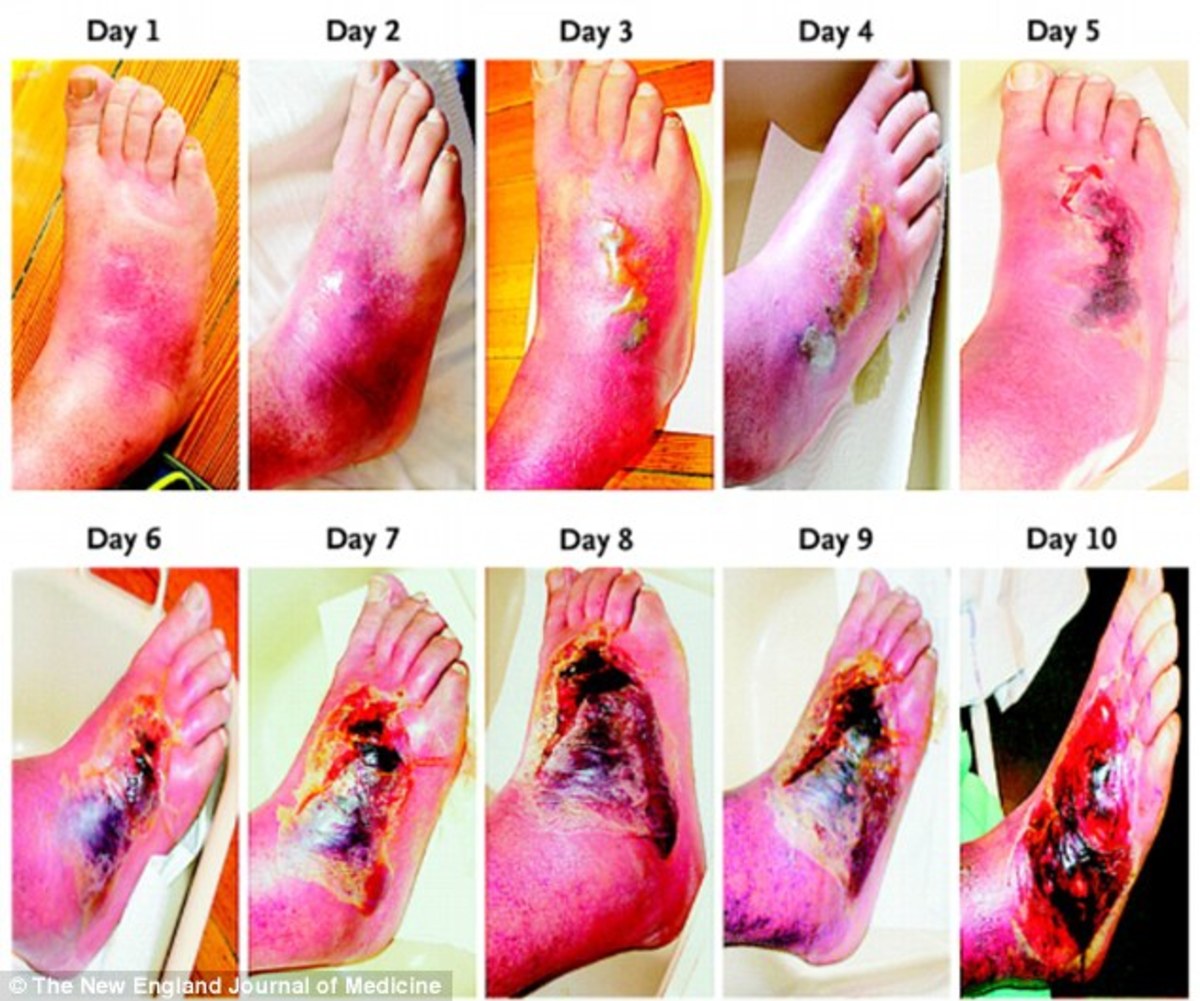
Fistula treated with Negative pressure wound therapy.
Different fistula different technique
This hub about fistula treatment is only meant for professionals preferably in a hospital or wound care clinic. However, if you have a fistula that is difficult to treat it may be of interest for you to know about this relatively new method of treating.
I will not be posting photos for this one as i do on many of the other hubs.
Hopefully the step by step techniques will be understood perfectly by health care workers already familiar with using negative pressure or vacuum machines in their practice.
Some of you may have seen these techniques before as i have sent them out and taught them in many hospital wards around the world.
Before you read further i am assuming that you know what a fistula is and aware of the importance of correct care.
Negative pressure must never be applied directly to this type of wound without taking the necessary precautions. If you do apply it directly you are in danger of perforations! Please treat these wound with the utmost of care.
Do not let this frighten you though as i have seen many successes using NPWT.
ACUTE ENTERIC FISTULA SIMPLE
This fistula is not within another wound and classified as a simple fistula.
Treating with Vacuum therapy:
- Clean the skin and wound , remove any type of oil or grease from the skin.
- Apply skinprep if preferred.
- Explore the fistula and use NAG which is a non adhesive gauze in the end of the fistula if needed
- Place hydrocolloid around the opening of the fistula at least 4cm around the edges.
- Depending on the amount of exudates use a channel drain directly into the fistula.
- If you are unsure of the depth and the wound is exudating more than normal use follow instructions for a complex fistula. If it is not too heavy and you are still concerned you can cover the channel drain with a layer of Non adhesive gauze ( NAG ) for protection. (As the drainage decreases the NAG can be replaced by AMD halfway down the drain but continue with NAG on the tip )
- Fill the wound cavity if needed with AMD gauze and cover with transparent dressing.
- Apply negative pressure in accordance to the clinical guidelines or the physicians prescription.
- Observe carefully the colour and amount of exudates each day .
- Observe the patient in relation to pain experience, this should not be worse than they experienced before the NPWT was applied.
- Observe for any swelling near or around the fistula, for example, if a lump should appear on the skin near the wound then suspect tunnelling or a new fistula opening. This is called the tunnel effect and is seen when the pressure is sucking on a new wound which has a very tiny opening. Stop treatment and contact the physician immediately. ( I have only ever experienced this twice and it was not a side effect of Vacuum therapy, but instead it was the therapy which was able to show up a very ugly hidden wound which was not noticed on examination. The only thing that can be done here is an extensive debriding of the wound. )
ACUTE ENTERIC FISTULA COMPLEX
This type of fistula is within a wound
· Cover the mouth of the fistula with several layers of petroleum based gauze
· Thoroughly irrigate and clean the abdominal wound
· Now remove the layers of gauze from the mouth of the fistula
· Cover the opening of the fistula with one layer of NAG
· Cover any other exposed areas of exposed bowel or organs with several layers of NAG ( Minimum 4 )
· Gently place 2 layers of AMD over the NAG making sure that this stays in place.
· Place a flat dran onto the AMD and fill with AMD over the drain
· Fix the drain firmly with strip paste ( a strip of paste which is used around stomi openings ) at the edge of the wound .
· If there is maceration around the edges of the wound use hydrocolloid for protection before fixing the strip paste.
· The pressure should be no less than 80mmHg.
· Always use continuous therapy and follow the observations above.
CHRONIC ENTERIC FISTULA
2 METHODS CAN BE USED.
Method 1 using a drainage tube:
· Cover the mouth of the fistula with minimum 3 layers of petroleum based gauze.
· Thoroughly irrigate and clean the wound cavity.
· Remove the layers of petroleum based gauze.
· Place a drainage tube (such as a foley catheter in our case we can use a 19fr round drain) over the mouth of the fistula but DO NOT enter the lumen of the bowel.
· Take a strip of petroleum based gauze and wrap this around the base of the drainage system and around the mouth of the fistula which will form a seal.
· Cover any exposed organs or bowel with several layers of NAG.
· Use a flat drain and place this about 1cm from the drainage device.
· Fill the rest of the cavity with AMD after fixing both the drainage device and the flat drain at the exit of the wound. ( Can be placed together or on either side, better on either side to prevent air leakage ) It is important that the extra drainage tube stays firmly in place as this will help remove the infectious exudates from the fistula before it is sucked into the AMD)
· Connect both the drainage system (our 19fr ) and our suction device (the flat drain) to a Y connector and connect to the 800ml canister.
· Negative pressure continuous at minimum 80mmHg.
· Observations as above.
Method 2 using a pouch:
· Cover the mouth of the fistula with 2-3 layers of petroleum based gauze.
· Irrigate and clean thoroughly.
· Remove these layers of gauze.
· Wrap NAG around the mouth of the fistula and cover any exposed organs or bowel with NAG.
· Place AMD in the rest of the wound but DO NOT place this over the mouth of the fistula.
· Insert a 19fr drain between the layers of AMD but not too close to the fistula opening(curl the drain around the edges )
· Place a doubled piece of 4”x4” ( now 2”x2” )NAG over the fistula opening.
· Place transparent film over the wound dressing as normal.
· Make a mark on the transparent film directly over the mouth of the fistula.
· Apply pressure for a few minutes.
· Now turn off the pressure again and allow the dressing to relax.
· Carefully cut away the transparent film over the 2”x2” NAG dressing which was placed over the mouth of the fistula.
· Remove the NAG and expose the chronic fistula.
· Apply a good barrier ring of strip paste on the transparent film around the fistula.
· Apply an ostomy device of your choice directly over the exposed fistula and the ring of paste.
· Make sure that the device is securely placed and that the appliance is adequately sealed.
· Apply negative pressure at 60mmHg.
· Observe for any dressing pulling down over the mouth of the fistula.( As the air is extracted from under the transparent film the drainage device may shrink and pull together. Just simply pinch the bag and hold it away from the mouth of the fistula during the application of negative pressure)
· Use continuous pressure and make sure that there are no breaks or pauses in the treatment. This type of wound needs 100% compliance.
· In addition to observations above, remember to change the ostomy bag before it is full. When changing this turn off the V1 and clamp.
· Observe on each shift for clamped tubes!