Leiomyomas - Types and Treatments Available
Did you suffer from myoma?
What are Leiomyomas
Leiomyomas which are more commonly known as Uterine Fibroids or Myomas are the benign tumors that grow in the muscular tissues or myometrium of the uterus. Their size can vary from fraction of an inch to larger than a grapefruit. Myomas are one of the leading causes of abnormal bleeding in women. Myomas may occur in singles or multiples. Even though non-cancerous it can cause lots of other problems like heavy and prolonged menstrual periods accompanied by pain. Development of large fibroids in women of reproductive age can lead to infertility as they may distort the uterine cavity or block the fallopian tube.
About 20% women of child bearing age suffer from this problem and it is one of the primary causes of hysterectomy.
In this article the terms Leiomyomas, Myomas and Fibroids will be used interchangeably.
Fibroid in the uterus

What causes fibroids
The cause of uterine fibroids is still unknown, but the researches point to few factors:
Hormones: It is believed to be related to the hormonal imbalance. They always develop during the reproductive years and had been shown to be dependent on the two steroid hormones of the ovary - estradiol and progesterone. Fibroids usually shrink after the menopause.
Family history: There is evidence that fibroids run in the family. Immediate relatives of women with fibroids have 2.5 times more risk of developing them at some point in their reproductive life.
Ethnicity: Fibroids are more common among the African Americans than among the Caucasian women.They run a a 2.9 times greater risk of developing fibroids. Studies hasve shown that African American women develop the problem at a much younger age and have much larger and more symptomatic myomas.
Other factors: Women with hypertension, obesity run a higher risk of developing fibroids. Diet is also said to play some role in the formation of fibroids. Intake of too much red meat may increase the chance of developing fibroids.
What type of myoma you suffered from?
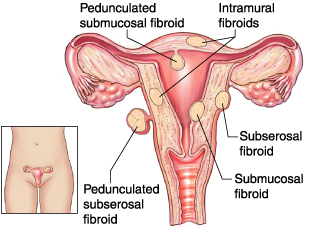
Types of fibroids
Subserosal
These fibroids grow on the outer wall of the uterus. If they grow large, subserosal fibroids put pressure on the surrounding organs in the pelvic area causing pain and discomfort. But excessive menstrual bleeding is usually not associated with this type of fibroid.
Intramural
It is another common fibroid found in about 70% women of child bearing age. They form in the inner cavity or myometrial wall of the uterus. These fibroids make the uterus look bulky as they grow in size. One of the problems with this type of fibroids is heavy and prolonged menstrual bleeding with the passing of clots. When large they tend to put pressure on the surrounding organs causing frequent urination and discomfort.
Though intramural fibroids don't cause infertility, it has been found that about 3% women suffering from these type of fibroids have difficulty conceiving. They prevent sperm from entering the uterine cavity especially if the formation is near the cervix.
Submucosal
These are the least common type of uterine fibroids, but can cause most severe symptoms. They develop just under the lining of the uterus or the endometrium. Common symptoms are bleeding between periods, heavy bleeding between menstrual cycle accompanied by severe pain.
These type of fibroids are known to cause infertility. Large and multiple submucosal fibroids distort the uterine cavity and interrupt the blood supply to the endometrium, resulting in ulceration or inflammation. They can also sometimes block the fallopian tube
Pedunculated
Subserosal and submucosal fibroids sometimes grow on a stalk like grape resulting in pedunculated fibroids. Sometimes they twist on the stalk causing pain and pressure in the abdominal area.
Ovarian fibroid
Symptoms
- Heavy and prolonged bleeding lasting for 7 days or more.
- Bleeding between periods.
- Pain in lower abdomen and pelvis during menstrual cycle.
- Pain during sexual intercourse.
- Pressure on the bladder, which leads to constant urge to urinate.
- Enlarged abdomen.
- Constipation.
- Pedunculated fibroid can cause sudden severe symptoms.
If you had myoma how was it diagnosed?
Diagnosis
If the fibroids are asymptotic it is difficult to ascertain their existence except during routine pelvic exam. Irregularities can be felt by the doctor who in turn may recommend further tests.
Ultra sonography
A picture of the uterus is obtained using sound wave. It confirms the location and size of the fibroids.
Trans vaginal sonography (TVS)
It is performed by placing a probe inside the vagina to get a better and more clearer image of the myomas.
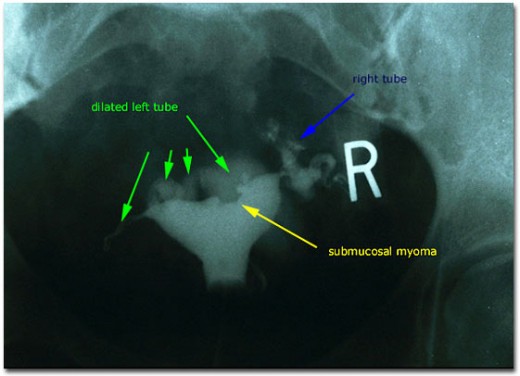
Hysterosalpingography (HSG)
A special dye is injected into the cervix to highlight the uterine cavity and fallopian tubes on X-ray. This test not only detects fibroids it can also determine whether the fallopian tubes are open or not.
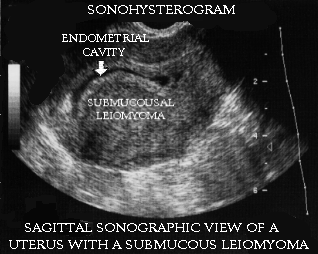
Hysterosonography
It is similar to ultrasonography, but provides a better image of uterus and endometrium than normal USG. It is also called saline infusion sonogram as sterile saline is injected into the uterine cavity making it easier to get the image. This technique is useful when USG gives a normal result in spite of heavy bleeding.
Detecting myoma using hysterosalpingogram
Detecting myoma with sonohysterogram
What was your treatment option?
If you had medicine based treatment, did you
If you opted for surgical treatment you had
Treatment
Modality of treatment varies from patient to patient and are determined by factors like patient's age, severity of symptoms and the need to preserve fertility.
Asymptotic myomas
Small myomas that are asymptotic and are discovered only during routine check ups do not usually require treatments. Such patients may go for a examination at periodic intervals.
But the need for treatment may arise for asymptotic myomas may arise under certain conditions:
If the patient has symptoms there are various treatment options available. These involve both medical and surgical treatments.
- The size of the fibroid is large.
- The mass is growing rapidly.
- Fibroid is putting pressure on the surrounding organs.
- Subserosal pedunculated fibroids may get twisted on their stalk and thus should be treated even if asymptotic.
Wait and watch
If the patient is nearing the age of menopause then sometimes doctors prefer to wait and watch depending upon the severity of the symptoms. Post menopause estrogen and progesterone levels drop considerably leading to the shrinkage of the myomas.
Medication to treat the symptoms
Intrauterine system
IUS is a small, plastic, t-shaped shaped device when placed in the uterus slowly releases progesterone. It causes the uterine lining to be thinner, resulting in lighter bleeding. It also acts as contraceptive.
Contraceptive pills
They help by lightening the bleeding and alleviating the pain.
Oral or injected progestogen
Progestogen is synthetic progesterone is synthetic progesterone that helps in reducing heavy bleeding. It works by reducing the growth of the uterine lining. Though not a contraceptive, it may reduce the chance of contraception.
Medication to shrink the fibroids
If the fibroid related symptoms remain despite the above mentioned treatments doctors may administer Gonadotropin Releasing Hormones (GnRH) to shrink the size of the fibroids. GnRH may be a short term alternative to surgery or may be used to shrink the fibroid preoperatively. It eases heavy periods and thus reduce menstrual related anemia.
GnRH are usually administered through injection and they work by affecting the pituitary gland that stops ovaries from producing estrogen. It stops the menstrual cycle but is not a contraceptive. GnRH produces certain menopause-like side effects e.g. hot flushes, muscle stiffness, dryness of vagina and increased sweating. Osteoporosis is another side effect.
Surgical treatments
Surgery is considered when the symptoms are severe and medication has failed to alleviate the suffering of the patient.
Myomectomy
It is the surgical removal of fibroids, leaving the uterus intact. It is the best treatment option for women who wish to have children later. But there is a chance that the fibroids may recur. This is especially true for women who developed multiple fibroids at a young age.
Though the procedure does not affect the reproductive ability, if the uterus is not properly repaired, it can rupture during pregnancy.
Hysterectomy
It is the surgical procedure to remove the uterus. This is the ultimate step taken when fibroids are large causing lot of pain and heavy bleeding. The procedure is suitable for those women who do not wish to have any more children. If the ovaries are kept intact, the woman will not go into menopause.
Uterine Artery Embolization (UAE)
UAE is an alternative to hysterectomy or myomectomy and is recommended for patients with large fibroids. Blood supply to the fibroids is cut off injecting tiny gel particles into the blood vessels, causing the fibroids to shrink. With this procedure the fibroids are not likely to grow back. There has not been enough study to evaluate the effect of UAE on the reproductive health of the patients. But some studies suggested there might be an increase in the risk of miscarriage or postpartum maternal hemorrhage.
Endometrial ablation
It is a minor procedure to destroy the lining of uterus. The main purpose is to reduce heavy bleeding. It can also be used to treat small tumors in the lining of the uterus. The procedure is performed by applying heat or microwave. Most women do not have periods after the procedure. Some have very light bleeding. It is possible to get pregnant but the procedure is not recommended for women who want to conceive.
Performance of myomectomy
Total abdominal hysterectomy
Uterine artery embolization
Summary
- What are leiomyomas?
- Different types of myomas.
- Symptoms
- Diagnosis
- Treatment options available
Fibroid and pregnancy
It is agreed by most physicians that submucous myomas have most negative effect on the fertility. But it was also found that fertility and pregnancy increases significantly after the treatment.
Fibroids may grow in size during pregnancy but tends to decrease after delivery. It may increase the risk of:
- Miscarriage.
- Premature birth.
- Breech and transverse position.
- More blood loss after delivery.