Guide to Vitamins
Vitamins are organic components in food that are needed in very small amounts for growth and for maintaining good health. Vitamins are classified as fat soluble vitamins and water soluble vitamins. Vitamins work together with enzymes and release energy from digested food and regulate the billions of chemical activities that occur in the body of every day.
Fat soluble vitamins: Vitamins A, D, E and K are fat soluble vitamins. They are stored in the fat tissues of the body for a few days to up to 6 months.
Water soluble vitamins: Water soluble vitamins are vitamin C and the B vitamins are stored in the body for only a brief period of time and are then excreted by the kidneys.
Ask your health care provider first about your daily vitamin intake.

Fat soluble vitamins: A, D, E and K
Vitamin A:
Vitamin A is needed for growth, healthy eyesight, healthy skin and night vision. It helps for immune system functioning. Lack of vitamin A results in night blindness, dry skin and rough skin.
Food sources:
Vitamin A foods: Milk, egg and calf liver. It also made in the body from beta carotene. Some fruits and vegetables contain compounds called carotenoids. Carotenoids is an antioxidant and responsible for the orange color of some fruits and vegetables.
Foods rich in beta carotene include carrots, bell peppers, tomatoes, winter squash, mangoes, broccoli, cantaloupe, pumpkin, braised spinach, boiled sweet potato, collard greens, turnip greens, kale and chard.
Vitamin A daily requirement:
Male: 10,000 IU/day
Females: 8,000 to 12,000 if lactating.
Children ages 1-3: 4000 IU
Children ages 4-6: 5000IU
Children ages 5-7: 7000 IU
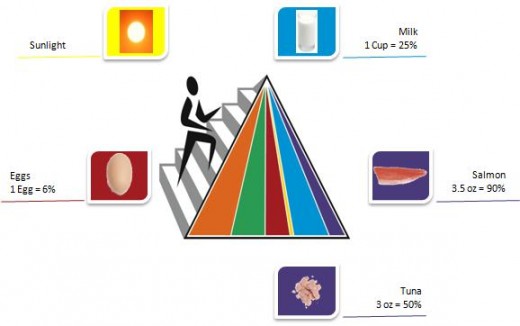
Vitamin D: Vitamin D is essential for promoting calcium absorption. It also helps bulid strong bones and teeth. vitamin D is produced when your skin is exposed to sunlight. Lack of sunlight can result in restlessness, weak feelings in your body, and rickets
Vitamin D foods: Food sources include salmon, sardines, milk, cod, and eggs.
Vitamin D daily requirement:
Adults: 5 mcg
Pregnant women: 10 mcg
Children: 5 mcg

Vitamin E: Vitamin E is an antioxidant and helps to prevent heart disease and promotes normal cell growth and development.
Vitamin E foods: Good sources of vitamin E include avocado, nuts, vegetable oils, egg yolk, mustard greens and turnip greens.
Vitamin E daily requirement:
Adults: 30 IU
Children: 6 to 11 mg
1 IU equal to 0.75 mg

Vitamin K: Vitamin K is necessary for normal blood clotting and synthesis of proteins found in plasma, bone, and kidneys.
Vitamin K food sources: Food sources of vitamin K include spinach, brussels sprouts, beans, asparagus, broccoli, green leafy vegetables, dairy products, eggs and carrots.
Daily requirement:
Men: 70 to 80 micrograms
Women: 60 to 65 micrograms
Children need half the amount depending on their age.

Water soluble vitamins: Vitamin B and vitamin C
Viatmin B complex: The Vitamin B-Complex consists of eight water soluble vitamins including vitamins B1, B2,B3, B5 B6, B9 or folic acid, B12, and biotin. These vitamins help to facilitate metabolic processes.
Vitamin B1: vitamin B1 also known as thiamin. This vitamin is needed for the healthy nervous system and digestive system.
Vitamin B1 foods: Good sources of vitamin B1 include whole grain breads, asparagus, romaine lettuce, mushrooms, spinach, sunflower seeds, tuna, nuts, tomatoes, and eggplant.
Vitamin B1 daily requirement:
Adult males: 1.2 mg
Women: 1.1 mg
Pregnant women: 1.5 mg
Children: 0.6 to 0.9mg
Vitamin B2: Vitamin B2 also known as riboflavin and is needed for healthy eyes, skin and nerves. It releases energy from carbohydrates.
Vitamin B2 foods: Good sources include calf liver, dairy products, mushrooms, spinach, meat and eggs.
Vitamin B2 daily requirment:
Adult males: 1.3 mg
Women: 1.1 mg
Children: 0.6 to 0.9 mg
Vitamin B3: Vitamin B3 is also called as niacin. It promotes healthy skin, nerves and digestion and reduces high blood pressure. Niacin plays an important role in removing toxic and harmful chemicals from the body.
Vitamin B3 foods: Dairy products, chicken, sardines, eggs, sea vegetables and whole grain cereals.
Vitamin B3 daily requirement:
Adult males: 16 mg
Women: 14 mg
Pregnant women: 17 to 18 mg
Children: 9 to 16 mg
Vitamin B5:
Vitamin B5 also known as pantothenic acid. It helps in the metabolism and synthesis of carbohydrates , proteins , and fats. Vitamin B5, is also helpful to fight against wrinkles as well as graying of the hair.
Vitamin B5 foods: Good sources of vitamin B5 include cauliflower, mushrooms, calf liver, yogurt, eggs and turnip greens.
Vitamin B5 daily requirement:
Adults: 5 mg
Women: 6-7 mg if pregnant/ lactating
Children: 2-4 mg
Viatmin B6: Pyridoxine or vitamin B6 aids in food assimilation and protein and fat metabolism. It is essential for manufacturing red blood cells and healthy pregnancies. It also promote proper breakdown of sugars and starches.
Vitamin B6 foods: Good sources of vitamin b6 include beans, lentils, bananas, garlic, tuna, cauliflower, spinach, turnip greens, eggs and bell peppers.
Vitamin B6 daily requirement:
Adults: 1.3 to 1.7 mg
Pregnant women: 2 mg
Children: 0.6 to 1.3 mg
Biotin or viatmin B7: It is essential in several of the body's metabolic reactions and plays an important role in cell growth
Biotin food sources: Almonds, chicken, eggs, milk, onions, oats, cabbage, cucumber, carrots, lettuce and cauliflower.
Biotin or viatmin B7: It is essential in several of the body's metabolic reactions and plays an important role in cell growth
Biotin daily requirement: 150 microgram

Vitamin B9 or Folic acid: Folic acid is needed for the formation of DNA and of the haemoglobin in red blood cells. It is essential for pregnant women. Pregnant women should consume enough folic acid in order to ensure proper development of the neural tube in the fetus.
Folic acid foods: Green leafy vegetables, citrus fruit, lentils, beans, cereals and nuts.
Folic acid daily requirement:
Adults: 400 mcgs
Pregnant and breastfeeding women: 600 mcgs
Children: 150 to 300 mcgs
The actual folate requirement for pregnancy rises to 600 micrograms per day and during breast-feeding, 500 micrograms is advised.
Vitamin B12:
Vitamin B12 alos known as cobalamin and is essential for growth and formation of red blood cells. It can lead to anemia.
Viatmin B12 foods: Good sources of vitamin B12 include snapper, dairy products, salmon, yogurt, fortified breakfast cereals and calf liver.
Vitamin B12 daily requirement:
Adults: 2.4 mcg
Pregnant women: 2.6 to 2.8 mcg
Children: 0.9 to 2.4 mcg

Vitamin C or ascorbic acid: Vitamin c is important for wound healing, infection resistance, healthy gums, healthy connective tissue and blood vessels. Lack of vitamin C can result in scurvy, joint pains, irritability, and shortness of breath. It helps iron absorption.
Vitamin C foods: Good sources of vitamin C include oranges, cantaloupe, strawberries, tomatoes, raspberries, broccoli and cabbage.
Viatmin C daily requirement:
Adults: 60 mg
Pregnant women: 70 mg
Children: 45 to 50 mg









