Diphtheria: The Health Significance Of Its Clinical Diagnosis And Phases Of Treatment
The Global Diphtheria Pandemic
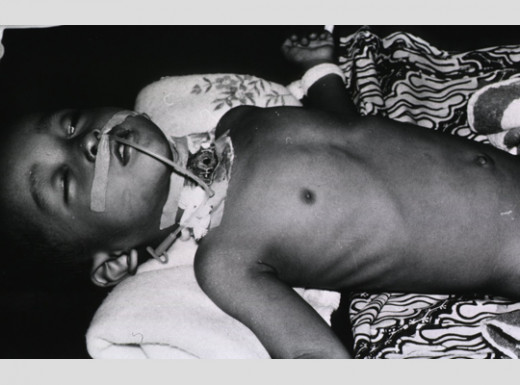
Clinical Diagnosis Of Diphtheria
The diagnosis of diphtheria is essentially clinical. Confirmation of the diagnosis depends on the demonstration of the organism in stained smears made from the membrane and by culture using Loeffler’s medium. Fluorescent antitoxin staining provides a method for rapid diagnosis. Toxigenicity can be assessed by guinea pig inoculation, passive agar gel diffusion (Elek plate method) or counter immunoelectrophoresis.
Differential diagnosis: Acute follicular tonsillitis with exudates over the tonsils may resemble diphtheria. In follicular tonsillitis, the exudates is confined to the tonsils, it is yellowish and can be easily wiped off without being adherent. The fever is high in acute tonsillitis whereas it is only mild in diphtheria. Regional lymphadenopathy is more marked in diphtheria than in acute tonsillitis.
Agranulocytosis and acute leukemia may lead to necrotic ulceration of the tonsils. In these, there is no true membrane. The tonsils are red, enlarged and necrotic or hemorrhagic. Hematological examination establishes the diagnosis. In all cases of reasonable clinical suspicion, the antitoxin should be given without delay.
The DPT Vaccine As A Prophylaxis Against Diphtheria
Prevention And Treatment Of Diphtheria
Treatment
The aims of treatment are to neutralize the formed toxins and eradicate the organisms from the primary site to prevent further production of toxin. The formed toxin is neutralized by the administration of diphtheria antitoxin (anti-diphtheritic serum- ADS) in adequate quantities. It can be given intramuscularly or intravenously. The dose can be roughly estimated from the extent of the membrane.
- Only one tonsil involved: 20,000 units
- Both tonsils: 40,000 units
- Laryngeal and pharyngeal forms: 80,000 units
- Severe cases: 120,000 units
The anti-diphtheric serum is prepared in the horse and so sensitivity to horse serum has to be tested by appropriate intra-dermal test using 0.1ml of 1/100 solution. One centimeter erythema developing within 20 minutes indicates allergy. In allergic cases, ADS should be administered only after desensitization or after taking appropriate measures to combat anaphylactic shock. Usually one dose of ADS is sufficient.
Corynbacterium disphtheriae is sensitive to penicillin and erythromycin. Procaine penicillin 600,000 units a day or erythromycin 40 mg/Kg body weight in four divided doses, for 6 to 7 days is adequate to eliminate the organisms. Since there is the possibility of developing carrier state and spread of the infection, the child should be allowed to mix with other children only after ensuring that three repeated throat cultures are negative. General measures of treatment include rest in bed for two weeks and soft liquid feeds.
Treatment of complications: Myocarditis is managed with strict bed rest, use of antiarrhythmic drugs, and digitalis when indicated. Caroticosteroids (betamethasone 8 mg four times daily) have been employed with beneficial results in some. Artificial pacing may be required if heart block develops. Neuritis is usually self- limiting and does not respond to any specific treatment. Supportive care and physiotherapy are indicated. Nasogastric tube may be required to aid feeding, if there is palatal and pharyngeal paralysis. Respiratory obstruction due to the presence of the membrane is an emergency indication for tracheostomy and maintenance of the airway. Respiratory paralysis is managed by artificial ventilation.
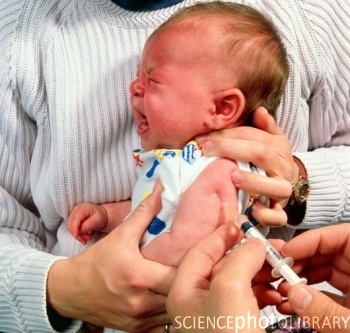
Prevention
Prevention includes general active immunization and management of contracts. Active immunization is done with diphtheria, pertussis, tetanus (DPT) vaccine, which is also known as triple antigen. The first dose should be given in the third month and thereafter two more doses at four-week intervals. Booster doses must be given at the second and fifth years. The DPT vaccine gives substantial immunity, but rarely the disease may occur even in immunized children.
Immediate contacts should be given 2000 units of ADS. Throat swab culture and if possible schik test should be done to identify the carrier state and susceptibility to infection.
Carriers should be given treatment. Penicillin or erythromycin is used to eradicate the infection. A booster does of DPT is required in previously immunized persons on fresh exposure.
© 2014 Funom Theophilus Makama