Senior Citizen Hearing Loss

Hearing Loss in Senior Citizens
Hearing loss (presbycusis) tends to happen gradually as we age. Approximately one-third of people between 65-75 have some degree of hearing loss and for people over the age of 75 the percentage increases to one of every two people. Chronic exposure to loud noises contributes to hearing loss.
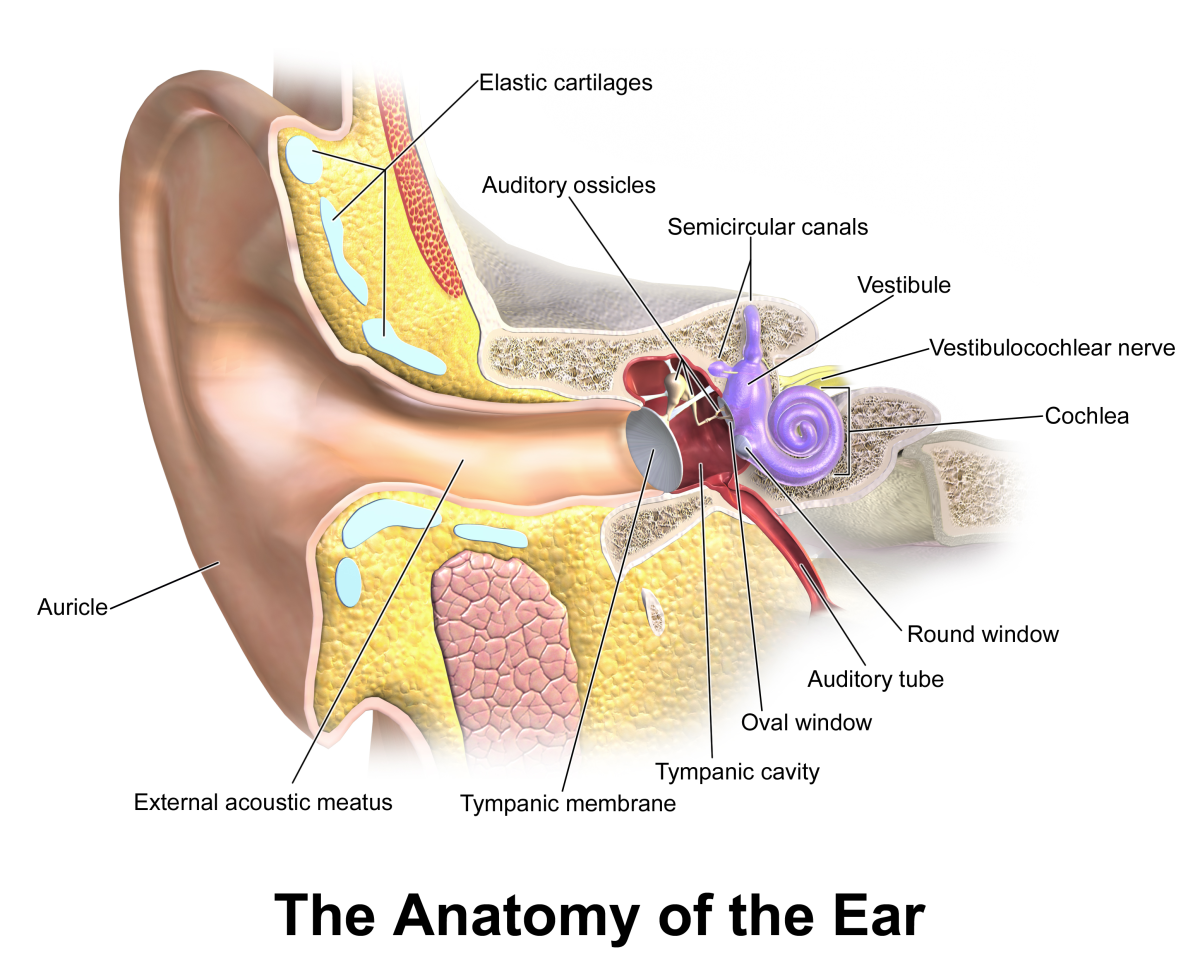
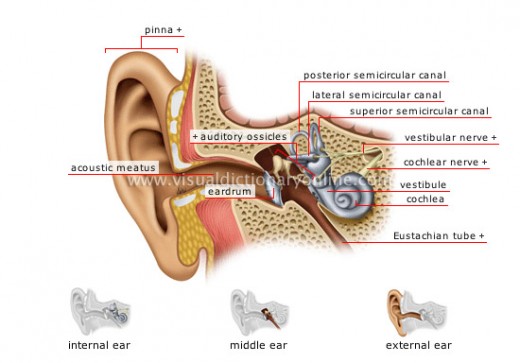
The Ear
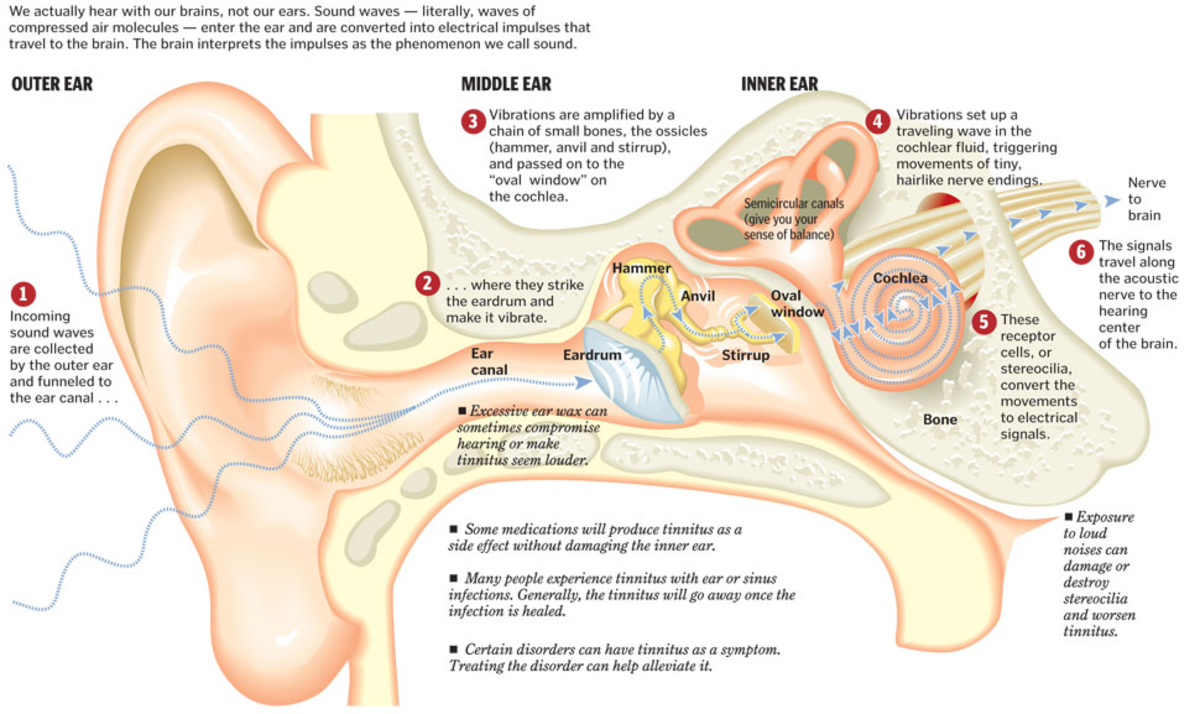
There are three primary parts of the ear: the outer, middle and inner ear. Each part plays a unique role in hearing by converting sound waves that cause vibrations on the eardrum into signals that go into the brain.
Types of Hearing Loss
The symptoms of hearing loss depend on the type and severity of the loss. It will be one of 3 types:
- Conductive - involving the middle of outer ear
- Sensorineural - involving the inner ear
- Mixed - a combination of two types listed above
While you can’t reverse most types of hearing loss, you can see a hearing specialist to take steps to improve your hearing.
Signs and Symptoms to Hearing Loss
There are several signs and symptoms of hearing loss, including:
- Muffled speech and other sounds
- Difficulty understanding word, particularly in crowds
- Difficulty in hearing consonants
- Needing to turn up the volume of the TV or radio
- Frequently asking others to speak up or speak more slowly
- Withdrawal from group conversations
- Actual avoidance of group settings
- Friends or family members may say the television is too loud
- Difficulty hearing people on the phone
- Frequently asking people to repeat themselves
- Noticing tinnitus (ringing in the ears)
- Paradoxically, some sounds seem too loud, known as “recruitment”
3 Types of Hearing Loss
Causes of Hearing Loss
In addition to age, which causes degeneration of the inner ear over time, there are several other possible causes of hearing loss and they include:
- Loud noise - exposure to loud noise damages cells of your inner ear
- Heredity - genetic DNA can make you more susceptible to ear damage
- Occupational noises - jobs with loud noise in the working environment
- Recreational noises - possible causes could be firearms, motorcycles or loud music
- Some medications - the antibiotic gentamicin, sildenafil (Viagra), very high aspirin doses, other pain relievers, antimalarial drugs, loop diuretics
- Some illnesses - diseases that cause a high fever, like meningitis
- Ear infections - may cause abnormal bone growth in the outer or middle ear
- Ruptured eardrum (tympanic membrane perforation) a loud blast of noise, sudden change in pressure, poking your eardrum with an object
Treatment for Hearing Loss
There is no urgency in seeing a doctor unless your hearing loss is sudden, especially if it is just in one ear. Earwax blockage is a reversible cause of hearing loss. There are some surgical procedures that may reverse hearing loss, which include repairing abnormalities of the eardrum or bones in the ear.
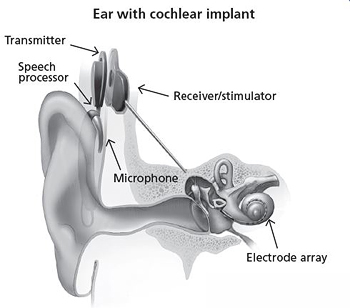
Hearing aids are always an option. Cochlear implants are small, complex electronic devices. They can help someone who is profoundly deaf or severely hard of hearing. The implants are often used for deaf children, but they may be used for adults.
Hearing aids do not restore normal hearing, but they sure do improve your hearing. Hearing aids are typically digital, while using a hearing aid battery. They simply carry sounds into your inner ear and make them louder. Hearing aids vary a great deal in price, size, special features and the way they're placed in your ears. The hearing aid designers are attempting to make them smaller and more attractive.
There are completely-in-the-canal hearing aids that are modified to fit inside the ear canal. They treat mild to moderate hearing loss. This hearing aid is:
- The smallest and least visible type
- Is less likely to pick up wind noise
- Uses very small batteries (they can be difficult to handle due to the small size)
- No extra features are included, such as volume control
- Susceptible to earwax clogging
Hearing aids are expensive and run from $1,000 to $6,000. Most people need a hearing aid for each ear and insurance typically does not cover this cost.
The Latest in Hearing Aids
In Conclusion
Hearing loss is so common with aging, and there is no way to stop this loss from occurring. It is good to avoid loud noises. If you have a loud hobby, wear ear plugs to protect your hearing. If you are losing your hearing you can check out hearing aids.
My mother passed away at 95 years of age last year, and her hearing aids were probably her biggest complaint. Hearing aids can be quite expensive and you probably get what you pay for in this case. If you are going deaf however, hearing aids may be a good choice. If you want to see how people rate hearing aids check our Best Hearing Aids for 2022.
References
This content is accurate and true to the best of the author’s knowledge and does not substitute for diagnosis, prognosis, treatment, prescription, and/or dietary advice from a licensed health professional. Drugs, supplements, and natural remedies may have dangerous side effects. If pregnant or nursing, consult with a qualified provider on an individual basis. Seek immediate help if you are experiencing a medical emergency.
© 2020 Pamela Oglesby