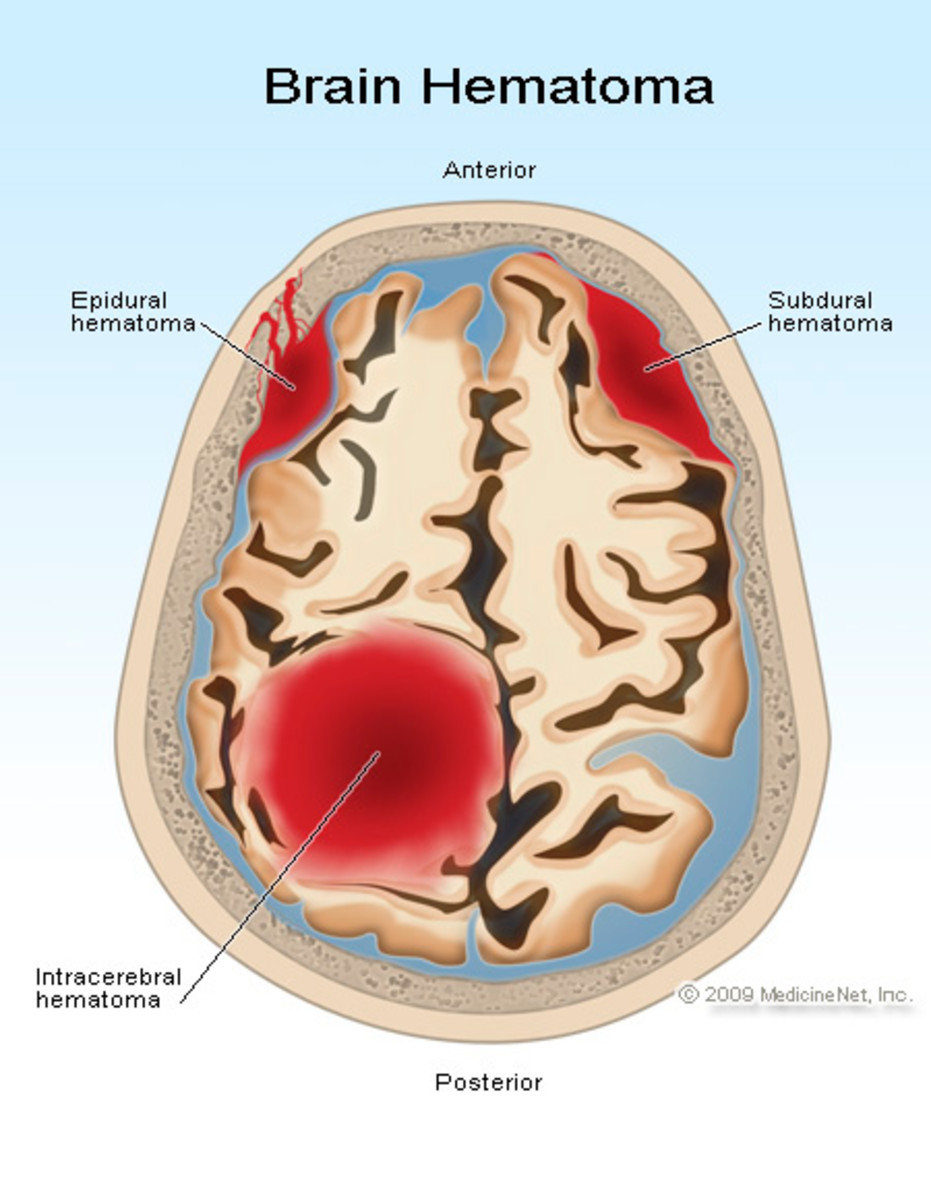
What Is An Epidural Hematoma (Extradural Hematoma)
X-Ray Of The Human Head
Head Trauma
Have you ever had a head trauma that caused an epidural hematoma
What is an Epidural Hematoma?
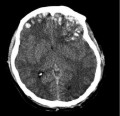
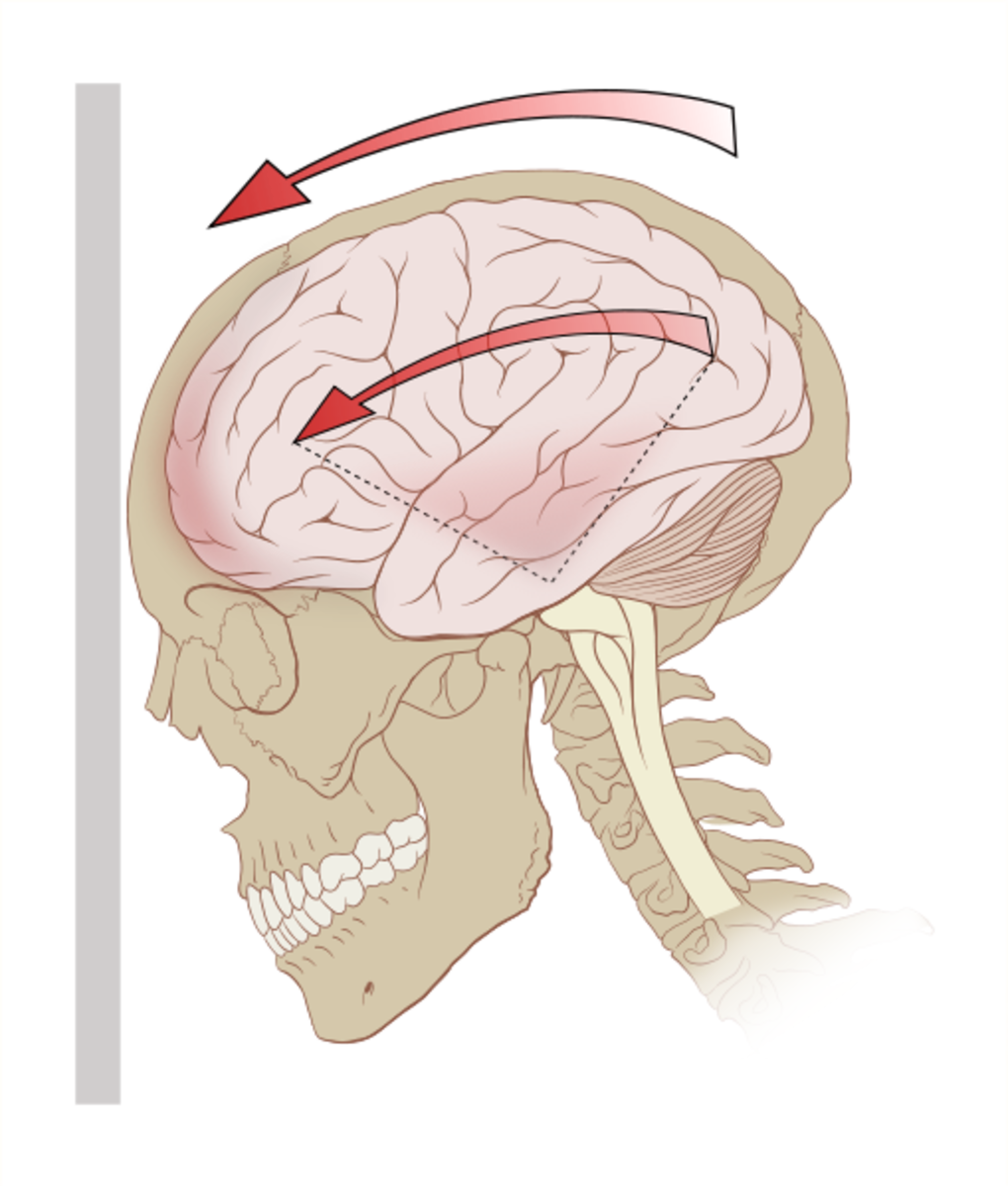
An epidural (extradural) hematoma occurs when the patient has experienced a traumatic head injury which causes blood from an artery to fill and clot between the dura matter (the tough membrane of the central nervous system) and the skull. A bleed of this nature in the brain can cause brain damage and even death in a very short amount of time. These types of injuries are very difficult to diagnose by anyone who is not a medical professional so this is why it is so important to get your head injuries looked at straight away.
It is not only the brain that has these epidural spaces which can become filled with blood. Epidural spaces are also located spine as well so spinal injury or medical procedures (such as a lumbar puncture) can cause bleeding in the spine; most women are aware of an epidural which is given to relieve pain during child birth and they are only given by specially trained medical staff to significantly lower the risk of injury or a bleed. If you do get a spinal injury in an epidural space then a bleed in the spine will cause compression on the spinal cord and potentially permanent damage resulting in symptoms such as numbness and paralysis.
The Right First Aid
Giving someone the right type of first aid is paramount to their recovery after an injury. If you are not sure what to do then leave it to the professionals as they are specially trained to deal with these types of emergencies. However, if you have the right knowledge you can be vital on the scene of an accident.
There are many courses that will give you training so that you can identify what type of first aid is needed for different scenarios and it is also the best way to get your training. However, if you've already had your training or you're looking for a manual to accompany you through your course then there is no harm whatsoever in getting some literature to help you along the way. Just remember that a professionally recognised course is the best way to get trained for first aid and the books are there to help, they cannot teach you everything.
Symptoms Bleeding In The Brain
A health care provider should be seen if a loss of consciousness, or any other symptoms are experienced after a head injury including a wound or other out of character behaviours.
With an epidural hematoma it has been noted that the following pattern often occurs: loss of consciousness followed by a brief passage of alertness and then another loss of consciousness, usually into a coma. It must be noted that this pattern is NOT present in 100% of cases and other symptoms may present. Basically what that means is that anyone who has experienced a loss of consciousness, even if it's just for a few seconds, needs to be seen by a doctor as soon as humanly possible.
Other symptoms of an epidural hematoma that may present themselves before any of the above occur include:
- Dizziness: feeling lightheaded or like the room is spinning
- Confusion: not sure where they are or what they're doing
- Drowsiness: not being able to stay awake for even short periods of time
- Headache, often severe: can be located at the site of the hematoma but can also be widespread
- One pupil is bigger: if the optic nerve or blood vessels to the eye are restricted then this will happen
- Nausea/vomiting: whether continuous or a one off
- Weakness: not being able to stand or support themselves properly or even to hold out their arms.
These symptoms are caused by increased intracranial pressure (the bleed is putting pressure on the brain) which causes blood vessels, nerves etc to become compressed thereby making them less efficient in retrieving signals, giving oxygen and eliminating CO2 etc. When the body is put under a lot of stress like this it will send out a lot of outward signals that it is in distress while it is also send out its own internal signals to try to repair the bleed before it gets worse.
The video below will take you through a computerized version of an epidural hematoma.
Epidural Hematoma Animation
A Hematoma Shown In The Brain
Diagnosis and Treatment of an Epidural Hematoma
Once the patient has arrived at the hospital a physician will do an MRI or CT scan to look for a convex mass (the clot), it will stand out like a sore thumb if it's large enough but if it's caught early they may need to spend some time looking to make sure they have the right information. If the results show that the mass is pushing on the brain and causing an increased intracranial pressure then surgery might be needed to remove the clot and restore the normal pressure in the skull.
During surgery a couple of things might happen to try and relieve the pressure but the surgeon and his team will do the best thing for the patient at the time. If the clot is so large or life threatening then they may need to remove a piece of the skull to manually remove the clot. However, if the clot is caught early then a stent might be placed in the skull which will give the brain some more breathing room so that the body can deal with the clot itself.
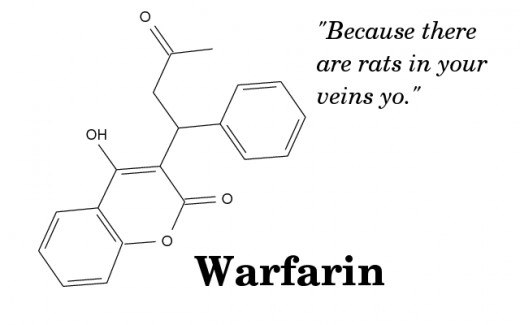
After surgery it may be advisable to take a course of anticoagulation medication to thin the blood whilst the body is healing. This will keep the blood thin during the course of treatment and prevent blood clots from forming while activity is restricted.
If you have a blood condition (see the further reading section below) that will make you more likely to clot and have complications from an injury then your doctor may suggest putting you on Warfarin (also know as Coumadin in the states) to keep you blood at a constantly thinned state. Although it may seem like a lot to take in having 1-2 tablets once a day and knowing that it is helping to keep you alive and healthy is much better than running the higher and potentially fatal risk of having an uncontrolled clot but that's just my opinion do with it as you may.
Complications and Preventions for an Epidural Hematoma
Brain damage may occur even if the hematoma is treated because damage may have been done prior to the surgery. There is a risk that recovery may not be 100% due to this issue.
Complications include symptoms such as paralysis, dizziness and seizures after the episode but have a tendency to improve over time as healing progresses.
An epidural hematoma may not be prevented once head trauma has occurred so it is always advisable to wear the correct safety equipment and avoid activities that pose risk specifically to head trauma.
Disclaimer
This article is for informational purposes only and should not replace the attention of your health care provider. If you are in any doubt about the severity of your condition then you should seek help immediately by contacting the emergency services who can assist.
More Information
- Living With Factor V Leiden: What is a Hematoma?
There are a whole bunch of other types of hematoma that can occur in the body so if you need more information then this should be your next stop.
© 2012 Bobby