Understanding Insomnia - Why Is It Difficult to Fall Asleep and to Stay Asleep

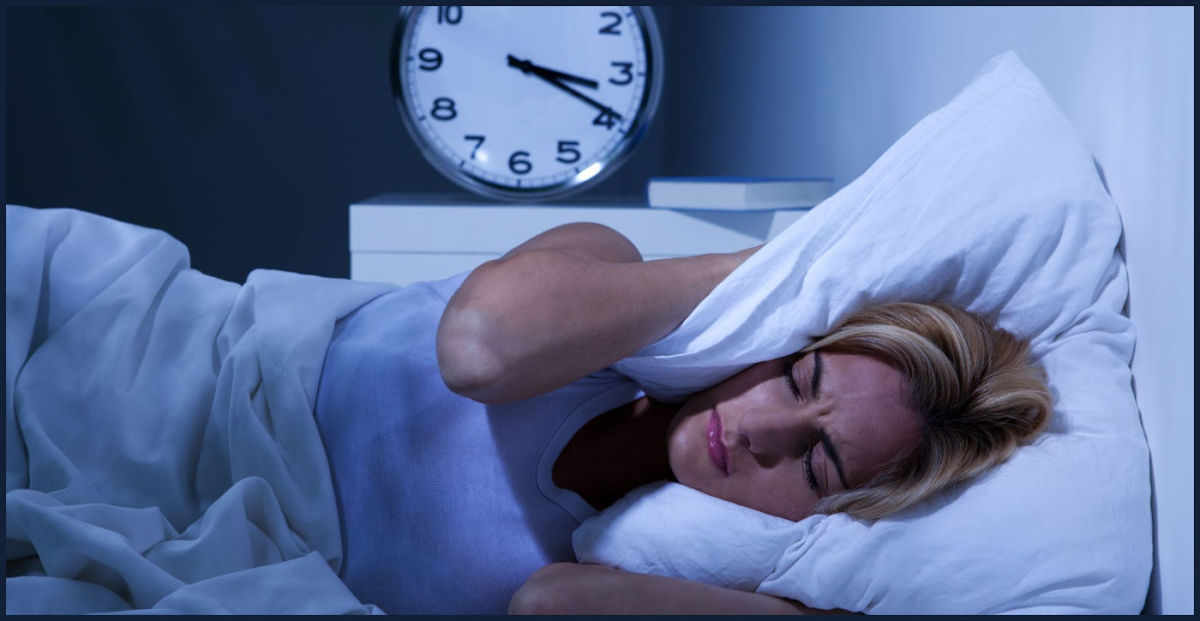
Do you have difficulty falling asleep?
If you answered yes to this question, then it's likely that you could be suffering from insomnia.
What is Insomnia?
Insomnia is the state of being awake and the inability to fall asleep at night.
Some of its symptoms are:
Feeling sleepy in the daytime
You feel sleepy in the daytime as you've been up all night because you couldn't get to sleep. This could affect your work, your performance in school, how you relate with others, and your personal life.
Irritability
You easily get irritated or agitated with someone or something. You tend to be rude to the people around you.
Anxiety
Medical references say that anxiety your body's natural response to stress.
Difficulty going to sleep
Waking up from sleep in the evening and having trouble going back to sleep again
What are the cause of insomnia?
Several factors may contribute to the symptoms of insomnia:
Predisposing factors
Examples of predisposing factors is when some people feel sleepy after drinking coffee after dinner while some have no problem falling asleep even if they have downed several cups of coffee.
Another example of predisposing factor is the lack of a strong desire to achieve a balanced sleep.
Precipitating factors
Examples of precipitating factors that contribute to sleeplessness is preparing for an exam, marital problems and work-related issues. A noisy environment and a very brightly-lit room can also trigger insomnia.
Perpetuating factors
Perpetuating causes of insomnia are changes in behavior and mental ability that happen when a person falls asleep continuously for sometime.
These changes in behavior include:
1. pursuing an irregular pattern of waking and sleeping
2. staying in bed longer trying to get more sleep
3. sleeping in the daytime
4. being active at night.
Classification of Insomnia
Insomnia is a type of sleep disorder wherein a person cannot go to sleep or cannot stay asleep as much as he wants to.
Primary and Secondary Insomnia
Medical experts use two categories, primary and secondary insomnia, to properly identify the causes of insomnia.
Primary insomnia is sleep disorder that is not associated with another medical, psychiatric or environmental factors. Depression and anxiety are two examples of primary disorders
Secondary insomnia is sleep disorder that is secondary to another primary disorder. Making this classification is very important for health experts in order that they can put their efforts in treating the primary disorder that's causing insomnia rather than merely treating the symptoms.
3 TYPES OF INSOMNIA THAT COMMONLY AFFECT PEOPLE
Chronic insomnia is the type of insomnia where the episodes of sleeplessness last more than a month. It can occur as a primary disorder or it can be due to another disease.
Chronic insomnia is what a larger portion of the population suffers from. Because of this statistics, it is recommended that chronic insomnia be distinctly identified from acute or transient insomnia so that proper treatment and management can be applied.
Chronic insomnia is believed to cause double vision.
Acute insomnia occurs when the episodes of sleeplessness last less than a period of one month. This type is also known as stress-related sleep disorder or short-term insomnia.
With transient insomnia, the duration of sleeplessness lasts less than a week. It could be caused by extremes tress, deep depression, the uncomfortable conditions in the sleeping environment, and the time a person goes to sleep.
How to Treat Insomnia
Doctors do not recommend the long-term use of prescription pills to treat insomnia.
Studies have been made to find the best way to treat insomnia aimed to better understand the causes and treatment of insomnia. The study suggest that treatment of insomnia should be based on the following factors:
1. The underlying disease should be properly treated
2. The present psychiatric illness should be properly treated
3. Individuals who hurt themselves and others should be referred to experts
4. Limit the use of hypnotic drugs to treat transient insomnia
5. Recognize the use of nonpharmaceutical treatment of insomnia
Treatment Options for Insomnia
Psychological and behavioral approach
Stimulation Control Therapy
This therapy is a set of 5 instructions for the insomnia sufferer aimed to make a connection between the bedroom and sleep and to make a consistent schedule of waking and sleeping. The instructions are:
- Go to bed only when you feel sleepy
- Get out of bed when you are not able to go to sleep yet
- Do not use the bedroom for reading or watching TV, use it only for sleeping.
- Wake up at the same time early in the morning
- Do not take short naps.
Sleep Restriction Therapy
This technique is to shorten or cut down the amount of time you spend in bed and the amount you actually spend sleeping. If a patient spends 6 hours in bed and spends only 5 hours sleeping, then the person should be trained to sleep within the 5 hour time limit.
Relaxation Training
This is a technique done in the clinic which is intended to reduce somatic tension and reduce disturbing thoughts that interrupts with a good night's sleep.
To reduce somatic tension, training on progressive muscle relaxation and autogenic training should be implemented.
To avoid disturbing thoughts before bedtime, imagery training and meditation are recommended.
Cognitive Therapy
This technique is intended to change the negative perception about sleep and insomnia and its consequences. Other cognitive techniques can include paradoxical methods intended to prevent too much worrying about having insomnia and what could happen in the future.
Sleep Hygiene Education
Cognitive Behavior Therapy
© 2013 Zee Formadero