- HubPages»
- Health»
- Women's Health»
- Pregnancy
Anemia in Pregnancy: The Irony Of Iron Supplementation

Maternal anemia in pregnancy: A public health problem
Iron supplementation is a very widely practiced public health measure in India for anemia in pregnancy but little is known about its benefits to the mother and offspring. The effect of anemia in pregnancy on its outcome needs to be reviewed with an attempt to identify current gaps in the information we have.
Prevalence Of Anemia In Pregnancy
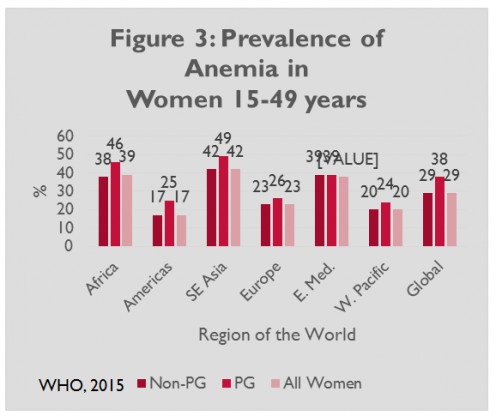
Around 35%-75% (56 % average) women in the developing world and 18 % in industrialized countries might be anemic at conception. Screening for the prevalence of iron deficiency as shown by a low serum ferritin and absent or sparse stainable iron in the bone marrow is not always practically feasible. The prevalence of iron deficiency is much greater than that of iron deficiency anemia in pregnancy. It may develop even in women who enter pregnancy with adequate iron stores because of the high demand in pregnancy.
Most anemic pregnant women are asymptomatic
Anemia in pregnancy is first recognized during routine checkup.
Causes of maternal mortality
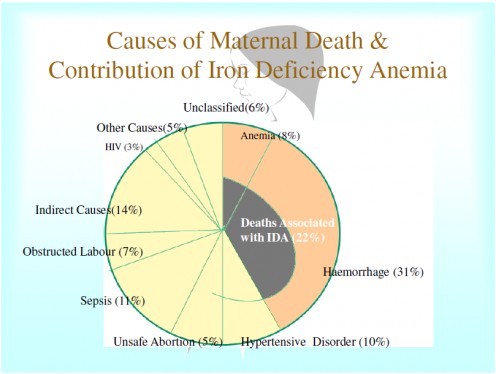
Iron deficiency anemia in pregnancy is a risk factor for preterm delivery with the child being born with a low birth weight and subsequently having poor health as a neonate. Although there is not sufficient evidence to derive any conclusion to the extent it contributes to maternal mortality.
A study done in Indonesian women showed that one-third of the women had a folic acid deficiency and two third had hook worm infestation. In tropical countries causes other than just iron deficiency may be prevalent as a cause of anemia in pregnancy.
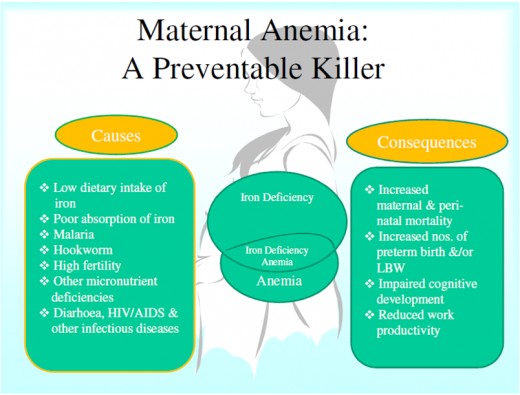
Causes of maternal anemia
Maternal effects of anemia
Maternal Effects
| |
|---|---|
Antepartum
| UTI
|
Pre term labour
| |
PROM
| |
LBW
| |
Aggravation of pre-eclampsia and APH
| |
Cardiac de-compensation with pulmonary edema
| |
Intrapartum
| Increased incidence of uterine inertia
|
Maternal exhaustion
| |
Poor ability to withstand excessive blood loss
| |
Puerperium
| Puerperal sepsis
|
Thromboemblic complications
| |
Sub involution of uterus
| |
Lactation failure
| |
Delayed wound healing`if Caesarian delivery
|
The affect anemia can have on mother during the course of her pregnancy
Severity :ICMR Data
Category
| Severity
| Hb (gm/dl)
|
|---|---|---|
1
| Mild
| 10-10.9
|
2
| Moderate
| 7-9.9
|
3
| Severe
| <7
|
4
| Very Severe
| <4
|
Objective hemoglobin cut off values to decide severity of anemia
There is an increase in maternal iron absorption during pregnancy but ferritin (stored iron in the body) falls during 12 -25 weeks of pregnancy because it is utilized for the expansion of red cell mass. Transfer of iron from mother to fetus occurs at around 30 weeks of gestation and this corresponds to the peak of maternal iron absorption.This transfer from mother to fetus is done by a carrier called transferrin. If maternal iron is poor there is an increase in transferrin receptors to take up more iron by the placenta.
Concern that anemia in pregnancy predisposes to a greater risk of mortality and morbidity to the mother
Retrospective observational studies have associated maternal hemoglobin concentration at or close to delivery with a high risk of maternal mortality if the anemia was severe. Whether this low hemoglobin is just a reflection of the greater amount of blood loss by the mother during delivery or late arrival at admission is debatable as both these factors can also affect mortality independently.
Maternal anemia in pregnancy- <7 gm/dl increases the risk of death*
Rapid cardiac decompression even without the additional stress of true postpartum hemorrhage.
< 500ml blood loss during delivery could be fatal with severe anemia.
— 2001 American Society for Nutritional Sciences. J. Nutr. 131: 604S–615S, 2001.No objective cutoff value
There is no established hemoglobin concentration below which the risk of mortality increases and the hemoglobin cutoff suggested needs to be substantiated.
Even if a woman is not anemic iron supplementation improves iron stores during pregnancy and after delivery.This is important in a subsequent pregnancy if the birth spacing is less. If the mother is iron deficient the fetus also has a low iron store. If the iron store is low in the first year it has adverse effects on the growth and development.
Maternal anemia and infant health
Patients with anemia have babies with low APGAR scores. These scores are significantly higher in those infants whose mothers received iron.
Children of anemic mothers may have
- More perinatal complications
- More growth stunted
- More likely to have low stores of iron and other nutrients.
Klebenoff et al. showed doubled risk of preterm delivery with anemia in pregnancy during the second trimester but not during the third trimester
— Klebanoff MA et al. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1991;164:59–63.Low APGAR scores
Higher maternal Hb -better APGAR scores and lower risk of birth asphyxia.
APGAR scores significantly higher in mothers who received iron supplementation.
Rusia U, Madan N, Agarwal N, Sikka M, Sood S. Effect of maternal
iron deficiency anemia on fetal outcome. Indian J Pathol
Microbiol 1995;38:273–9.`
Preziosi P, Prual A, Galan P, Daouda H, Boureima H, Hercberg S.
Effect of iron supplementation on the iron status of pregnant women:
consequences for newborns. Am J Clin
More perinatal complications.
Stunted growth
Deficient iron stores and subsequent anemia
Lowered childhood intellectual ability
Greenwood R, Golding J, McCaw-Binns A, Keeling J, Ashley D.
The epidemiology of perinatal death in Jamaica. Paediatr Perinat
Epidemiol 1994;8:143–57.
Anemia + Iron deficiency in the first and second trimester 1.87 fold higher risk of preterm birth but anemia alone was not a risk factor
Dreyfuss M. Anemia and iron deficiency during pregnancy: etiologies
and effects on birth outcomes in Nepal. Ph.D. dissertation. Johns
Hopkins University, Baltimore, 1998
Intervention trials-The difficulties:
Prospective controlled intervention trials to examine the efficacy of iron supplementation for reducing maternal mortality are difficult
- They require a large sample size
- It will be unethical not to treat a known anemic woman who can be used as a control subject.
It should also be noted that the risk of maternal mortality can be greatly affected by the quality of health care a woman receives.
Maternal anemia in pregnancy & birth outcome
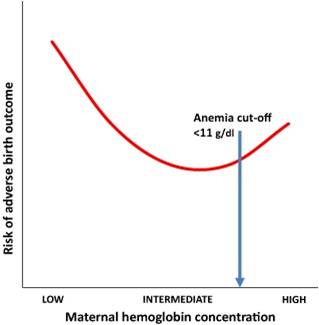
Anemia in pregnancy and birth weight of the child
There is a U shaped association curve between the mother's hemoglobin and birth outcome.This means that an abnormally high hemoglobin concentration is also a risk for low birth weight in the baby. High hemoglobin might represent poor blood volume expansion which is an important physiological change in pregnancy.




Fetal effects of anemia in pregnancy
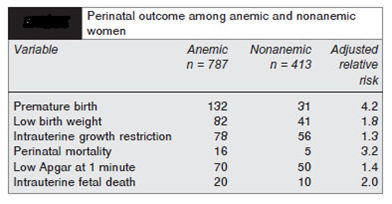
Intergenerational cycle of Anemia
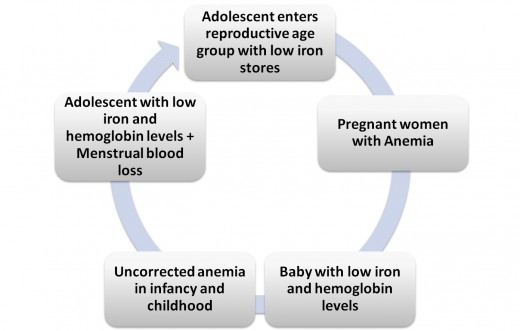
Attempt to understand the mechanisms involved in increasing the risk of mortality and iron deficiency anemia in pregnancy
Maternal death at or close to delivery may be related to --
- A poor ability to tolerate the bad effects of excessive blood loss.
- Increased risk of infection.
- Maternal fatigue
These factors have not been evaluated very systematically but iron deficiency is associated with low lymphocyte activity and supplementation improved lymphocytic function.
Increased risk of infection
suppressed immunity
Iron deficiency associated with low lymphocyte stimuli indexes and supplementation improved lymphocyte stimulation
— A case control study. Das et al 2016, Ekiz C et al 2005
WHO Recommendations
WHO recommendation: 60 mg elemental iron with 400 ugs of Folic acid daily for 6 months where the prevalence is < 40% and this dose to be supplemented for another 3 months postpartum in areas where prevalence >40% to prevent anemia in pregnancy.
Indian Guideline
As per National Nutritional Anemia Control Programme, 100 mg of elemental iron and 500 ugs of Folic acid for prophylactic supplementation for at least 100 days starting in the second trimester and double this dose for treatment of anemia in pregnancy and to continue it for 3-6 months postpartum for replacement of iron stores.
Chocrane


A lot still needs to be learned regarding anemia in pregnancy. Till we are able to fill the gaps in our knowledge women should get the benefit of iron supplementation in pregnant women.