Good Fat, Bad Fat
Fat, fat, fat - over 50% of Americans have too much of it!
Obesity rates are growing in leaps and bounds. What’s happened to our population? Why can't we control our weight? Do we consider how the excess fat we carry around is affecting our health and longevity?
We're told to go low fat - not good fat!

Why You Need Fat in Your Diet
Getting enough of the right kinds of fat in your diet will help you stay satiated, energized and mentally sharp. That’s because fats are basically energy. Fats are one of the three macronutrients in our diet, along with protein and carbohydrates.
Fats also necessary to the absorption of certain vitamins and minerals. The fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E, and K are only absorbed if taken with fat.
Fat is an excellent source of energy, providing 9 calories per gram. Proteins and carbs provide just 4 calories per gram. Because they take longer to break down in the stomach, fats will keep you feeling full longer.
Fats also help regulate the release and production of hormones. They are essential to brain health and general body metabolism.
Fats also add flavor to foods, making them taste better.
Butter is Better

Know the Different Kinds of Fat
The kind of fat many people consume - fried, deep fried, hydrogenated, saturated - are often the cause of over-eating and weight gain. These unhealthy fatty acids can trigger an inflammatory response in our bodies.
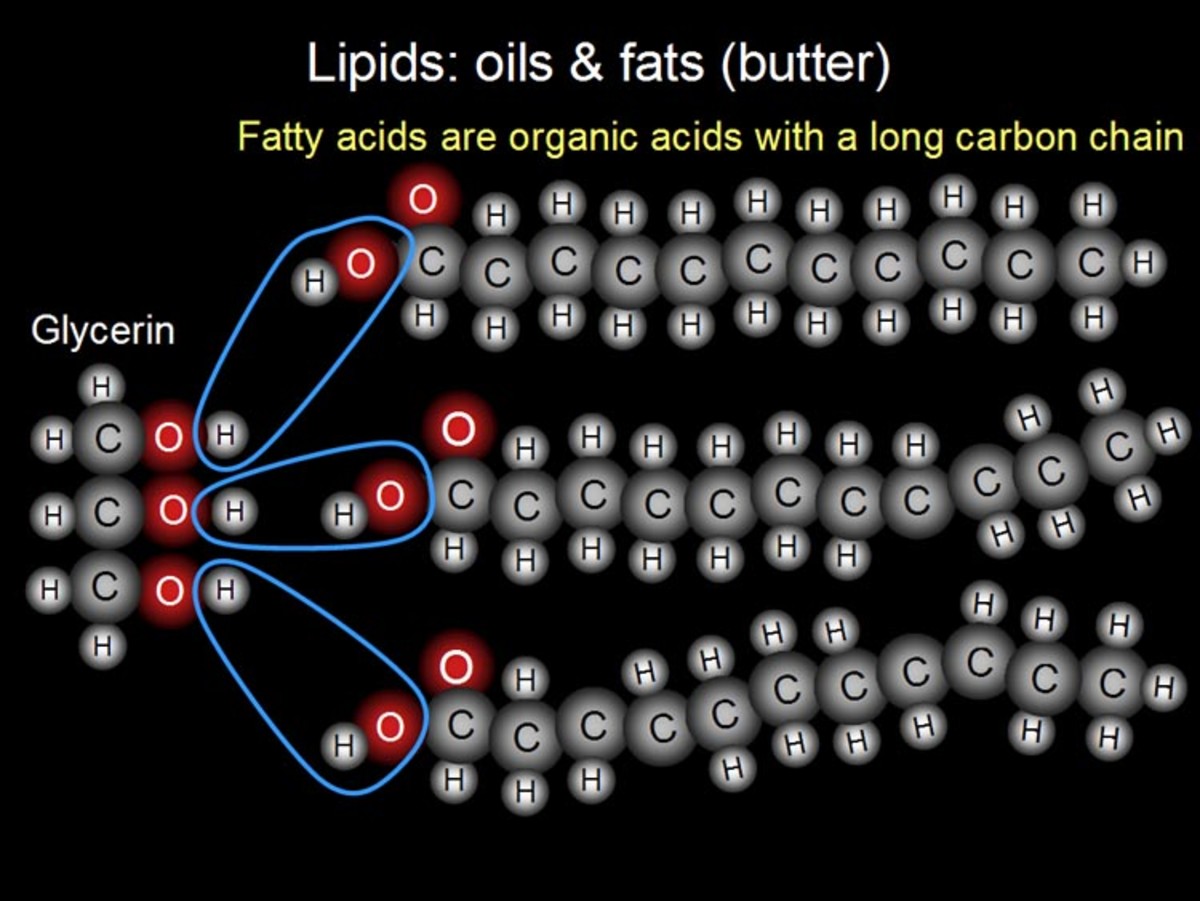
Fatty acids are grouped by their molecular structure. The number of double bonds between the carbons in their carbon chains determines how they are classified.
Monounsaturated fats have a single double bond. These are the healthiest fats, with a number of health benefits. The most common monounsaturated fat is oleic acid, found in olive oil
Polyunsaturated fats contain two or more double bonds. They include both omega-e and omega-6 fats, depending on the location of the bonds. Omega-6 fats may be inflammatory, while omega-3 fats are anti-inflammatory.
Saturated fats are generally fats that remain solid at room temperature. They contain carbon molecules doubly connected or ‘saturated’ with hydrogen molecules.
A trans fat is a highly processed oil made by adding hydrogen to a liquid vegetable oil, making it more solid.
Unsaturated Goodness



Know Your Unsaturated Fats
Unsaturated fats are generally liquid at room temperature, although they can appear in foods that are solid. The most common liquid forms of mono-unsaturated fat are olive oil, peanut oil, and avocado oil. Most nuts, seeds and avocados contain high amounts of mono-unsaturated fat.
Poly unsaturated fats are essential for many body functions, necessary for muscle and joint movement, heart health, and blood clotting. The most familiar forms are omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids.
The best sources for omega-3 fatty acids are fatty fish (sardines, anchovies, salmon, herring and mackerel), flaxseed oil, walnuts, sunflower seeds, chia seeds and hemp seeds. Pastured eggs and grass-fed meats are higher in omega-3 fatty acids than grain-fed animal products, so choose them if you can.
Omega-6 fatty acids are found in canola oil, soybean oil, sunflower oil, walnut oil, and safflower oil. Many of these oils have been highly refined, and according to a 2018 study, may have detrimental health effects. Heating and reheating these vegetable oils can increase free radical formation. If using them, avoid overheating them or re-using the oils.
Foods With Saturated Fats


Understanding Saturated Fats
Saturated fats are generally fats that remain solid at room temperature. They contain carbon molecules doubly connected or ‘saturated’ with hydrogen molecules. Lard, full fat dairy (butter and cream), cheese, coconut oil, palm oil and fatty meats all contain saturated fats.
However, many ‘fats’ are a combination of different fats, and none are pure saturated fats. They will contain both mono- and polyunsaturated fats.
Cardiologists recommend limiting the amount of saturated fats you consume, although there is no proof they can cause coronary disease.
Liquid Cooking Oils - Good or Bad?

Trans Fats - Silent Killers
Not all fats are created equal, however. Many processed foods and fast foods are loaded with the wrong kind of fat - trans fats and highly processed vegetable oils.
A trans fat is a highly processed oil made by treating liquid vegetable oil with hydrogen at extremely high temperatures, making it more solid. Trans fats can raise our ‘bad’ cholesterol and lower the good kind of cholesterol.
They often appear on labels as “partially hydrogenated oil”. They are found in vegetable shortenings and margarine, and are used to make certain snack foods, fried foods and commercially baked products.
It is estimated that during the heyday of trans fats in the 1990s, they led to roughly 50,000 preventable deaths every year in the US.
Health Canada has banned the use of artificial trans fat, and this ban will be phased in completely by September 2020. They have been banned by the FDA since June 2018, and manufacturers must be in full compliance by January 2020.
Which Fats are Best for You?
Most authorities and medical people recommend you limit your intake of saturated fats. Originally saturated fats were thought to cause heart disease and to raise cholesterol in the blood. This has never been proven, and no experimental evidence has ever linked the two.
Other studies, however, have shown that replacing saturated fat with polyunsaturated vegetable oils (liquid safflower oil and margarine) will result in higher risk of death.
Monounsaturated oils found in avocados, fish, nuts and olive oils will actively lower your cholesterol and keep you heart-healthy. They should be a daily part of a healthy diet.
Keep saturated fats as part of the diet, as they contribute to a satiated feeling, possibly keeping you from consuming refined carbs. Meats and dairy products, all containing saturated fats, are okay in moderation.
Avoid vegetable oils high in omega-6 and processed foods that contain them. Cut out trans fats or hydrogenated oils altogether by limiting your intake of packaged snack foods. Always check the ingredient list on packaged foods for hydrogenated oil.
Don't Allow This to Happen
Many people have found that by switching from a carbohydrate-dominant diet to one where healthy fats supply most of the calories, they can lose weight, reduce certain medications, get rid of chronic aches and pain and feel more healthy and energetic.
How does your family's diet shape up?