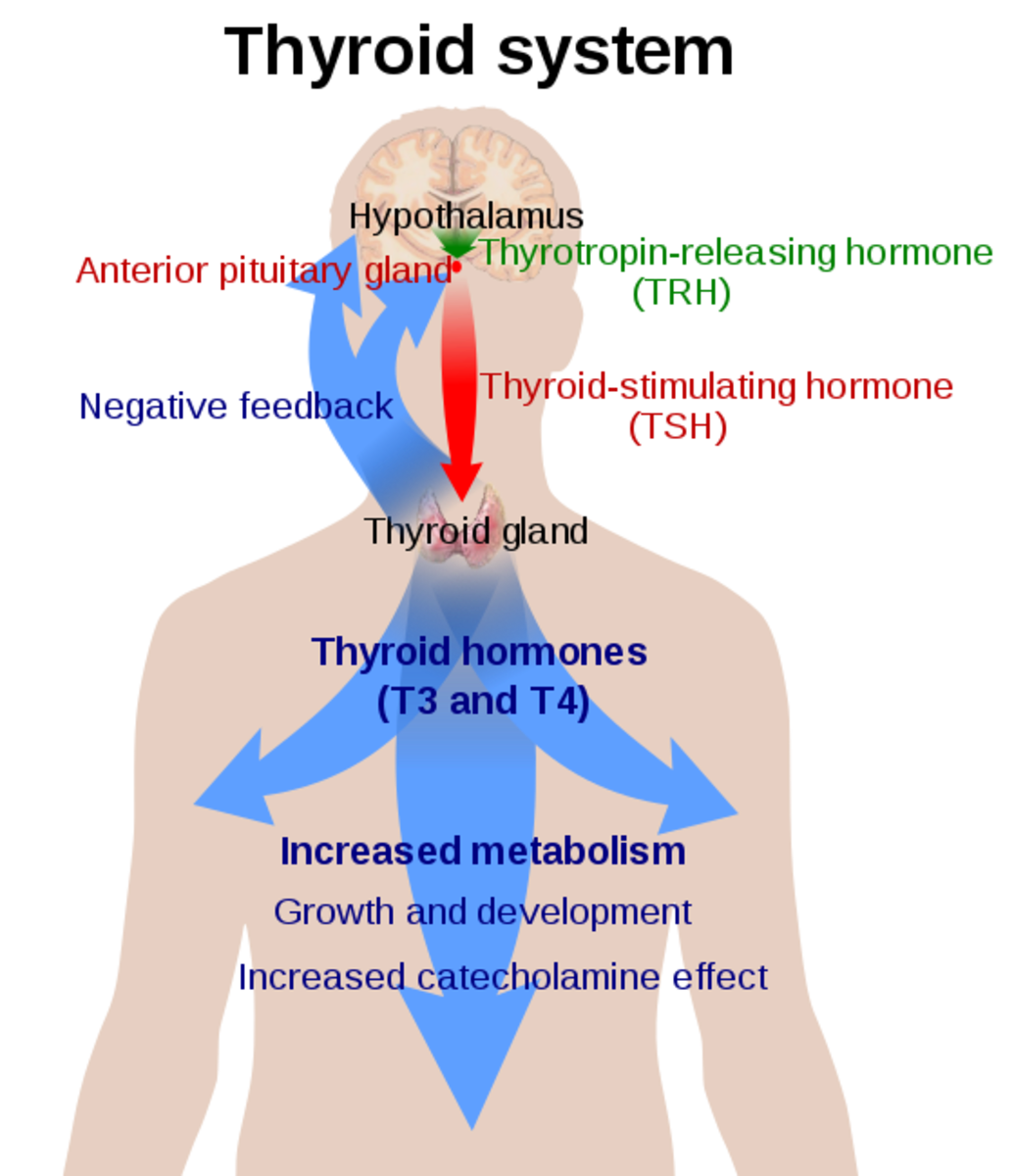
Doctors will order some testing that will measure thinking skills, such as reasoning, judgment, orientation, language skills and attention. Blood tests are often ordered to check for things that affect brain function, like vitamin B1, B12 or an underactive thyroid gland.
Brain scans may include a CT or MRI to look for evidence of a stroke, tumor, hydrocephalus or bleeding in the brain. A PET scan may be ordered as it shows patterns of brain activity, amyloid protein that is an indication of Alzheimer’s disease.
Medications to Treat Dementia
There are several medications that treat dementia. Even though there is no cure for dementia there are medications that help treat the symptoms.
Cholinesterase inhibitors (Aricept, Exelon, Razadyne) and memantine (Namenda) treat the cognitive symptoms of confusion, memory loss and difficulties with thinking and reasoning because it boosts the levels of a chemical messenger that is involved in memory and judgment. Namenda may cause some dizziness.
Other medications may be prescribed for sleep, depression hallucinations, parkinsonism or agitation.
Improved cognitive performance may be helped with natural nootropics that are made of natural or synthetic vitamins, amino acids, antioxidants, fatty acids and some herbal ingredients.
Phosphatidylserine has been shown to aid memory function in middle-aged or older adults. It helps rejuvenate brain cell membranes.
In Ayurvedic medicine bacopa has been used for centuries for its ability to enhance memory retention, to improve spatial learning and for its ability to receive new information about one’s environment, plus it helps reduce stress.
What is Alzheimer's Disease?
Therapies
Occupational therapy may be ordered to help modify the patient’s environment to make it safer and to teach coping behaviors. Patients are also taught to simplify tasks.
Mayo Clinic also suggests other therapies, which include:
- “Music therapy, which involves listening to soothing music
-
Light exercise
-
Watching videos of family members
-
Pet therapy, which involves use of animals, such as visits from dogs, to promote improved moods and behaviors in people with dementia
-
Aromatherapy, which uses fragrant plant oils
-
Massage therapy
-
Art therapy, which involves creating art, focusing on the process rather than the outcome”
In Conclusion
Dementia is a very difficult disorder to cope with for patients and their family members. There are day care centers for patients when all family members work or maybe the patient is too difficult to deal with around the clock. There are also nursing homes that specifically care for patients with any type of dementia. There are some medications and therapies that aid patients and family members.
References
- https://www.medstargeorgetown.org/our-services/neurosciences/neurology/conditions/alzheimers-disease-and-dementia/
- https://www.aarp.org/health/drugs-supplements/info-2017/caution-these-10-drugs-can-cause-memory-loss.html
- https://www.alz.org/alzheimers-dementia/treatments/medications-for-memory
- https://www.nia.nih.gov/health/managing-personality-and-behavior-changes-alzheimers
- https://www.healthline.com/health/types-dementia
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/dementia/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20352019
This content is accurate and true to the best of the author’s knowledge and does not substitute for diagnosis, prognosis, treatment, prescription, and/or dietary advice from a licensed health professional. Drugs, supplements, and natural remedies may have dangerous side effects. If pregnant or nursing, consult with a qualified provider on an individual basis. Seek immediate help if you are experiencing a medical emergency.
© 2020 Pamela Oglesby