Herbal & Self-Help Treatments for Tinnitus or Ringing in the ears

When using herbal medicine, in all cases, it is important to adhere to these Safety Guidelines
v Don’t take the herb identity for granted
v Use only recommended amounts for recommended periods
v Start with the lowest strength possible for the elderly (as they have increased sensitivity to drugs)
v Be extra cautious if there’s a presence of Chronic disease (due to drug interactions)
v Pay attention to any symptoms of toxicity (If patient develops stomach upset, nausea, diarrhoea and/or headache within an hour or two of taking any healing herb, stop taking it and see if symptoms subside. When in doubt, contact the Poison Control centre or a physician or pharmacist. If any severe reaction is experienced, call a doctor immediately)
v Be extra careful when using herb oils (Aromatic herbs termed ‘essential’ or ‘volatile’ oils are highly concentrated, and amounts that seem small may cause serious harm. A little as a teaspoon of pennyroyal oil can cause death)
v With few exceptions, Pregnant and Nursing women should not use medicinal amounts of healing herbs (because herbs that cause no problems for adults may harm the unborn and newborns. Only use medicinal amounts of herbs with the consent and supervision of their obstetrician)
v With few exceptions, medicinal amounts of healing herbs should not be given to children below 2 years old (Give only very dilute preparations if giving herbal medicines to infants and obtain okay from the pediatrician)
An Example Case Study: 80 year old male with tinnitus
- Consent for treatment has to first be obtained
- Assess client’s health according to standard guidelines relating to age and sex
- Many elderly people develop increased sensitivity to drugs so it is important to start with low strength preparations for the elderly
- This step is important so that specialised treatment is then implemented allowing for these factors and other findings
- Physical examination or questioning of the patient to prepare for treatment:
- How do they feel?
- What are they experiencing? Any other symptoms, signs or worrying conditions?
- Do they suffer from other medical conditions?
- Are they on any other medicines (prescribed or otherwise)? (This helps to see potential drug interactions)
- Are there any other issues to treat holistically?
- How long have they had tinnitus?
- Are there any other tests or medical reports/results (e.g. X-Rays, Pathology results)?
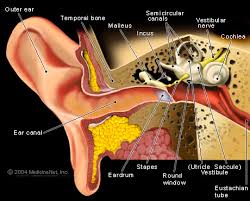
- Find out the cause of tinnitus? (e.g. ear, nose and throat problems, pressure, circulation)
- Specialised treatment plan (Choose three herbs initially and indicate reasons for choosing them):
- Tinnitus is a condition where one hears a noise within the ear. It can be caused by catarrhal congestion or circulatory problems
- Tinnitus is a condition that occurs in many people with hearing loss. Aging is a major factor in the loss of ability to hear a full range of frequencies in everyday communication and thus we need to look at this cause as well .
- Studies suggest that people with high cholesterol levels have greater hearing loss as they age than people with normal cholesterol levels
- Herbs to Use :
- Please note that for the following herbs, only the Adult doses have been provided.
- As this patient is 80 years old and above, the following doses should be adjusted for them to become 2/3 of an adult dose
- (1)Goldenseal root and/or rhizome :
- has powerful tonic qualities towards the mucous membranes of the body and thus will be useful for tinnitus associated with catarrhal congestion
- helps with all catarrhal states especially upper respiratory tract catarrh
- Adult Dose: Pour 1 cup of boiling water onto ½ to 1 teaspoonful of powdered herb and infuse for 10 to 15 minutes. Drink this three times daily
- An alternative would be to take a Tincture: 2-4mL three times daily (Adult Dose)
- Do not take Goldenseal internally on a daily basis for more than 1 week at a time
- Is not to be taken during pregnancy, breastfeeding
- Caution to be taken if there is a allergy to ragweed [3]
- Doctor’s supervision is required if there is a history of cardiovascular disease, diabetes or glaucoma
- (2) Black Cohosh
- Emmenagogue, anti-spasmodic, alterative, sedative
- Is a relaxing nervine
- Decreases spasm therefore in helps in treatment if pulmonary complaints and since the ear, nose and throat are all related and has been found to help with tinnitus [1]
- Can treat rheumatic conditions of all kinds and can be helpful in the elderly
- Doses:
- Decoction ; pour 1 cup of water onto ½ to 1 teaspoon of dried root and bring to a boil. Simmer for 10 to 15 minutes. Drink three times daily.
- Tincture: Take 2 to 4mLs three times daily
- (3) Ginkgo Biloba leaves
- Actions: Vasodilator, Antispasmodic, Anti-inflammatory, Anti-oxidant
- Improves blood circulation. As poor blood circulation has often been linked to tinnitus, Ginkgo may help with tinnitus
- It has beneficial medicinal uses in the Cardiovascular system without increasing blood pressure, the respiratory tract, the nervous system, the reproductive tract and the endocrine system e.g. early diabetic neuropathy
- Adult Dose: (to be taken three times daily) can take either of the following;
- Infusion of dried herb = 2-3 g
- Standardised extract = 40mg
- It may take 12 weeks before improvements are seen
- Do not take Ginkgo biloba if there’s bleeding disorder or are scheduled for surgery or dental procedure
- {other herbs that can be used to improve blood flow to the ear area: butcher’s broom, cayenne, chamomile, ginger root, turmeric and yarrow
*Other herbs that are beneficial include Bayberry bark, burdock root, goldenseal, hawthorn leaf and flower and myrrh gum which purify the blood and counteract infection
*Eucalyptus, hyssop, mullein and thyme have decongestant properties and can help alleviate ringing in the ears
Lifestyle Factors and Dietary Advice
- Limit consumption of alcohol and sugars (especially if infection is present); this advice will discourages the growth of yeast
- Take measures to lower cholesterol level so that hearing loss is not as severe and will thus improve
- Protect your hearing when listening to music (keep it soft and at a volume where the music can only be heard by yourself if wearing headphones)
- Eat fresh pineapple regularly to reduce inflammation (if any). Also to include plenty of garlic, kelp and sea vegetables in the diet
- Regular exercise to improve blood circulation (e.g. walking)
- Eat wholesome fresh foods as much as possible
- Advise patient to get a hearing test check done to assess their hearing status and if there’s any presence of anomalies with the physical structure of the eardrum or otherwise
- Limit intake of eggs and dairy products as they can thicken mucus and worsen catarrhal states
- Drink plenty of water (not cold water)
- Take supplemental antioxidants to help protect inner ear from traumatic and age-related hearing loss